Abstract
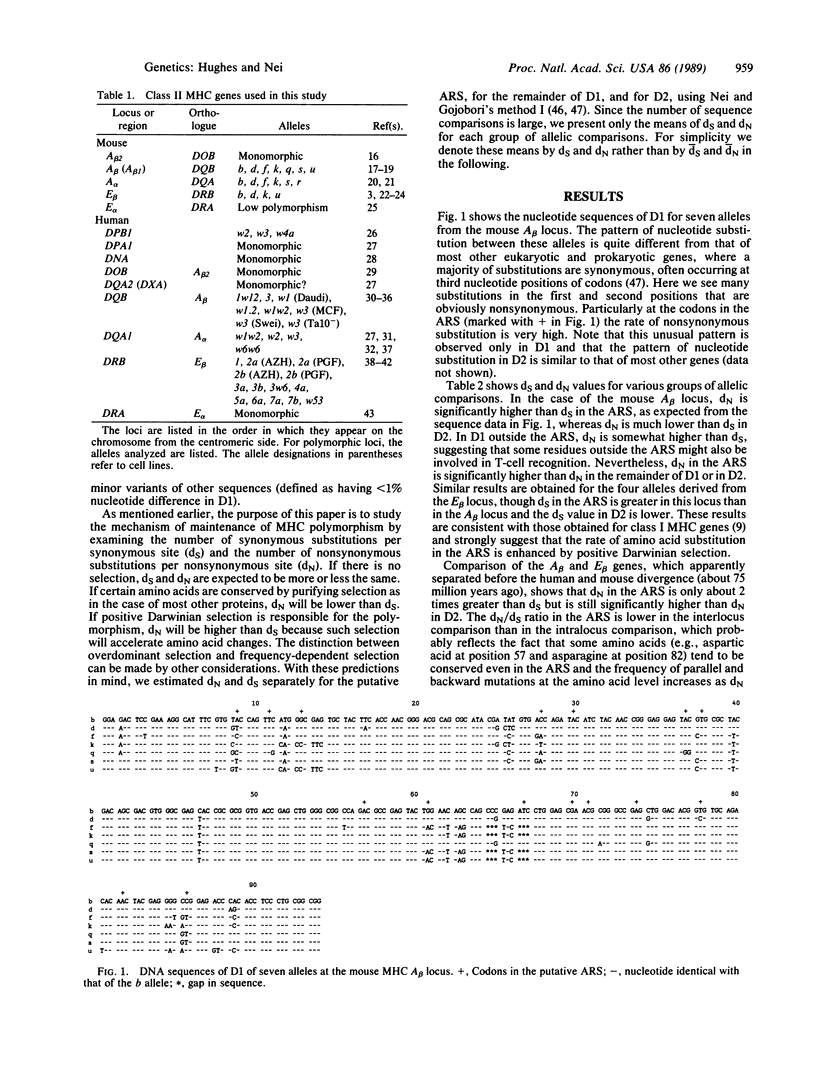
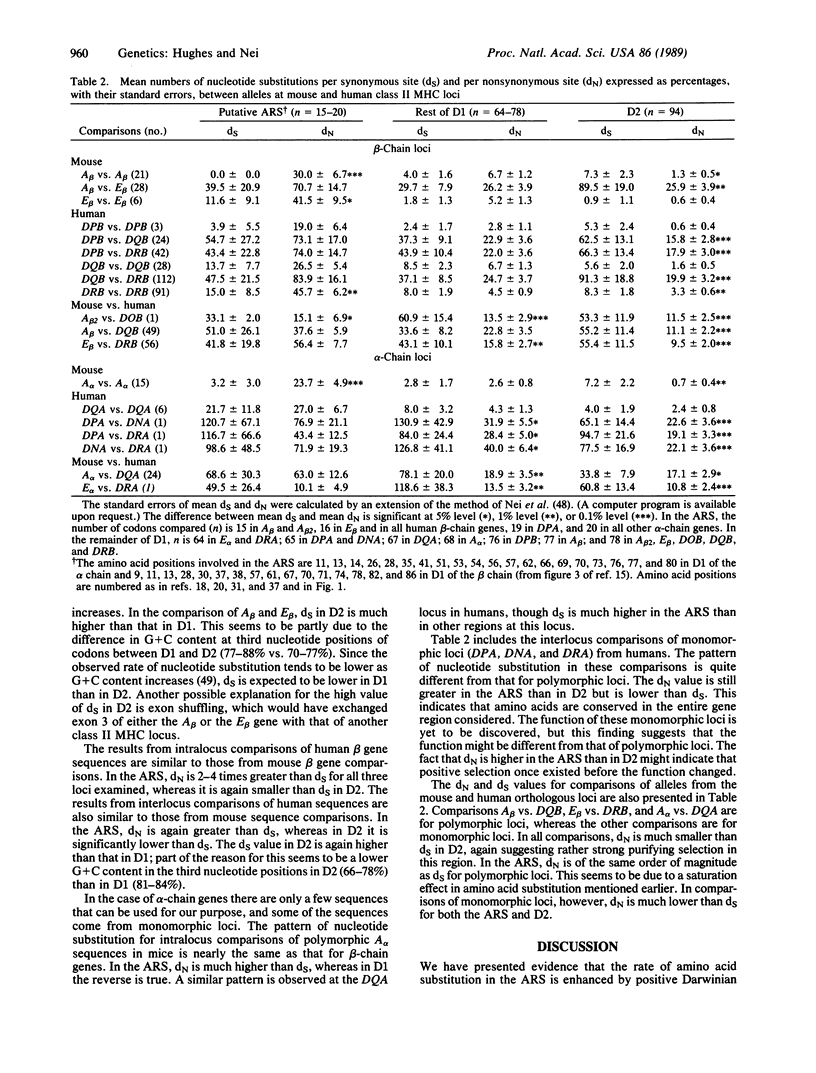
To study the mechanism of maintenance of polymorphism at major histocompatibility complex (MHC) loci, synonymous and nonsynonymous (amino acid-altering) nucleotide substitutions in the putative antigen-recognition site (included in the first domain of the MHC molecule) and other regions of human and mouse class II genes were examined. In the putative antigen-recognition site, the rate of nonsynonymous substitution was found to exceed that of synonymous substitution, whereas in the second domain the former was significantly lower than the latter. In light of a previous theoretical study and parallel findings in class I MHC loci, we conclude that the unusually high degree of polymorphism at class II MHC loci is caused mainly by overdominant selection (heterozygote advantage) operating in the antigen-recognition site.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Lillie J. W., Arnot D., Grossberger D., Kappes D., Strominger J. L. Isotypic and allotypic variation of human class II histocompatibility antigen alpha-chain genes. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):327–333. doi: 10.1038/308327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. W., Kohn H. I. Inherited histocompatibility changes in progeny of irradiated and unirradiated inbred mice. Genet Res. 1965 Nov;6(3):330–340. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300004225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, Foster L., Belt T., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. Allelic variation in the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. Regions of allelic hypervariability in the murine A alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Evolutionary significance of the HL-A system. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):139–passim. doi: 10.1038/237139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Trowsdale J., Young J., Bodmer J. Gene clusters and the evolution of the major histocompatibility system. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Jan 29;312(1154):303–315. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the human major histocompatibility complex gene DC-3 beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5199–5203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buus S., Sette A., Colon S. M., Miles C., Grey H. M. The relation between major histocompatibility complex (MHC) restriction and the capacity of Ia to bind immunogenic peptides. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1353–1358. doi: 10.1126/science.2435001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S., Trowsdale J. Molecular organization of the class II genes of the human and mouse major histocompatibility complexes. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1986;3:63–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Moriuchi T., Silver J. The heavy chain of human B-cell alloantigen HLA-DS has a variable N-terminal region and a constant immunoglobulin-like region. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):813–815. doi: 10.1038/305813a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtsinger J. M., Hilden J. M., Cairns J. S., Bach F. H. Evolutionary and genetic implications of sequence variation in two nonallelic HLA-DR beta-chain cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):209–213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. Enhanced immunological surveillance in mice heterozygous at the H-2 gene complex. Nature. 1975 Jul 3;256(5512):50–52. doi: 10.1038/256050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estess P., Begovich A. B., Koo M., Jones P. P., McDevitt H. O. Sequence analysis and structure-function correlations of murine q, k, u, s, and f haplotype I-A beta cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa F., Günther E., Klein J. MHC polymorphism pre-dating speciation. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):265–267. doi: 10.1038/335265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folsom V., Gay D., Tonegawa S. The beta 1 domain of the mouse E beta chain is important for restricted antigen presentation to helper T-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Ashwell J. D., Lechler R. I., Margulies D. H., Nickerson K. M., Suzuki G., Tou J. Y. "Exon-shuffling" maps control of antibody- and T-cell-recognition sites to the NH2-terminal domain of the class II major histocompatibility polypeptide A beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2940–2944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson K., Wiman K., Emmoth E., Larhammar D., Böhme J., Hyldig-Nielsen J. J., Ronne H., Peterson P. A., Rask L. Mutations and selection in the generation of class II histocompatibility antigen polymorphism. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1655–1661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02026.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. L., Nei M. Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature. 1988 Sep 8;335(6186):167–170. doi: 10.1038/335167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(4):295–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lair B., Alber C., Yu W. Y., Watts R., Bahl M., Karr R. W. A newly characterized HLA-DP beta-chain allele. Evidence for DP beta heterogeneity within the DPw4 specificity. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1353–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landais D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. A molecular basis for the Ia.2 and Ia.19 antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2930–2934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Denaro M., Lund T., Flavell R. A., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Structure of the murine immune response I-A beta locus: sequence of the I-A beta gene and an adjacent beta-chain second domain exon. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Hammerling U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Sequence of gene and cDNA encoding murine major histocompatibility complex class II gene A beta 2. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14111–14119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor D. A., Ward F. E., Ennis P. D., Jackson A. P., Parham P. HLA-A and B polymorphisms predate the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):268–271. doi: 10.1038/335268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B. S., Rust N. A., McMichael A. J., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DR2 subtypes form an additional supertypic family of DR beta alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Trowsdale J., Travers P. J., Carey J., Grosveld F., Jenkins J., Bodmer W. F. Sequence of an HLA-DR alpha-chain cDNA clone and intron-exon organization of the corresponding gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):750–752. doi: 10.1038/299750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock C. B., So A. K., Welsh K. I., Parkes J. D., Trowsdale J. MHC class II sequences of an HLA-DR2 narcoleptic. Immunogenetics. 1988;27(6):449–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00364432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Nucleotide sequence of a light chain gene of the mouse I-A subregion: A beta d. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.6410508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama T., Nei M. Genetic variability maintained by mutation and overdominant selection in finite populations. Genetics. 1981 Jun;98(2):441–459. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C. O., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M. R., McDevitt H. O. The murine E alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):745–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell T. J., Talbot W. S., McIndoe R. A., Wakeland E. K. The origin of MHC class II gene polymorphism within the genus Mus. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):651–654. doi: 10.1038/332651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Genetics and expression of mouse Ia antigens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:367–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengle-Gaw L., McDevitt H. O. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone for the murine I-E beta polypeptide chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchiroud D., Gautier C. High codon-usage changes in mammalian genes. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 Mar;5(2):192–194. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Stephens J. C., Saitou N. Methods for computing the standard errors of branching points in an evolutionary tree and their application to molecular data from humans and apes. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):66–85. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Maki R. A., Clayton L. K., Tonegawa S. Complete primary structures of the E beta chain and gene of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5520–5524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenning L., Larhammar D., Bill P., Wiman K., Jonsson A. K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Both alpha and beta chains of HLA-DC class II histocompatibility antigens display extensive polymorphism in their amino-terminal domains. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffenbauer J., Didier D. K., Klearman M., Rice K., Shuman S., Tieber V. L., Kittlesen D. J., Schwartz B. D. Complete sequence of the HLA DQ alpha and DQ beta cDNA from a DR5/DQw3 cell line. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):228–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A., Buus S., Colon S., Miles C., Grey H. M. I-Ad-binding peptides derived from unrelated protein antigens share a common structural motif. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):45–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell G. D. The H-2 locus of the mouse: observations and speculations concerning its comparative genetics and its polymorphism. Folia Biol (Praha) 1968;14(5):335–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So A. K., Lindsay J., Bodmer J., Trowsdale J. Molecular variation of human major histocompatibility complex DQw3 beta-chains. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3506–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnelle C., DeMars R., Long E. O. DO beta: a new beta chain gene in HLA-D with a distinct regulation of expression. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Kelly A. The human HLA class II alpha chain gene DZ alpha is distinct from genes in the DP, DQ and DR subregions. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2231–2237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto K., Yasunami M., Kimura A., Inoko H., Ando A., Hirose T., Inayama S., Sasazuki T. DQw1 beta gene from HLA-DR2-Dw12 consists of six exons and expresses multiple DQw1 beta polypeptides through alternative splicing. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(5):343–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00404428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco E., Care A., Compagnone-Post P., Robinson C., Cascino I., Trucco M. Allelic forms of the alpha- and beta-chain genes encoding DQw1-positive heterodimers. Immunogenetics. 1987;26(4-5):282–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00346523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widera G., Flavell R. A. The nucleotide sequence of the murine I-E beta b immune response gene: evidence for gene conversion events in class II genes of the major histocompatibility complex. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1221–1225. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. A., Wilkinson D., Bodmer W. F., Trowsdale J. Sequence and evolution of HLA-DR7- and -DRw53-associated beta-chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4929–4933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



