Abstract
We have used elevated levels of plasma creatine phosphokinase activity to identify muscular dystrophy phenotypes in mice and to screen the progeny of chemical mutagen-treated male mice for X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy mutations. We were not successful in identifying heterozygous carriers of these induced muscular dystrophy mutations in greater than 8000 progeny. However, we were highly successful in identifying three additional alleles of the characterized mdx locus. These alleles of mdx were recovered from various mutagen-treated males and they occur on an X chromosome that carries flanking markers that allow us to follow the mutations in genetic crosses and in the development of corresponding mutant stocks. These alleles have been designated as mdx2Cv, mdx3Cv, and mdx4Cv. Preliminary data show that mice with mdx2Cv and mdx3Cv mutations have muscular dystrophic phenotypes that do not grossly differ from the characterized mdx mutation. These additional mdx mutations expand the value of mouse models of X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy and potentially define additional sites of mutation that impair dystrophin expression.
Full text
PDF
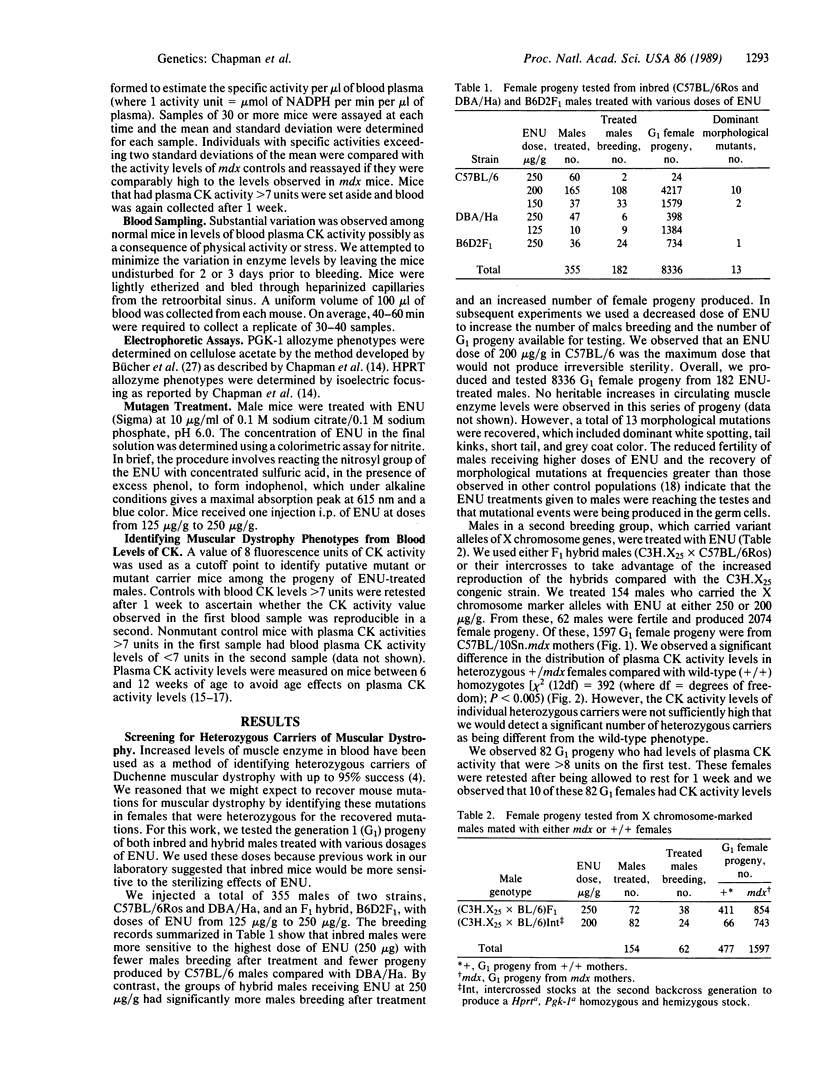


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bridges L. R. The association of cardiac muscle necrosis and inflammation with the degenerative and persistent myopathy of MDX mice. J Neurol Sci. 1986 Feb;72(2-3):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Cross G. S., Cavanna J. S., Fisher E. M., Lyon M. F., Davies K. E., Brown S. D. The mapping of a cDNA from the human X-linked Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene to the mouse X chromosome. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):166–168. doi: 10.1038/328166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücher T., Bender W., Fundele R., Hofner H., Linke I. Quantitative evaluation of electrophoretic allo-and isozyme patterns. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 30;115(2):319–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Grant S. G., Reeves A. A., Mullins L. J., Stephenson D. A., Hoffman E. P., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Caskey C. T., Chapman V. M. Regional localization of the murine Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the mouse X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Nov;13(6):671–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01534487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Pearlman J. A., Muzny D. M., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Caskey C. T., Reeves A. A. Expression of the murine Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in muscle and brain. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.3347839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Grant S. G., Benz R. A., Miller D. R., Stephenson D. A. X-chromosome linked mutations affecting mosaic expression of the mouse X chromosome. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1988;137:183–190. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-50059-6_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V. M., Kratzer P. G., Quarantillo B. A. Electrophoretic variation for X chromosome-linked hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) in wild-derived mice. Genetics. 1983 Apr;103(4):785–795. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangain J., Vrbova G. Muscle development in mdx mutant mice. Muscle Nerve. 1984 Nov-Dec;7(9):700–704. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E., Dreifuss F. E. Unusual type of benign x-linked muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Aug;29(4):338–342. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Genetic aspects, carrier detection and antenatal diagnosis. Br Med Bull. 1980 May;36(2):117–122. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery A. E., Skinner R. Clinical studies in benign (Becker type) X-linked muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1976 Oct;10(4):189–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Lemaire C., Mandel J. L., Dandolo L., Amar L., Avner P. Localization of the region homologous to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the mouse X chromosome. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):168–170. doi: 10.1038/328168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Monaco A. P., Feener C. C., Kunkel L. M. Conservation of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in mice and humans. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):347–350. doi: 10.1126/science.3659917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson F. M., Lewis S. E. Electrophoretically detected germinal mutations induced in the mouse by ethylnitrosourea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3138–3141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Bode V. C. Induction of new mutations in a mouse t-haplotype using ethylnitrosourea mutagenesis. Genet Res. 1986 Jun;47(3):187–192. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300023119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J. T., Chapman V. M. Electrophoretic variation for x-chromosome-linked phosphoglycerate kinase (pgk-1) in the mouse. Genetics. 1977 Oct;87(2):319–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Hunsicker P. R., Carpenter D. A., Cornett C. V., Guinn G. M. Effect of dose fractionation on the ethylnitrosourea induction of specific-locus mutations in mouse spermatogonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3592–3593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Hunsicker P. R., Raymer G. D., Steele M. H., Stelzner K. F., Thompson H. M. Dose--response curve for ethylnitrosourea-induced specific-locus mutations in mouse spermatogonia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3589–3591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. L., Kelly E. M., Hunsicker P. R., Bangham J. W., Maddux S. C., Phipps E. L. Specific-locus test shows ethylnitrosourea to be the most potent mutagen in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5818–5819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder-Cook A. S., Sicinski P., Thomas K., Davies K. E., Worton R. G., Barnard E. A., Darlison M. G., Barnard P. J. Localization of the mdx mutation within the mouse dystrophin gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3017–3021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03165.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
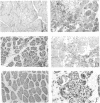
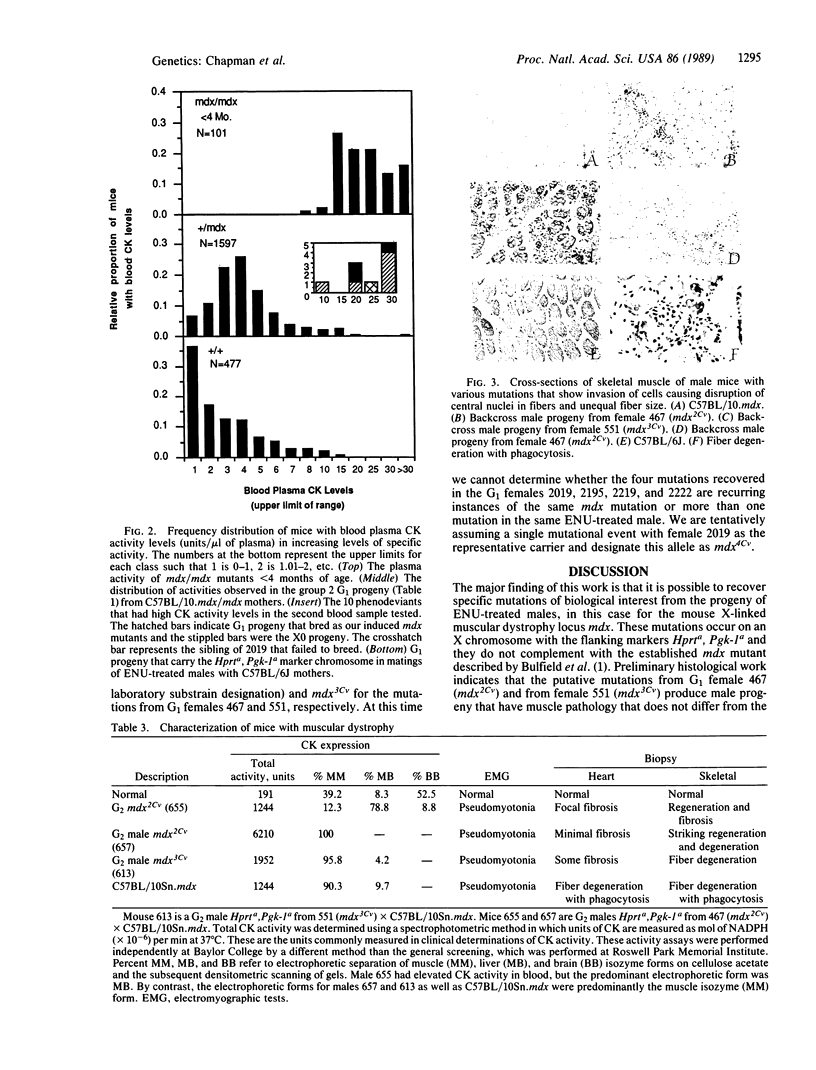
- Tanabe Y., Esaki K., Nomura T. Skeletal muscle pathology in X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mouse. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(1-2):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00687043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres L. F., Duchen L. W. The mutant mdx: inherited myopathy in the mouse. Morphological studies of nerves, muscles and end-plates. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):269–299. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]