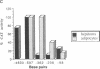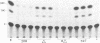Abstract
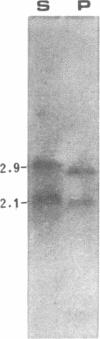
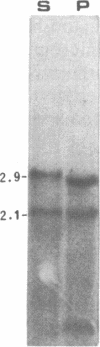
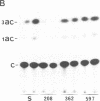
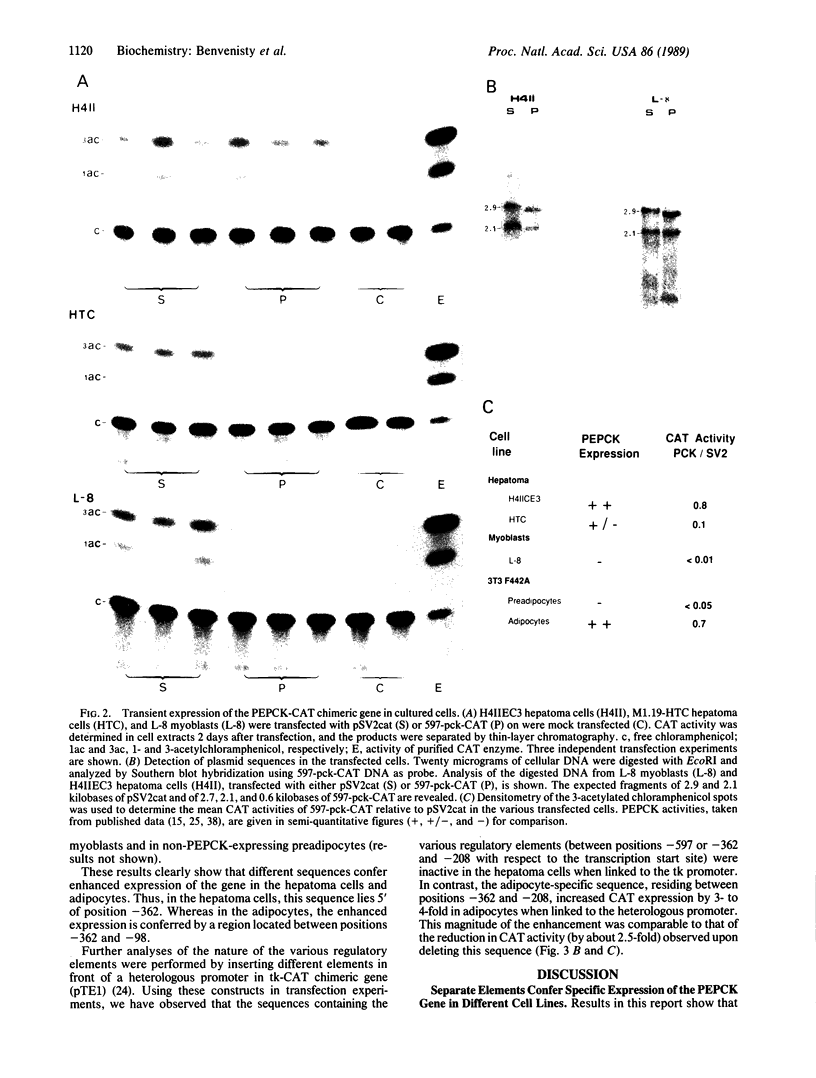
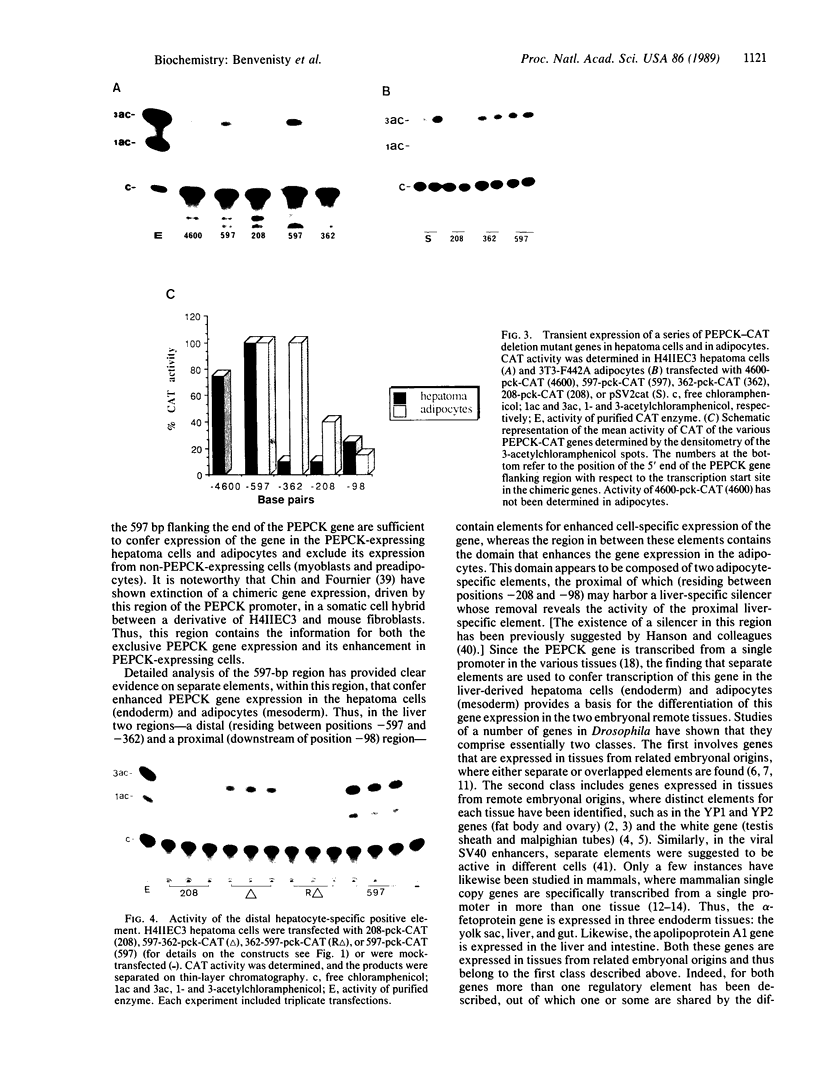
The gene encoding cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) [PEPCK; GTP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lyase (transphosphorylating), EC 4.1.1.32], a key enzyme in gluconeogenesis and glyceroneogenesis, is expressed in tissues that arise from different embryonal origins: the gluconeogenic liver arises from endoderm, whereas the gluconeogenic kidney cortex and glyceroneogenic adipose tissue arise from the mesoderm. To identify the cis-regulatory elements conferring the differential gene expression, PEPCK chimeric genes were transfected into two rat hepatoma cell lines (H4IIEC3 and HTC-M1.1) and mouse adipocytes (3T3F442A), which express the endogenous gene, and into myoblasts and preadipocytes, which do not express it. The results demonstrate that 597 base pairs of the 5' flanking region of the PEPCK gene are sufficient to confer cell-specific gene expression in the PEPCK-expressing hepatoma cells and adipocytes. However, different elements within this 597-base-pair region enhance the gene expression in the hepatoma cells (endoderm) and adipocytes (mesoderm). In the hepatocytes, expression is conferred by two elements--one 5' of position -362 and the other 3' of position -98 with respect to the transcription start site. The region in between these two elements (from -362 to -98), which seems to inhibit the gene expression in the hepatocytes, confers enhanced expression in the adipocytes. Moreover, the distal positive regulatory element of the hepatocytes seems to be orientation and PEPCK promoter dependent. In contrast, the positive regulatory element of the adipocytes seems to act as a more typical enhancer. These results suggest that separate cis-regulatory elements confer cell-specific expression of the PEPCK gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall C. J., Hirsh J. Regulation of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene in neuronal and glial cells. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):510–520. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Mencher D., Meyuhas O., Razin A., Reshef L. Sequential changes in DNA methylation patterns of the rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene during development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):267–271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benvenisty N., Szyf M., Mencher D., Razin A., Reshef L. Tissue-specific hypomethylation and expression of rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene induced by in vivo treatment of fetuses and neonates with 5-azacytidine. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5015–5019. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin A. C., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-regulation of 16 liver-specific genes in hepatoma-fibroblast hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Moore E. E., Dubois M., Weiss M. C. Dedifferentiated variants of a rat hepatoma:reversion analysis. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Drosophila Adh: a promoter element expands the tissue specificity of an enhancer. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90165-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Independent control elements that determine yolk protein gene expression in alternative Drosophila tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Corces V. G. Separate regulatory elements are responsible for the complex pattern of tissue-specific and developmental transcription of the yellow locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):996–1004. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Spontaneous heritable changes leading to increased adipose conversion in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Jenson H., Countryman J., Heston L., Gradoville L., Miller G. Transfection of a rearranged viral DNA fragment, WZhet, stably converts latent Epstein-Barr viral infection to productive infection in lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Cook J. S., Weldon S. L., Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Hanson R. W. Differential expression of the genes for the mitochondrial and cytosolic forms of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:31–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Hammer R. E., Tilghman S. M., Brinster R. L. Developmental regulation of alpha-fetoprotein genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1639–1648. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Separable cis-acting control elements for expression of the white gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3489–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nechushtan H., Benvenisty N., Brandeis R., Reshef L. Glucocorticoids control phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression in a tissue specific manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6405–6417. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir U., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J. Regulation of rat insulin 1 gene expression: evidence for negative regulation in nonpancreatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3180–3184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. HEPATOMAS IN TISSUE CULTURE COMPARED WITH ADAPTING LIVER IN VIVO. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 Apr;13:229–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Steller H., Bozzetti M. P. Multiple upstream regulatory elements control the expression of the Drosophila white gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry K. N., Seedorf U., Karathanasis S. K. Different cis-acting DNA elements control expression of the human apolipoprotein AI gene in different cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):605–614. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Bray S. J., Morgan B. A., McCormick C. A., Hirsh J. CNS and hypoderm regulatory elements of the Drosophila melanogaster dopa decarboxylase gene. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):998–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.3095924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen R. F., Li Y., Sifers R. N., Wang H., Hardick C., Tsai S. Y., Woo S. L. Tissue-specific expression of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene is controlled by multiple cis-regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8399–8415. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Wynshaw-Boris A., Short H. P., Hanson R. W. Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) promoter-regulatory region. II. Identification of cAMP and glucocorticoid regulatory domains. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9721–9726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Tomkins G. M., Curran J. F. Induction of tyrosine alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase by steroid hormones in a newly established tissue culture cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):296–303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. A myogenic cell line with altered serum requirements for differentiation. Differentiation. 1977;7(3):159–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1977.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn H., Bevers M. M., van Wijk R., Wicks W. D. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and tyrosine transaminase in hepatoma cell cultures. 3. Comparative studies in H35, HTC, MH1C1 and RLC cells. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):181–191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]