Abstract
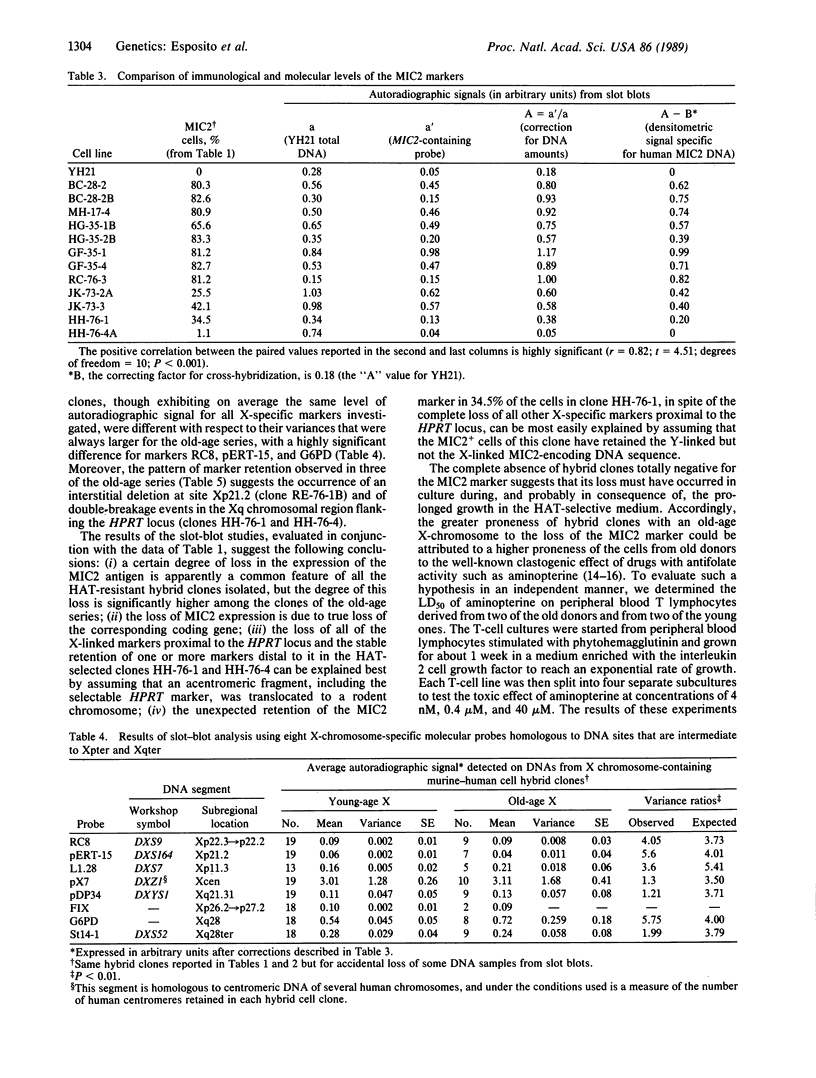
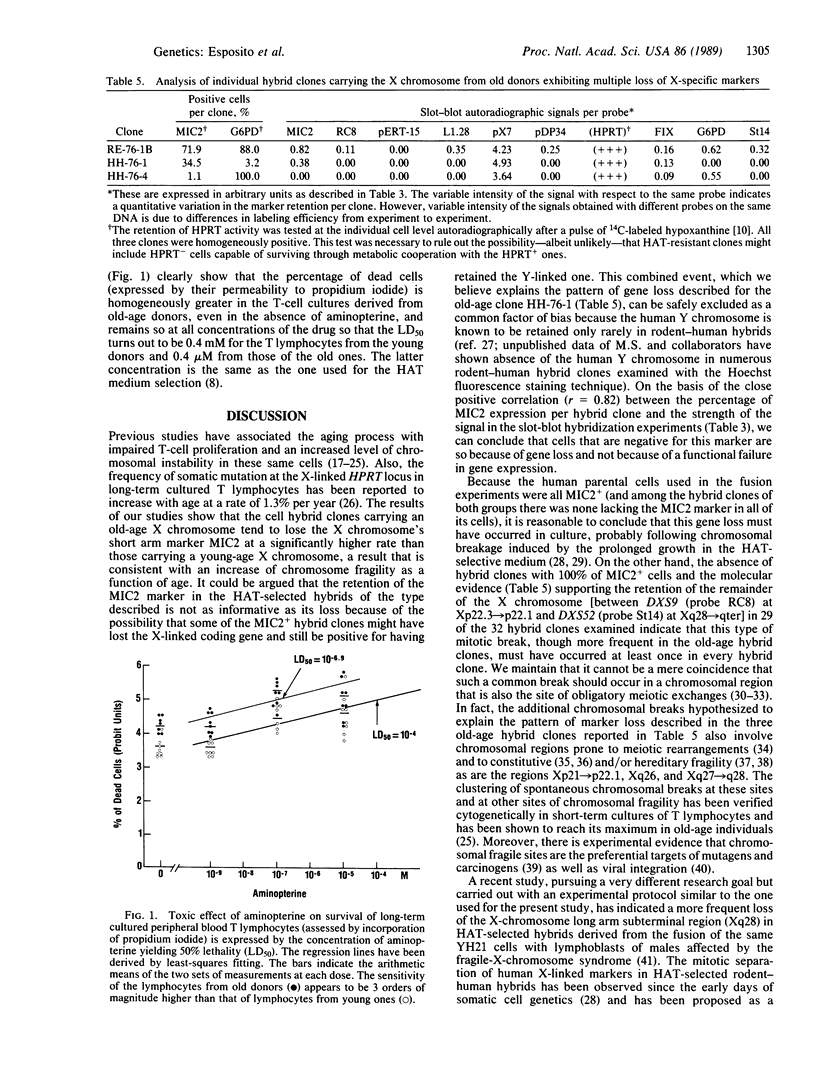
We have adopted a simplified version of the "cell hybrid cotransfer method" to test the hypothesis that human lymphocytes derived from elderly individuals have a higher chromosome instability. Peripheral blood lymphocytes from "old" male individuals and "young" controls were fused with a Chinese hamster cell line (CHO-YH21), yielding 10 HAT-resistant rodent-human clones from the old propositi and 22 from the young controls (HAT = hypoxanthine/aminopterin/thymidine). Both series of hybrid clones were analyzed with respect to the retention of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and the surface antigen MIC2 identified by monoclonal antibody 12E7, two human X chromosome-linked markers located at opposite ends of the X chromosome. Cell hybrid clones with an X chromosome from a young control retained both markers in about 70% of the cells. In contrast, cell hybrid clones with an X chromosome from an old donor retained the MIC2 marker in only 30% of their cells. Slot-blot hybridization studies have established that the observed loss of the MIC2 marker is due to loss of the coding gene, not to suppression of its expression. Similar hybridization studies with molecular probes specific for other regions of the X chromosome suggest preferential chromosomal breakage sites. T lymphocytes from old donors were also found to have an LD50 for aminopterine significantly lower than the concentration of this drug in the HAT medium used to grow the hybrids, suggesting that the higher level of gene loss observed in the X chromosomes from old donors may be directly related to their increased sensitivity to the clastogenic effect of aminopterine. We speculate that the higher rate of chromosomal breakage and of marker loss observed along the "old-age" X chromosomes could be the result of "molecular scars" accumulated with aging at sites of constitutive chromosomal fragility.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhadeff B., Velivasakis M., Pagan-Charry I., Wright W. C., Siniscalco M. High rate of sister chromatid exchanges of Bloom's syndrome chromosomes is corrected in rodent human somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(1):8–23. doi: 10.1159/000131459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedler J. L., Albrecht A. M., Spengler B. A. Biochemical and karyological properties of cells resistant to the quinazoline antifolate, methasquin. Eur J Cancer. 1978 Jan;14(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(78)90136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling S. M., Banting G. S., Pym B., Wolfe J., Goodfellow P. N. Cloning an expressed gene shared by the human sex chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):135–139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutkowski R. T., Lesh R., Staiano-Coico L., Thaler H., Darlington G. J., Weksler M. E. Increased chromosomal instability in lymphocytes from elderly humans. Mutat Res. 1985 May;149(3):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90169-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Kozak R., Durante M., Weksler M. E. Immunological studies of aging. Decreased production of and response to T cell growth factor by lymphocytes from aged humans. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):937–942. doi: 10.1172/JCI110143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover T. W. FUdR induction of the X chromosome fragile site: evidence for the mechanism of folic acid and thymidine inhibition. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Mar;33(2):234–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. J., Darling S. M., Thomas N. S., Goodfellow P. N. A pseudoautosomal gene in man. Science. 1986 Nov 7;234(4777):740–743. doi: 10.1126/science.2877492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Banting G., Levy R., Povey S., McMichael A. A human X-linked antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Nov;6(6):777–787. doi: 10.1007/BF01538976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goss S. J., Harris H. New method for mapping genes in human chromosomes. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):680–684. doi: 10.1038/255680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. Subpopulations of human T lymphocytes. XVII. Imbalance of T cell subsets in patients with progeria and Werner's syndrome. Gerontology. 1981;27(4):181–186. doi: 10.1159/000212471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefton J. M., Darlington G. J., Casazza B. A., Weksler M. E. Immunologic studies of aging. V. Impaired proliferation of PHA responsive human lymphocytes in culture. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1007–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. The inheritance of epigenetic defects. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):163–170. doi: 10.1126/science.3310230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlhens F., Achkar W. A., Aurias A., Couturier J., Dutrillaux A. M., Gerbault-Sereau M., Hoffschir F., Lamoliatte E., Lefrançois D., Lombard M. The rate of chromosome breakage is age dependent in lymphocytes of adult controls. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):290–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00279088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Cook P. R., Meera Khan P., Shin S., Siniscalco M. Mitotic separation of two human X-linked genes in man--mouse somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):116–120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgel L. E. Ageing of clones of mammalian cells. Nature. 1973 Jun 22;243(5408):441–445. doi: 10.1038/243441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 18 DNA is integrated at a single chromosome site in cervical carcinoma cell line SW756. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1682–1685. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1682-1685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard C. A., Goodfellow P. N. Investigation of chromosome-mediated gene transfer using the HPRT region of the human X chromosome as a model. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):172–178. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstraus M., Chasin L. A. Isolation of mammalian cell mutants deficient in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity: linkage to hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Johnsson C., Vergnaud G., Cooke H. J., Weissenbach J. A gradient of sex linkage in the pseudoautosomal region of the human sex chromosomes. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):291–295. doi: 10.1038/319291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., SZYBALSKA E. H. Drug sensitivity as a genetic marker for human cell lines. Med Bull (Ann Arbor) 1962 Sep-Oct;28:277–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R., Hausman P. B., Rinnooy-Kan E., Weksler M. E. Immunological studies of ageing. X. Impaired T lymphocytes and normal monocyte response from elderly humans to the mitogenic antibodies OKT3 and Leu 4. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):677–684. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab R., Staiano-Coico L., Weksler M. E. Immunological studies of aging. IX. Quantitative differences in T lymphocyte subsets in young and old individuals. Diagn Immunol. 1983;1(3):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siniscalco M., Klinger H. P., Eagle H., Koprowski H., Fujimoto W. Y., Seegmiller J. E. Evidence for intergenic complementation in hybrid cells derived from two human diploid strains each carrying an X-linked mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):793–799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiano-Coico L., Darzynkiewicz Z., Hefton J. M., Dutkowski R., Darlington G. J., Weksler M. E. Increased sensitivity of lymphocytes from people over 65 to cell cycle arrest and chromosomal damage. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1335–1337. doi: 10.1126/science.6828861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiano-Coico L., Darzynkiewicz Z., Melamed M. R., Weksler M. E. Immunological studies of aging. IX. Impaired proliferation of T lymphocytes detected in elderly humans by flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1788–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes II. Distribution, phenotypic effects, and cytogenetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):136–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilard L. ON THE NATURE OF THE AGING PROCESS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Jan;45(1):30–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor K. J., Wigmore D. J., Chrysostomou A., Dempsey J. L., Seshadri R., Morley A. A. Mutation frequency in human lymphocytes increases with age. Mech Ageing Dev. 1984 Sep;27(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(84)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Zhang F., Licameli G. R., Peters J. F. The fragile X site in somatic cell hybrids: an approach for molecular cloning of fragile sites. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):420–423. doi: 10.1126/science.3603029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F., Skolnick M. H., Pearson P. L., Mandel J. L. Report of the Committee on Human Gene Mapping by Recombinant DNA Techniques. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):360–489. doi: 10.1159/000132180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L., Bowe A. E. Fragile sites are targets of diverse mutagens and carcinogens. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):59–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Soreng A. L. Constitutive fragile sites and cancer. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1199–1204. doi: 10.1126/science.6239375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



