Abstract
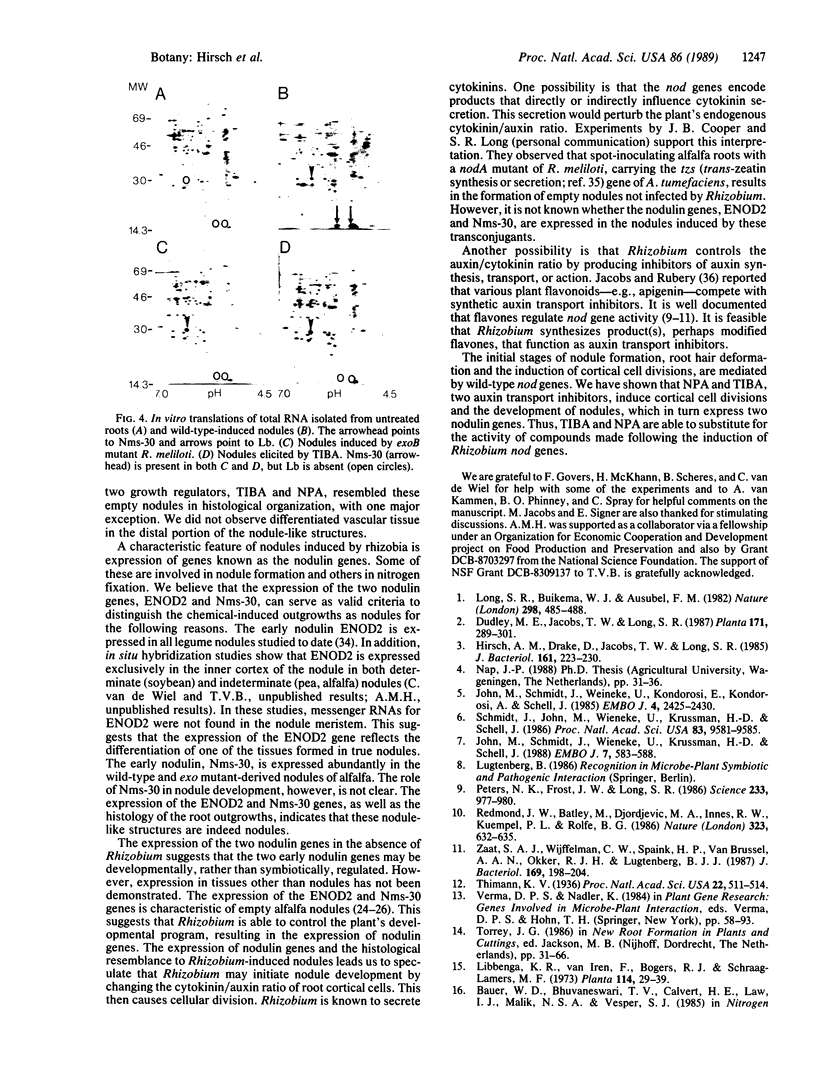
Rhizobium nod genes are essential for root hair deformation and cortical cell division, early stages in the development of nitrogen-fixing root nodules. Nod- mutants are unable to initiate nodules on legume roots. We observed that N-(1-naphthyl)phthalamic acid and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid, compounds known to function as auxin transport inhibitors, induced nodule-like structures on alfalfa roots. The nodule-like structures (pseudonodules) were white, devoid of bacteria, and resembled nodules elicited by Rhizobium meliloti exopolysaccharide (exo) mutants at both the histological and molecular level. Two nodulin genes, ENOD2 and Nms-30, were expressed. RNA isolated from the nodule-like structures hybridized to pGmENOD2, a soybean early nodulin cDNA clone. RNA isolated from roots did not hybridize. We determined by in vitro translations of total RNA that the alfalfa nodulin transcript Nms-30 was also expressed in the nodule-like structures. The late expressed nodulin genes, such as the leghemoglobin genes, were not transcribed. Because N-(1-naphthyl)phthalamic acid and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid induce the development of nodules on alfalfa roots, we suggest that the auxin transport inhibitors mimic the activity of compound(s) made upon the induction of the Rhizobium nod genes.
Keywords: nodules, nodule-specific genes, development
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D. A., Jen G., Gordon M. P. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the tzs gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain T37. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2773–2788. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickstein R., Bisseling T., Reinhold V. N., Ausubel F. M. Expression of nodule-specific genes in alfalfa root nodules blocked at an early stage of development. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):677–687. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hirsch A. M., Leigh J. A., Johansen E., Kuldau G. A., Deegan S., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that uncouple plant from bacterial differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H. J., Nap J. P., Gloudemans T., Stiekema W., Van Dam H., Govers F., Louwerse J., Van Kammen A., Bisseling T. Characterization of cDNA for nodulin-75 of soybean: A gene product involved in early stages of root nodule development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govers F., Gloudemans T., Moerman M., van Kammen A., Bisseling T. Expression of plant genes during the development of pea root nodules. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):861–867. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Bang M., Ausubel F. M. Ultrastructural analysis of ineffective alfalfa nodules formed by nif::Tn5 mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):367–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.367-380.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Drake D., Jacobs T. W., Long S. R. Nodules are induced on alfalfa roots by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Rhizobium trifolii containing small segments of the Rhizobium meliloti nodulation region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):223–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.223-230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Rubery P. H. Naturally occurring auxin transport regulators. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):346–349. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4863.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Kondorosi E., Kondorosi A., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nod C of Rhizobium meliloti in Escherichia coli: role of the nod C gene product in nodulation. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2425–2430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John M., Schmidt J., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Transmembrane orientation and receptor-like structure of the Rhizobium meliloti common nodulation protein NodC. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):583–588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Reed J. W., Hanks J. F., Hirsch A. M., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti mutants that fail to succinylate their calcofluor-binding exopolysaccharide are defective in nodule invasion. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris J. H., Macol L. A., Hirsch A. M. Nodulin gene expression in effective alfalfa nodules and in nodules arrested at three different stages of development. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):321–328. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters N. K., Frost J. W., Long S. R. A plant flavone, luteolin, induces expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3738520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., John M., Wieneke U., Krüssmann H. D., Schell J. Expression of the nodulation gene nodA in Rhizobium meliloti and localization of the gene product in the cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9581–9585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimann K. V. On the Physiology of the Formation of Nodules on Legume Roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1936 Aug;22(8):511–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.22.8.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Brussel A. A., Zaat S. A., Cremers H. C., Wijffelman C. A., Pees E., Tak T., Lugtenberg B. J. Role of plant root exudate and Sym plasmid-localized nodulation genes in the synthesis by Rhizobium leguminosarum of Tsr factor, which causes thick and short roots on common vetch. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):517–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.517-522.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaat S. A., Wijffelman C. A., Spaink H. P., van Brussel A. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Induction of the nodA promoter of Rhizobium leguminosarum Sym plasmid pRL1JI by plant flavanones and flavones. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):198–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.198-204.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]