Abstract
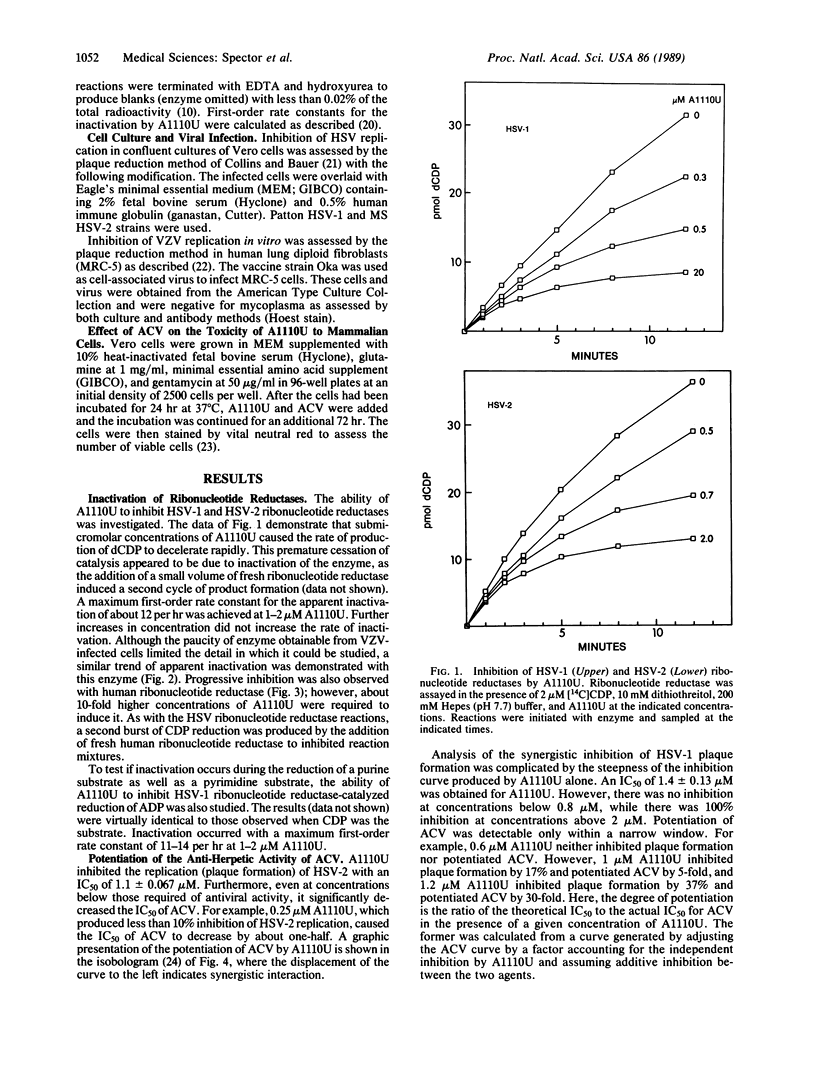
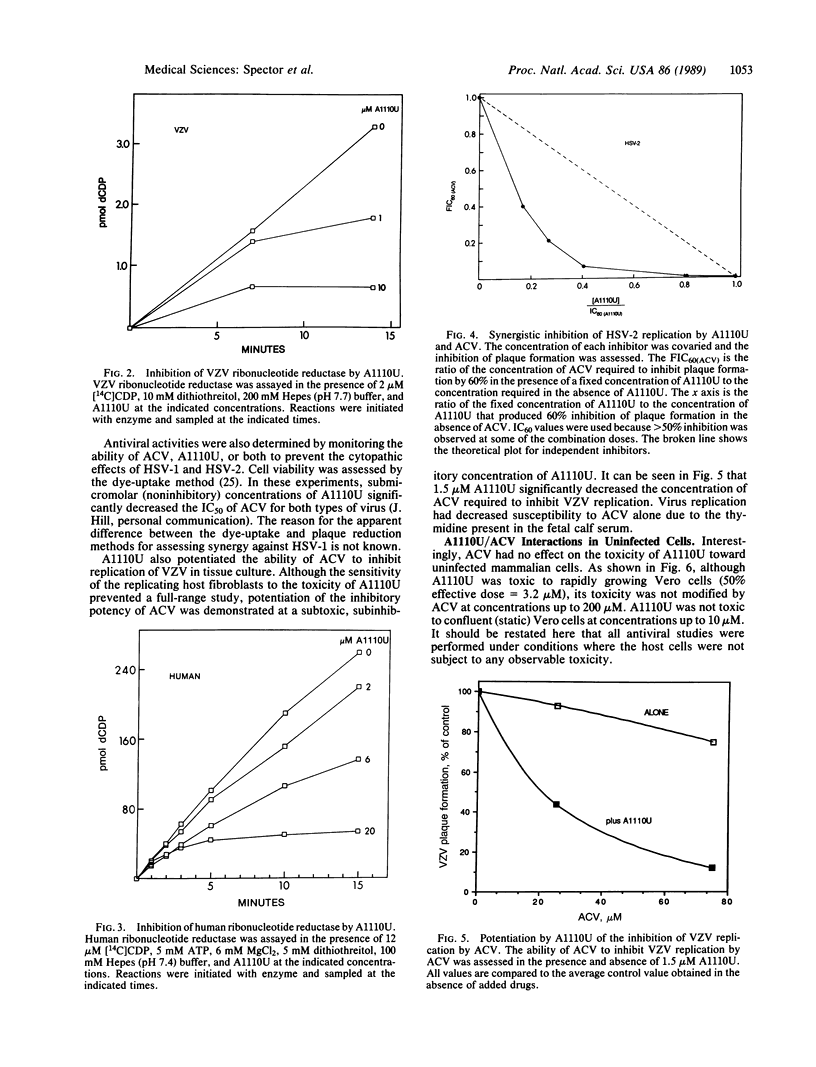
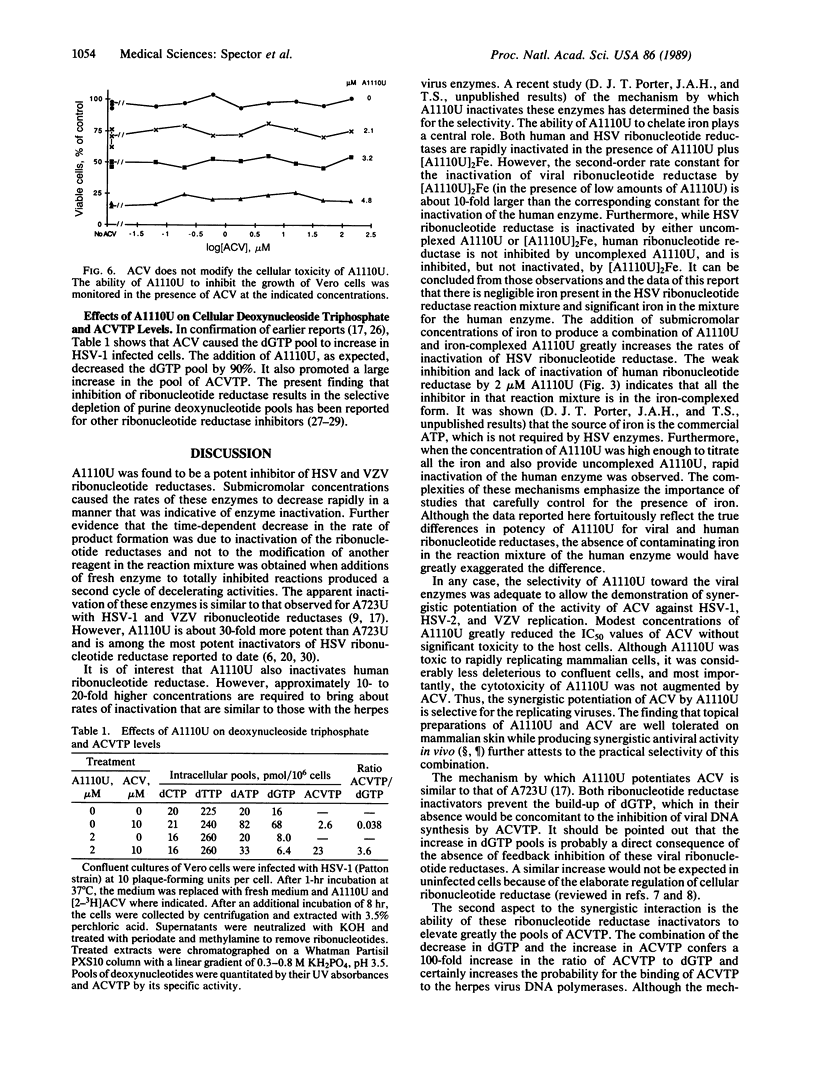
2-Acetylpyridine 5-[(dimethylamino)thiocarbonyl]thiocarbonohydrazone (A1110U) was found to be a potent inactivator of the ribonucleotide reductases (EC 1.17.4.1) encoded by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and by varicella-zoster virus and to be a weaker inactivator of human ribonucleotide reductase. It also markedly potentiated the antiherpetic activity of acyclovir against these viruses in tissue culture. A1110U both decreased the dGTP pool that builds up when infected cells are treated with acyclovir and induced a large increase in the pool of acyclovir triphosphate. The resultant 100-fold increase in the ratio of the concentrations of acyclovir triphosphate to dGTP should facilitate the binding of the fraudulent nucleotide to its target enzyme, herpes virus-encoded DNA polymerase, and could account for the synergy between A1110U and acyclovir. A similar change in the acyclovir triphosphate-to-dGTP ratio was previously reported to be induced by another ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor, 2-acetylpyridine 4-(2-morpholinoethyl)thiosemicarbazone (A723U). However, A1110U is considerably more potent and may have better clinical potential. Synergistic toxic interactions between A1110U and acyclovir were not detected in uninfected cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averett D. R., Furman P. A., Spector T. Ribonucleotide reductase of herpes simplex virus type 2 resembles that of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):981–983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.981-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averett D. R., Lubbers C., Elion G. B., Spector T. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex type 1 virus. Characterization of a distinct enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9831–9838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron K. K., Elion G. B. In vitro susceptibility of varicella-zoster virus to acyclovir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):443–447. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P., Bauer D. J. Relative potencies of anti-herpes compounds. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Inhibition of purified human and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerases by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine triphosphate. Effects on primer-template function. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11447–11451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutia B. M. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus has a virus-specified constituent. J Gen Virol. 1983 Mar;64(Pt 3):513–521. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELION G. B., SINGER S., HITCHINGS G. H. Antagonists of nucleic acid derivatives. VIII. Synergism in combinations of biochemically related antimetabolites. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jun;208(2):477–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Furman P. A., Fyfe J. A., de Miranda P., Beauchamp L., Schaeffer H. J. Selectivity of action of an antiherpetic agent, 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl) guanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5716–5720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Lambe C. U., Nelson D. J. Effect of acyclovir on the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pool levels in Vero cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):14–17. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Spector T. Acyclovir triphosphate is a suicide inactivator of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9575–9579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Weller S. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1-induced ribonucleotide reductase activity is dispensable for virus growth and DNA synthesis: isolation and characterization of an ICP6 lacZ insertion mutant. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):196–205. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.196-205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunting D., Henderson J. F. Models of the regulation of ribonucleotide reductase and their evaluation in intact mammalian cells. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(4):325–348. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson A., Harmenberg J. Effects of ribonucleotide reductase inhibition on pyrimidine deoxynucleotide metabolism in acyclovir-treated cells infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):1100–1102. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary K., Bratton J., Francke B. Replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 on hydroxyurea-resistant baby hamster kidney cells. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):224–226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.224-226.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren C., Ellis M. N., Hunter G. A. A colorimetric assay for the measurement of the sensitivity of herpes simplex viruses to antiviral agents. Antiviral Res. 1983 Nov;3(4):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(83)90001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Erbe J. Intracellular conversions of deoxyribonucleosides by Novikoff rat hepatoma cells and effects of hydroxyurea. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Jun;83(3):321–336. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Palfreyman J. W., Dutia B. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide which is a component of the virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skoog L., Nordenskjöld B. Effects of hydroxyurea and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-cytosine on deoxyribonucleotide pools in mouse embryo cells. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):81–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. D. The role of deoxynucleoside triphosphate pools in the inhibition of DNA-excision repair and replication in human cells by hydroxyurea. Mutat Res. 1984 Mar-Apr;131(3-4):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Averett D. R. A simple method to purify ribonucleotide reductase. Anal Biochem. 1983 Oct 15;134(2):467–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Averett D. R., Nelson D. J., Lambe C. U., Morrison R. W., Jr, St Clair M. H., Furman P. A. Potentiation of antiherpetic activity of acyclovir by ribonucleotide reductase inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4254–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Improvement of a simple method to purify ribonucleotide reductase. Prep Biochem. 1985;15(3):183–188. doi: 10.1080/10826068508062271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Inhibition of ribonucleotide reductases encoded by herpes simplex viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;31(3):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Jones T. E. Herpes simplex type 1 ribonucleotide reductase. Mechanism studies with inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8694–8697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T., Stonehuerner J. G., Biron K. K., Averett D. R. Ribonucleotide reductase induced by varicella zoster virus. Characterization, and potentiation of acyclovir by its inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;36(24):4341–4346. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90682-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Galloway D. A. Herpes simplex virus specifies two subunits of ribonucleotide reductase encoded by 3'-coterminal transcripts. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):802–808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.802-808.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelander L., Reichard P. Reduction of ribonucleotides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:133–158. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk S. R., Shipman C., Jr, Drach J. C. Selective inhibition of herpes simplex virus ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase by derivatives of 2-acetylpyridine thiosemicarbazone. Biochem Pharmacol. 1986 May 1;35(9):1539–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(86)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


