Abstract
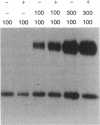
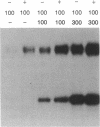
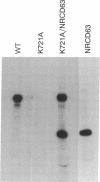
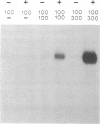
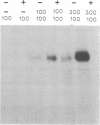
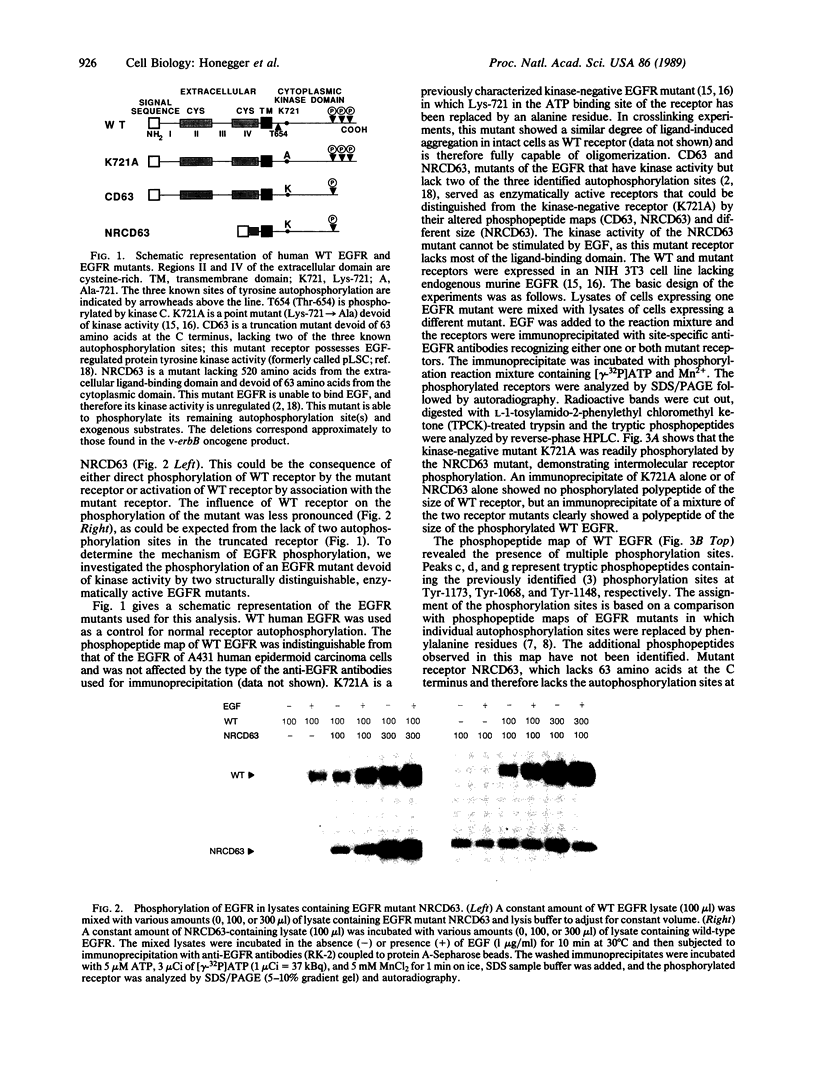
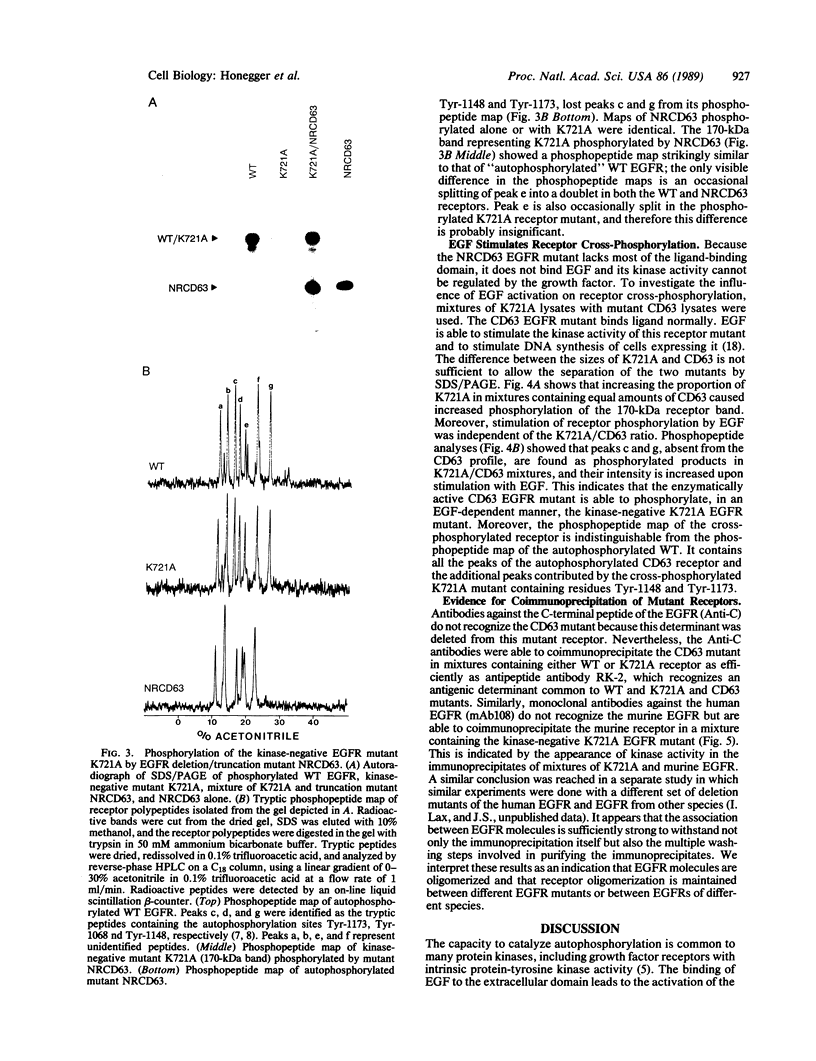
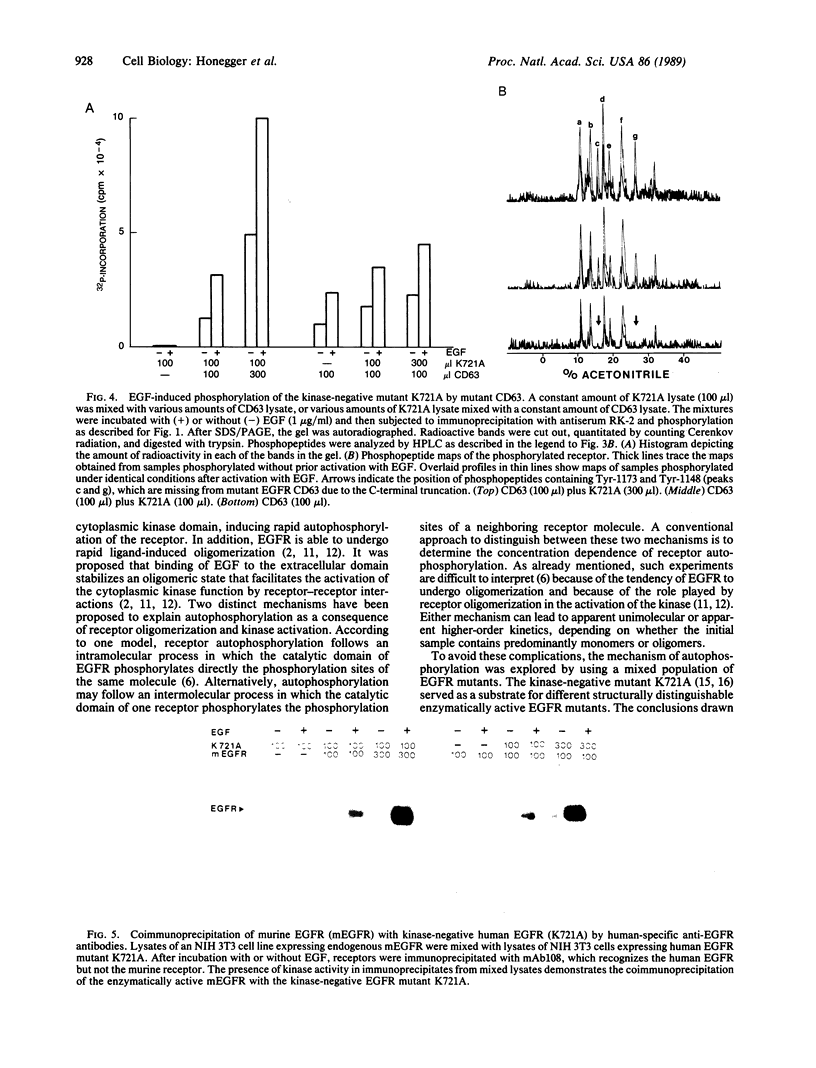
Structurally distinguishable mutants of human epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) were used to investigate the mechanism of EGFR autophosphorylation. Mutant receptors generated by site-directed mutagenesis were expressed in transfected NIH 3T3 cells lacking endogenous receptors. After coincubation of cell lysates in the presence or absence of EGF, receptor immunoprecipitates were incubated with [gamma-32P]ATP. A kinase-negative mutant EGFR (K721A), in which Lys-721 in the ATp binding site was replaced by an alanine residue, was shown to be phosphorylated in an EGF-dependent manner by an enzymatically active EGFR deletion mutant lacking two autophosphorylation sites. A mutant EGFR lacking the EGF-binding domain as well as the phosphorylation sites also phosphorylated the kinase-negative mutant. In both cases the kinase-negative mutant K721A was phosphorylated on sites virtually identical to the sites that are autophosphorylated by wild-type recombinant or native human EGFRs. With four different site-specific anti-EGFR antibodies, it was shown that deletion mutants devoid of epitopes recognized by the antibodies were coimmunoprecipitated together with wild-type or mutant receptors recognized by the antibodies. This indicates that EGFR oligomers were preserved during immunoprecipitation. On the basis of these results, we propose that autophosphorylation of solubilized EGFR is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation, probably facilitated by receptor oligomerization.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertics P. J., Gill G. N. Self-phosphorylation enhances the protein-tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14642–14647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F. Mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation and high-affinity binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Kashles O., Chambaz E. M., Borrello I., King C. R., Schlessinger J. Demonstration of epidermal growth factor-induced receptor dimerization in living cells using a chemical covalent cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H. T., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Direct visualization of the binding and internalization of a ferritin conjugate of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):382–395. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Lyall R., Van Obberghen E., Dull T. J., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A mutant epidermal growth factor receptor with defective protein tyrosine kinase is unable to stimulate proto-oncogene expression and DNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4568–4571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Bellot F., Van Obberghen E., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Biological activities of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A., Dull T. J., Szapary D., Komoriya A., Kris R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Kinetic parameters of the protein tyrosine kinase activity of EGF-receptor mutants with individually altered autophosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3053–3060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kris R. M., Lax I., Gullick W., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Fridkin M., Schlessinger J. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide as a probe for the kinase activity of the avian EGF receptor and v-erbB protein. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Prywes R., Kashles O., Reiss N., Sasson I., Mory Y., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Reconstitution of human epidermal growth factor receptors and its deletion mutants in cultured hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12490–12497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Bierman A. J., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Defize L. H., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. A point mutation at the ATP-binding site of the EGF-receptor abolishes signal transduction. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):707–710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02866.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Livneh E., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of EGF receptor affect EGF binding and receptor internalization. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2179–2190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Allosteric regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2067–2072. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Shechter Y., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Direct visualization of binding, aggregation, and internalization of insulin and epidermal growth factor on living fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2659–2663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Molecular analysis of signal transduction by growth factors. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3113–3119. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zidovetzki R., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J., Jovin T. M. Rotational diffusion of epidermal growth factor complexed to cell surface receptors reflects rapid microaggregation and endocytosis of occupied receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6981–6985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]