Abstract
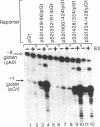
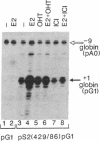
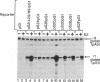
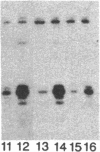
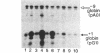
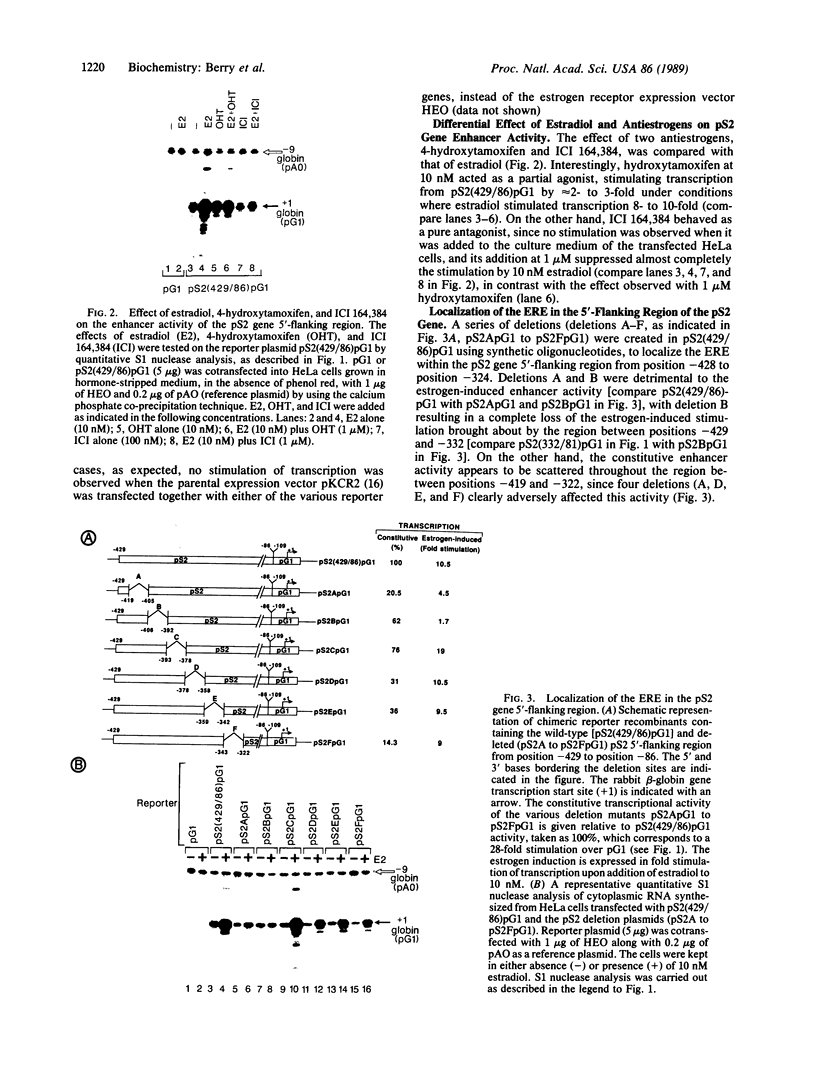
Using chimeric recombinants transfected into HeLa cells and a transient expression assay, we demonstrate that the 5'-flanking region of the pS2 gene from position -428 to position -324 exhibits both constitutive and estrogen-inducible enhancer activity. The estrogen-inducible activity, but not the constitutive activity, was inhibited by antiestrogens. ICI 164,384 behaved as a pure antagonist, whereas hydroxytamoxifen was a partial agonist-antagonist. The estrogen-responsive element of the pS2 gene has been narrowed down by site-directed deletion mutagenesis to a 13-base-pair (position -405 to position -393) imperfectly palindromic sequence, which in isolation can confer estrogen inducibility to the heterologous rabbit beta-globin gene promoter. On the other hand, the sequences responsible for the constitutive enhancer activity are spread over the entire region.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berthois Y., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Phenol red in tissue culture media is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2496–2500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Harris B. A. Plasmids for the cloning and expression of full-length double-stranded cDNAs under control of the SV40 early or late gene promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7119–7136. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Jeltsch J. M., Roberts M., Chambon P. Activation of pS2 gene transcription is a primary response to estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6344–6348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundström T., Zenke W. M., Wintzerith M., Matthes H. W., Staub A., Chambon P. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis by microscale 'shot-gun' gene synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3305–3316. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Fromental C., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A mutated polyoma virus enhancer which is active in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells is not repressed by adenovirus-2 E1A products. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):249–251. doi: 10.1038/321249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., McGuire W. L. Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer. Correlation with nuclear processing of estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2223–2228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakowlew S. B., Breathnach R., Jeltsch J. M., Masiakowski P., Chambon P. Sequence of the pS2 mRNA induced by estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2861–2878. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch J. M., Roberts M., Schatz C., Garnier J. M., Brown A. M., Chambon P. Structure of the human oestrogen-responsive gene pS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1401–1414. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Kaling M., Ryffel G. U. Synergism of closely adjacent estrogen-responsive elements increases their regulatory potential. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90635-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Ryffel G. U., Heitlinger E., Cato A. C. A 13 bp palindrome is a functional estrogen responsive element and interacts specifically with estrogen receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):647–663. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klock G., Strähle U., Schütz G. Oestrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements are closely related but distinct. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):734–736. doi: 10.1038/329734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Stack G., Berry M., Jin J. R., Chambon P. Functional domains of the human estrogen receptor. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez E., Givel F., Wahli W. The estrogen-responsive element as an inducible enhancer: DNA sequence requirements and conversion to a glucocorticoid-responsive element. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3719–3727. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Breathnach R., Bloch J., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hormone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7895–7903. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Westley B. R. Effects of tamoxifen and 4-hydroxytamoxifen on the pNR-1 and pNR-2 estrogen-regulated RNAs in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15894–15899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez A. M., Jakowlev S., Briand J. P., Gaire M., Krust A., Rio M. C., Chambon P. Characterization of the estrogen-induced pS2 protein secreted by the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1759–1765. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Wallace J., Jeltsch J. M., Berry M. The 5' flanking region of the human pS2 gene mediates its transcriptional activation by estrogen in MCF-7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):306–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90594-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Duboule D., Chambon P. Viral enhancer activity in teratocarcinoma cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:747–752. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westley B., May F. E., Brown A. M., Krust A., Chambon P., Lippman M. E., Rochefort H. Effects of antiestrogens on the estrogen-regulated pS2 RNA and the 52- and 160-kilodalton proteins in MCF7 cells and two tamoxifen-resistant sublines. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10030–10035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]