Abstract
CD28 is a 44-kDa glycoprotein expressed as a homodimer on the surface of a major subset of human T cells. Previous studies have demonstrated that the binding of monoclonal antibodies to the CD28 surface antigen can augment the proliferation of purified human T cells stimulated with suboptimal doses of mitogens or anti-T-cell receptor/CD3 complex antibodies. In this report, we show that CD28 stimulation augments T-cell immune responses by specifically inducing a 5- to 50-fold enhancement in the expression and secretion of interleukin 2, tumor necrosis factor type alpha, lymphotoxin, interferon gamma, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in normal human T cells stimulated to proliferate by crosslinking of the T-cell receptor/CD3 complex. This CD28-mediated induction of lymphokine/cytokine gene expression occurred even in T cells stimulated with optimal concentrations of mitogens or anti-T-cell receptor/CD3 antibodies, although under these conditions CD28 activation failed to enhance the proliferative response. The activation pathway induced by stimulation of CD28 is distinct from other biochemical pathways that induce lymphokines/cytokines because CD28 stimulation can induce lymphokine/cytokine gene expression in the presence of the immunosuppressant cyclosporine. Together these data suggest that the CD28 cell surface molecule is part of a distinct activation pathway that specifically modulates the expression of multiple lymphokine/cytokine genes.
Full text
PDF
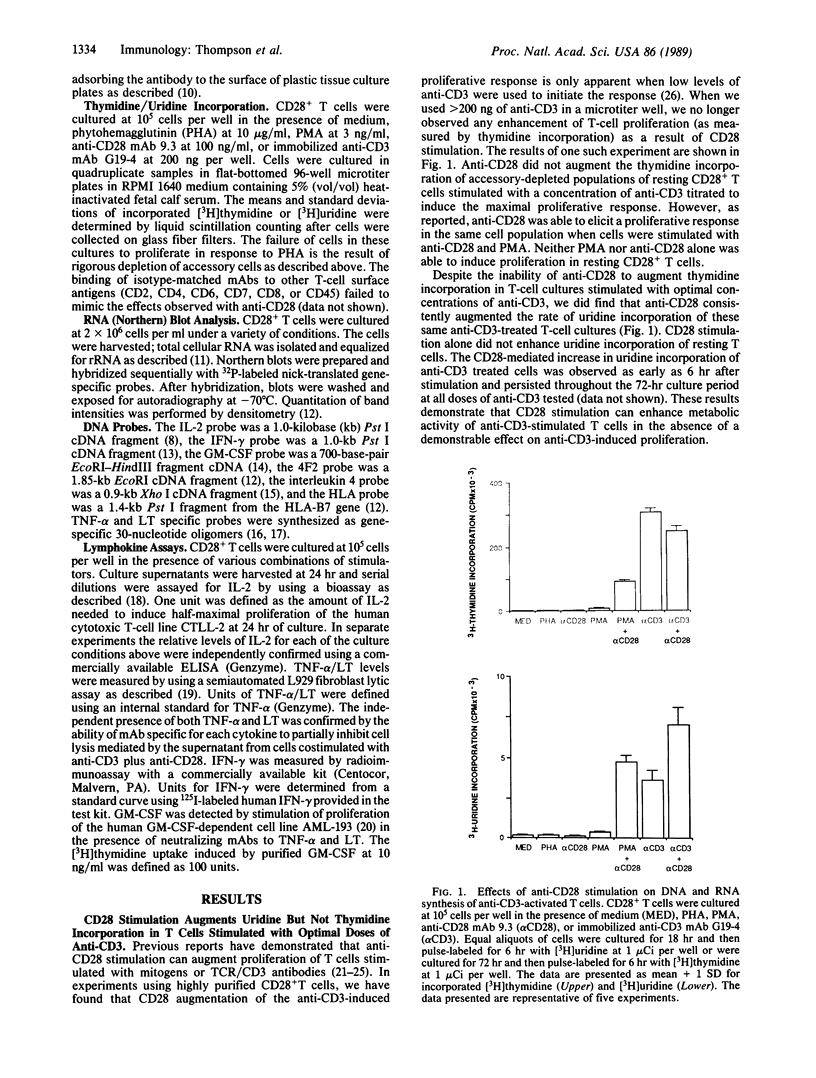

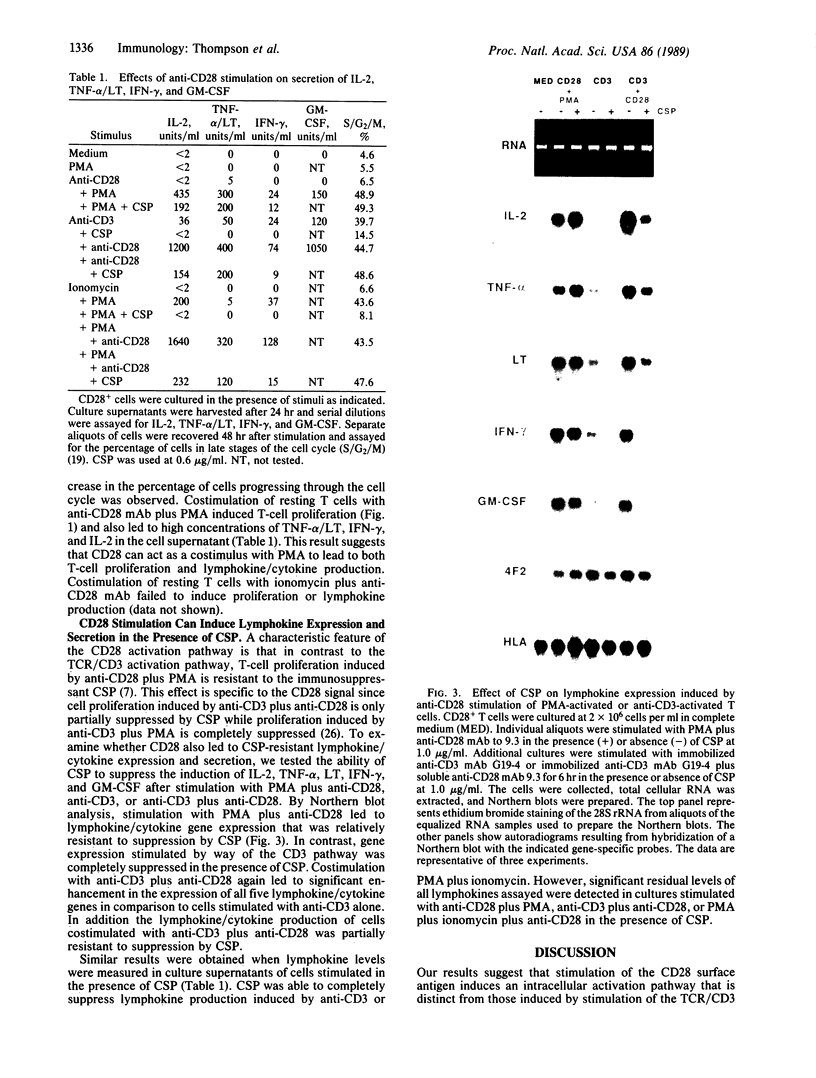

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aruffo A., Seed B. Molecular cloning of a CD28 cDNA by a high-efficiency COS cell expression system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppert T. D., Lipsky P. E. Accessory cell independent proliferation of human T4 cells stimulated by immobilized monoclonal antibodies to CD3. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 15;138(6):1660–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmünder H., Lesslauer W. A 45-kDa human T-cell membrane glycoprotein functions in the regulation of cell proliferative responses. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jul 2;142(1):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A. Human T cell activation. II. A new activation pathway used by a major T cell population via a disulfide-bonded dimer of a 44 kilodalton polypeptide (9.3 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1513–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Gillespie M. M., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Spengler M., May M. A., Spengler R., Larrick J., Remick D. Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing T. J., Weiss A. Evidence for IL-2 independent proliferation in human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1056–1062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange B., Valtieri M., Santoli D., Caracciolo D., Mavilio F., Gemperlein I., Griffin C., Emanuel B., Finan J., Nowell P. Growth factor requirements of childhood acute leukemia: establishment of GM-CSF-dependent cell lines. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Gentry L. E., June C. H., Rabinovitch P. S., Purchio A. F. Stimulation of T cells through the CD3/T-cell receptor complex: role of cytoplasmic calcium, protein kinase C translocation, and phosphorylation of pp60c-src in the activation pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):650–656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Martin P. J., Spooner C. E., Wofsy D., Tsu T. T., Beatty P. G., Gladstone P. Antibodies to Tp67 and Tp44 augment and sustain proliferative responses of activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2331–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Regulation of 4F2 heavy-chain gene expression during normal human T-cell activation can be mediated by multiple distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3820–3826. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsten T., June C. H., Thompson C. B. Multiple mechanisms regulate c-myc gene expression during normal T cell activation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2787–2794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R. The structure of the CD4 and CD8 genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:561–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The T cell receptor. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1073–1079. doi: 10.1126/science.3317824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P. J., Ledbetter J. A., Morishita Y., June C. H., Beatty P. G., Hansen J. A. A 44 kilodalton cell surface homodimer regulates interleukin 2 production by activated human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3282–3287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Moretta L. Involvement of T44 molecules in an antigen-independent pathway of T cell activation. Analysis of the correlations to the T cell antigen-receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):823–838. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen M., Ottmann O. G., Moore M. A. Simultaneous production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin by normal T cells after induction with IL-2 and anti-T3. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2621–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Creasey A. A., Ladner M. B., Lin L. S., Strickler J., Van Arsdell J. N., Yamamoto R., Mark D. F. Molecular cloning of the complementary DNA for human tumor necrosis factor. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.3856324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Manger B., Imboden J. Synergy between the T3/antigen receptor complex and Tp44 in the activation of human T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):819–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. G., Witek J. S., Temple P. A., Wilkens K. M., Leary A. C., Luxenberg D. P., Jones S. S., Brown E. L., Kay R. M., Orr E. C. Human GM-CSF: molecular cloning of the complementary DNA and purification of the natural and recombinant proteins. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):810–815. doi: 10.1126/science.3923623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Otsuka T., Mosmann T., Banchereau J., DeFrance T., Blanchard D., De Vries J. E., Lee F., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a human interleukin cDNA clone, homologous to mouse B-cell stimulatory factor 1, that expresses B-cell- and T-cell-stimulating activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Dray J. F., Farrar W. L. Expression of transfected human interferon-gamma DNA: evidence for cell-specific regulation. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4700–4703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




















