Abstract
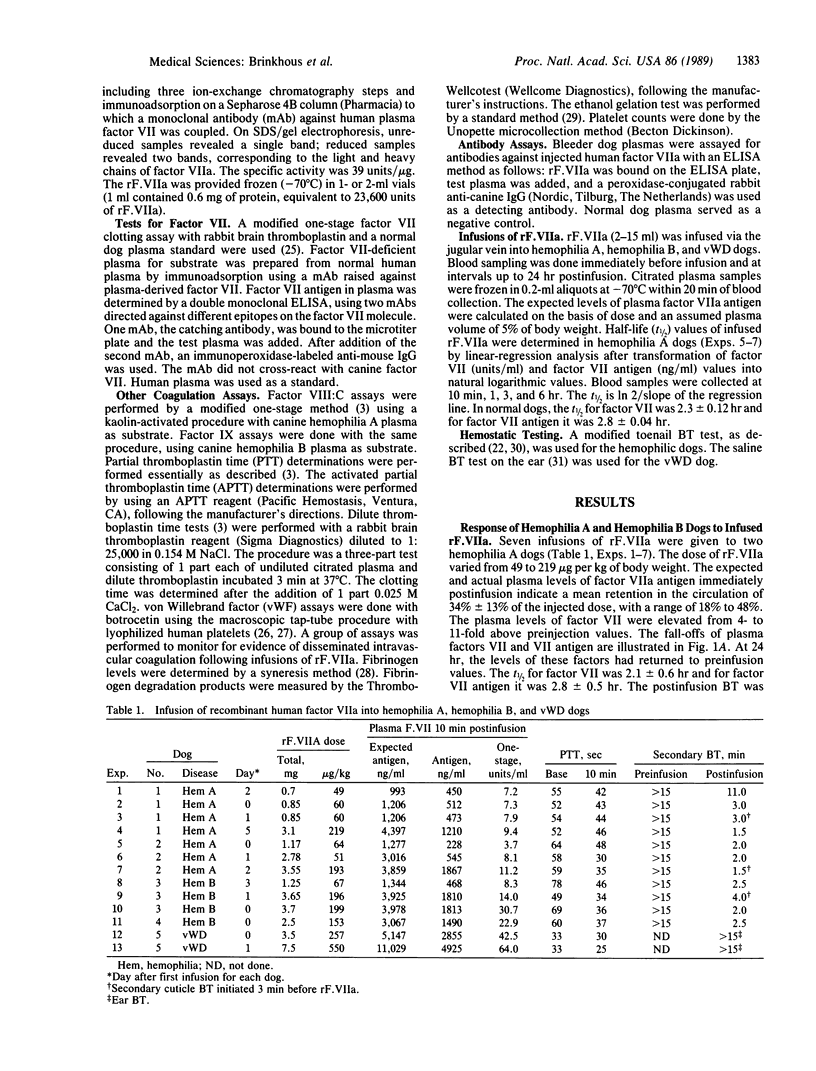
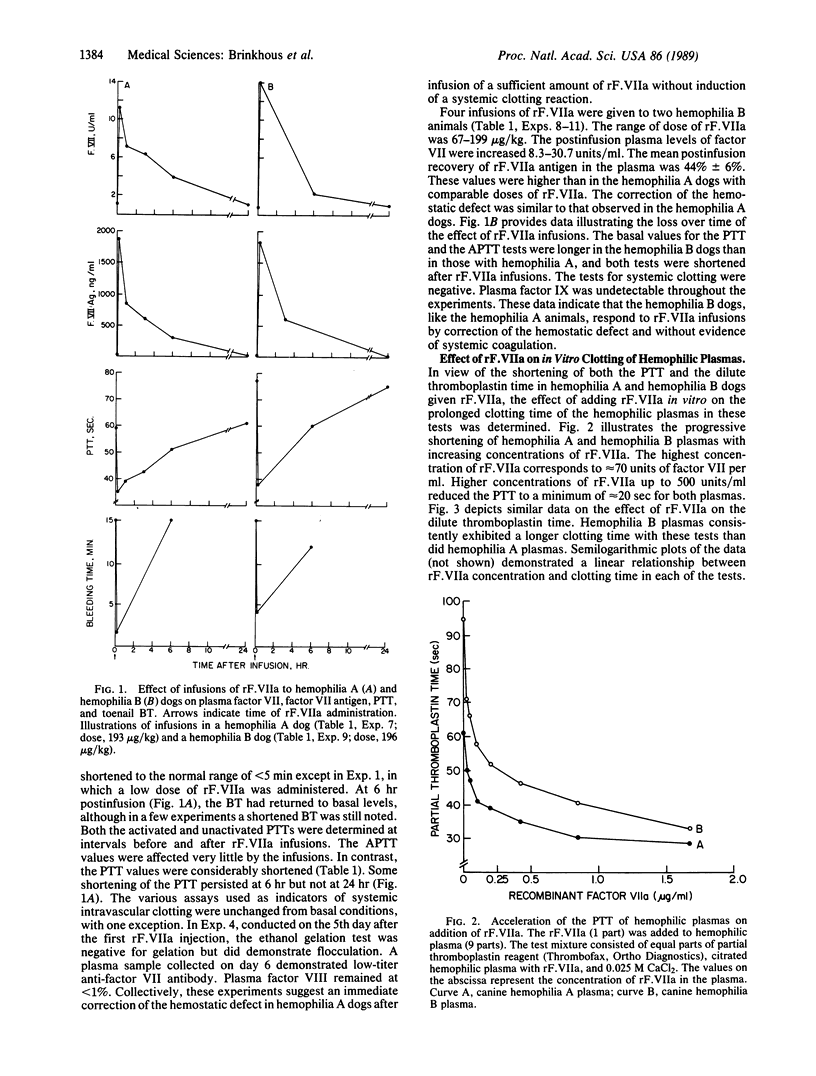
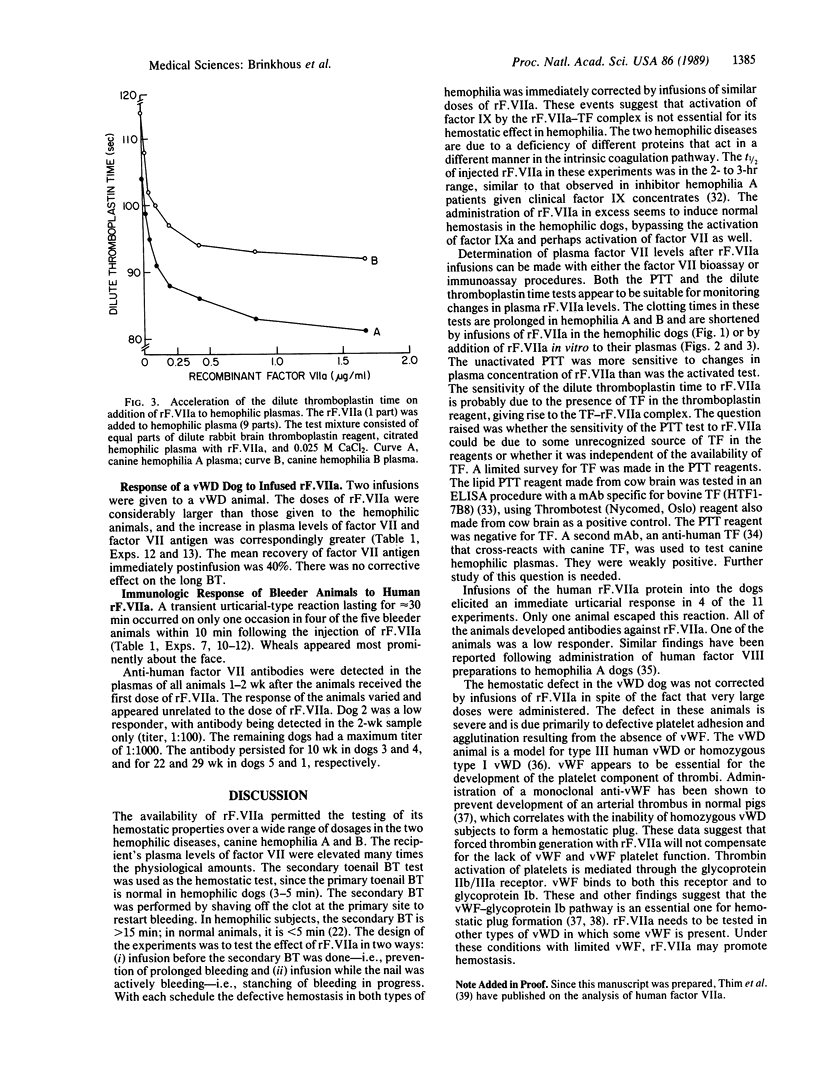
Recombinant factor VIIa (rF.VIIa) is a two-chain procoagulant enzyme (Mr, approximately 50,000) active only when complexed with tissue factor in the extrinsic clotting system. We administered human rF.VIIa to hemophilic and von Willebrand disease (vWD) dogs to determine its hemostatic effectiveness and survival in the circulation. Hemophilia A dogs lacking factor VIII demonstrated an immediate increase in plasma rF. VIIa and prompt stoppage of hemorrhage at bleeding time (BT) sites. In seven studies in two dogs, the range of dose of rF. VIIa was 50-220 micrograms/kg, with an apparent 7- to 11-fold increase in plasma factor VII and a mean recovery in plasma of 34%. The t1/2 was 2.8 +/- 0.5 hr. The BT was normalized except in an animal given the minimum dose. In four studies in two hemophilia B dogs lacking factor IX, BT was normalized. The elevation in plasma factor VII was by a factor of 8-30, with a mean recovery of rF.VIIa in plasma of 44%. In two studies in a homozygous vWD dog lacking von Willebrand factor, which is needed for platelet function, BT was not corrected even though large doses of rF. VIIa were given. The human rF. VIIa protein was immunogenic for dogs. These studies indicate that factor VIIa corrects the hemostatic defect in dogs with hemophilia A and B, diseases primarily of the intrinsic clotting system, but does not correct the hemostatic defect in vWD.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellinger D. A., Nichols T. C., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Lamb M. A., Brinkhous K. M., Evatt B. L., Griggs T. R. Prevention of occlusive coronary artery thrombosis by a murine monoclonal antibody to porcine von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8100–8104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breen F. A., Jr, Tullis J. L. Ethanol gelation: a rapid screening test for intravascular coagulation. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Davis P. D., Graham J. B., Dodds W. J. Expression and linkage of genes for X-linked hemophilias A and B in the dog. Blood. 1973 Apr;41(4):577–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S., Reddick R. L., Griggs T. R. Pathophysiology of platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor: applications of the venom coagglutinin vWF assay. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:191–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Read M. S. Use of venom coagglutinin and lyophilized platelets in testing for platelet-aggregating von Willebrand factor. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Sandberg H., Garris J. B., Mattsson C., Palm M., Griggs T., Read M. S. Purified human factor VIII procoagulant protein: comparative hemostatic response after infusions into hemophilic and von Willebrand disease dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8752–8756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Majerus P. W. Purification and properties of human coagulation factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1242–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D., Bach R., Carson S. M. Monoclonal antibodies against bovine tissue factor, which block interaction with factor VIIa. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):152–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D., Ross S. E., Bach R., Guha A. An inhibitory monoclonal antibody against human tissue factor. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D. Tissue factor-initiated blood coagulation. Prog Clin Pathol. 1984;9:1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles A. R., Tinlin S., Greenwood R. A canine model of hemophilic (factor VIII:C deficiency) bleeding. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):727–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Packham M. A., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Cattaneo M., Mustard J. F. Effect of calcium ion concentration on the ability of fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor to support the ADP-induced aggregation of human platelets. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):827–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U., Kisiel W. Use of human factor VIIa in the treatment of two hemophilia A patients with high-titer inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1836–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI110939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J. The inhibition of activated bovine coagulation factors X and VII by antithrombin III. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):165–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josso F., Prou-Wartelle O. Interaction of tissue factor and factor VII at the earliest phase of coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1965;17:35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurczynski E. M., Penner J. A. Activated prothrombin concentrate for patients with factor VIII inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jul 25;291(4):164–167. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407252910402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood J. D., Barrowcliffe T. W. The development and characterisation of antibodies to human factor VIII in haemophilic dogs. Thromb Haemost. 1987 Jun 3;57(3):314–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusher J. M., Shapiro S. S., Palascak J. E., Rao A. V., Levine P. H., Blatt P. M. Efficacy of prothrombin-complex concentrates in hemophiliacs with antibodies to factor VIII: a multicenter therapeutic trial. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 21;303(8):421–425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008213030803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Kleiss A. J., Griffin J. H. An alternative extrinsic pathway of human blood coagulation. Blood. 1982 Dec;60(6):1353–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B. C., Hultin M. B., Jesty J. Altered factor VII activity in hemophilia. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):845–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON I. M., OLOW B. Determination of fibrinogen and fibrinogenolytic activity. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1962 Nov 15;8:297–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y., Bach R. Tissue factor revisited. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1982;6:237–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. Tissue factor and hemostasis. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Miller-Andersson M., Abildgaard U., Prydz H. The effect of antithrombin III on the activity of the coagulation factors VII, IX and X. Thromb Haemost. 1976 Apr 30;35(2):295–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploplis V. A., Edgington T. S., Fair D. S. Initiation of the extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Association of factor VIIa with a cell line expressing tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9503–9508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor VII bound to tissue factor: a key early step in the tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6687–6691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read M. S., Potter J. Y., Brinkhous K. M. Venom coagglutinin for detection of von Willebrand factor activity in animal plasmas. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jan;101(1):74–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Kasper C. K., Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activated factor VII: presence in factor IX concentrates and persistence in the circulation after infusion. Blood. 1979 May;53(5):828–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Bjoern S., Christensen M., Nicolaisen E. M., Lund-Hansen T., Pedersen A. H., Hedner U. Amino acid sequence and posttranslational modifications of human factor VIIa from plasma and transfected baby hamster kidney cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7785–7793. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Lages B. Evidence for tissue factor-dependent activation of the classic extrinsic coagulation mechanism in blood obtained from bleeding time wounds. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):629–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ruggeri Z. M. von Willebrand disease. Hum Pathol. 1987 Feb;18(2):140–152. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Nemerson Y. The esterase activity of coagulation factor VII. Evidence for intrinsic activity of the zymogen. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2203–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


