Abstract
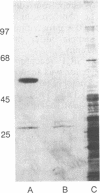
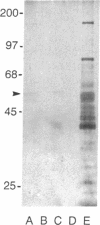
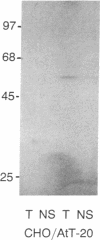
The brain somatostatin (somatotropin release-inhibiting factor; SRIF) receptor was purified by affinity chromatographic techniques. A protein of 60 kDa could be purified from rat brain. The protein was eluted from a [D-Trp8]SRIF affinity column with either sodium acetate (pH 5.5) or free [D-Trp8]SRIF. The binding of the protein to the affinity column was prevented by free [D-Trp8]SRIF or the stable SRIF analogue SMS 201-996 but not by the inactive somatostatin 28-(1-14). The purified receptor could be covalently labeled by the 125I-labeled SRIF analogue CGP 23996. Excess [D-Trp8]SRIF blocked the binding of 125I-labeled CGP 23996 to the purified receptor, but somatostatin 28-(1-14) did not affect the binding. A 60-kDa protein was also purified from the anterior pituitary cell line AtT-20, which has a high expression of SRIF receptors. In contrast, no 60-kDa protein could be purified from CHO cells, which have no detectable SRIF receptors. These findings present evidence for the purification of the SRIF receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonner T. I., Buckley N. J., Young A. C., Brann M. R. Identification of a family of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):527–532. doi: 10.1126/science.3037705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Rivier J., Vale W. Somatostatin-28: selective action on the pancreatic beta-cell and brain. Endocrinology. 1981 Jun;108(6):2391–2396. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-6-2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernik A. J., Petrack B. Somatostatin receptor binding in rat cerebral cortex. Characterization using a nonreducible somatostatin analog. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5525–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epelbaum J. Somatostatin in the central nervous system: physiology and pathological modifications. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;27(1):63–100. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquin T., Champagnat J., Madamba S., Denavit-Saubié M., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin depresses excitability in neurons of the solitary tract complex through hyperpolarization and augmentation of IM, a non-inactivating voltage-dependent outward current blocked by muscarinic agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):948–952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Dorflinger L. J., Schonbrunn A. Pertussis toxin blocks both cyclic AMP-mediated and cyclic AMP-independent actions of somatostatin. Evidence for coupling of Ni to decreases in intracellular free calcium. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13138–13145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B. D., Schonbrunn A. The somatostatin receptor is directly coupled to adenylate cyclase in GH4C1 pituitary cell membranes. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1784–1790. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahy N., Woolkalis M., Thermos K., Carlson K., Manning D., Reisine T. Pertussis toxin modifies the characteristics of both the inhibitory GTP binding proteins and the somatostatin receptor in anterior pituitary tumor cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):779–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L., Stenner D., Blanchard W., Nissen S., Gerich J., Ling N., Brazeau P., Bohlen P., Esch F., Guillemin R. Selective effects of somatostatin-14, -25 and -28 on in vitro insulin and glucagon secretion. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):76–77. doi: 10.1038/291076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Iverson M. T., Radke J. M., Vincent S. R. The effects of cysteamine on dopamine-mediated behaviors: evidence for dopamine-somatostatin interactions in the striatum. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1986 Jun;24(6):1707–1714. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(86)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollard P., Vacher P., Dufy B., Barker J. L. Somatostatin blocks Ca2+ action potential activity in prolactin-secreting pituitary tumor cells through coordinate actions on K+ and Ca2+ conductances. Endocrinology. 1988 Aug;123(2):721–732. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-2-721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. H., Benoit R., Magistretti P. J., Bloom F. E. Immunohistochemical distribution of pro-somatostatin-related peptides in cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1983 Mar 7;262(2):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P. S., Heisler S., MacDonald J. F. A potassium conductance contributes to the action of somatostatin-14 to suppress ACTH secretion. Brain Res. 1988 Mar 22;444(2):346–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90944-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman Q. J., Siggins G. R. Somatostatin hyperpolarizes hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. Brain Res. 1981 Sep 28;221(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90791-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pless J., Bauer W., Briner U., Doepfner W., Marbach P., Maurer R., Petcher T. J., Reubi J. C., Vonderscher J. Chemistry and pharmacology of SMS 201-995, a long-acting octapeptide analogue of somatostatin. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;119:54–64. doi: 10.3109/00365528609087432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T. Multiple mechanisms of somatostatin inhibition of adrenocorticotropin release from mouse anterior pituitary tumor cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2259–2266. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto C., Goldfine I. D., Williams J. A. The somatostatin receptor on isolated pancreatic acinar cell plasma membranes. Identification of subunit structure and direct regulation by cholecystokinin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9623–9627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srikant C. B., Patel Y. C. Receptor binding of somatostatin-28 is tissue specific. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):259–260. doi: 10.1038/294259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thermos K., Reisine T. Somatostatin receptor subtypes in the clonal anterior pituitary cell lines AtT-20 and GH3. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;33(4):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran V. T., Beal M. F., Martin J. B. Two types of somatostatin receptors differentiated by cyclic somatostatin analogs. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.2858917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto A., Tanaka S. Stimulatory effect of somatostatin on norepinephrine release from rat brain cortex slices. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 23;28(8):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolkalis M. J., Nakada M. T., Manning D. R. Alterations in components of adenylate cyclase associated with transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3408–3413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]