Abstract
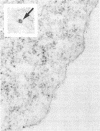
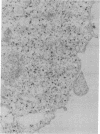
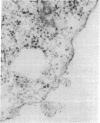
Primary murine trophoblast giant cells (TGC) do not express detectable major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens and are refractory to the MHC-increasing effects of alpha and beta (virus-induced) interferons and gamma (immune type) interferon during early implantation (postcoital days 3.5-6). West Nile virus infection of primary TGC monolayers from postcoital-day-3.5 preimplantation blastocysts induced paternal MHC antigen expression within 16 hr, as detected by immunogold labeling for electron microscopy. Induction is unlikely to have been mediated by secreted virus-induced interferons or other factors, as it occurred in the presence of high concentrations of anti-alpha/beta interferon antibodies and was not induced by virus-inactivated supernatants from MHC-induced primary TGC cultures. Attempts to induce MHC antigen expression with poly(I.C) or recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha in primary TGC cultures also failed. Thus, the apparent inhibition of MHC antigen expression in primary TGC during early implantation and their refractoriness to induction of de novo MHC antigen expression is not absolute. This may represent a maternal-and/or species-protective evolutionary device. As such, manipulation of this phenomenon may allow a conclusive assessment of the significance of inhibition of MHC antigen expression on trophoblast cells in the implanting semiallogeneic embryo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. P., Randle B. J., Burke D. C. Interferon synthesis in the early post-implantation mouse embryo. Differentiation. 1984;27(3):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B. L., King N. J., Maxwell L. E., Rodger J. C. Class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on early murine trophoblast and its induction by lymphokines in vitro. J Reprod Immunol. 1987 Apr;10(4):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(87)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Schmid E., Bürki K., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. Intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):161–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Skidmore B., White J., Marrack P. Antigen-inducible, H-2-restricted, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridomas. Lack of independent antigen and H-2 recognition. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1198–1214. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. J., Drake B. L., Maxwell L. E., Rodger J. C. Class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression on early murine trophoblast and its induction by lymphokines in vitro. II. The role of gamma interferon in the responses of primary and secondary giant cells. J Reprod Immunol. 1987 Sep;12(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(87)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. J., Hegre O., Blanden R. V. The appearance of surface H-2 antigens on fetal and postnatal murine hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro: a comparative study of MHC control. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(1):18–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00376517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. J., Kesson A. M. Interferon-independent increases in class I major histocompatibility complex antigen expression follow flavivirus infection. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2535–2543. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. J., Sinickas V. G., Blanden R. V. H-2K and H-2D antigens are independently regulated in mouse embryo fibroblasts. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1985;2(4):206–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., van Damme J., Jeunhomme G. M., Buurman W. A. Interferon beta 1, an intermediate in the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced increased MHC class I expression and an autocrine regulator of the constitutive MHC class I expression. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1180–1185. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Wan Y. J., Orrison B. M. Mouse major histocompatibility class I gene expression begins at midsomite stage and is inducible in earlier-stage embryos by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2427–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancéau J., Sondermeyer P., Béranger F., Falcoff R., Vaquero C. Intracellular human gamma-interferon triggers an antiviral state in transformed murine L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2906–2910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellens M. H. Antigen expression on early mouse trophoblast. Nature. 1977 Sep 1;269(5623):60–61. doi: 10.1038/269060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellens M. H., Jenkinson E. J., Billington W. D. Major histocompatibility complex and non-major histocompatibility complex antigens on mouse ectoplacental cone and placental trophoblastic cells. Transplantation. 1978 Apr;25(4):173–179. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197804000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugamata M., Miura T. Japanese encephalitis virus infection in fetal mice at different stages of pregnancy I. Stillbirth. Acta Virol. 1982 Jul;26(4):279–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. P., Marshall I. D. Adaptation studies with Ross River virus: laboratory mice and cell cultures. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jul;28(1):59–72. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner C. M., Spannaus D. J. Demonstration of H-2 antigens on preimplantation mouse embryos using conventional antisera and monoclonal antibody. J Exp Zool. 1984 Apr;230(1):37–52. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402300107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb C. G., Gall W. E., Edelman G. M. Synthesis and distribution of H-2 antigens in preimplantation mouse embryos. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):923–932. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley L. M., Pedersen R. A. Morphology of mouse egg cylinder development in vitro: a light and electron microscopic study. J Exp Zool. 1977 Jun;200(3):389–402. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402000309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden A., Shure-Gottlieb H., Chebath J., Revel M., Kimchi A. Autogenous production of interferon-beta switches on HLA genes during differentiation of histiocytic lymphoma U937 cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):969–973. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F. A., Head J. R. Expression of MHC antigens on murine trophoblast and their modulation by interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]