Abstract
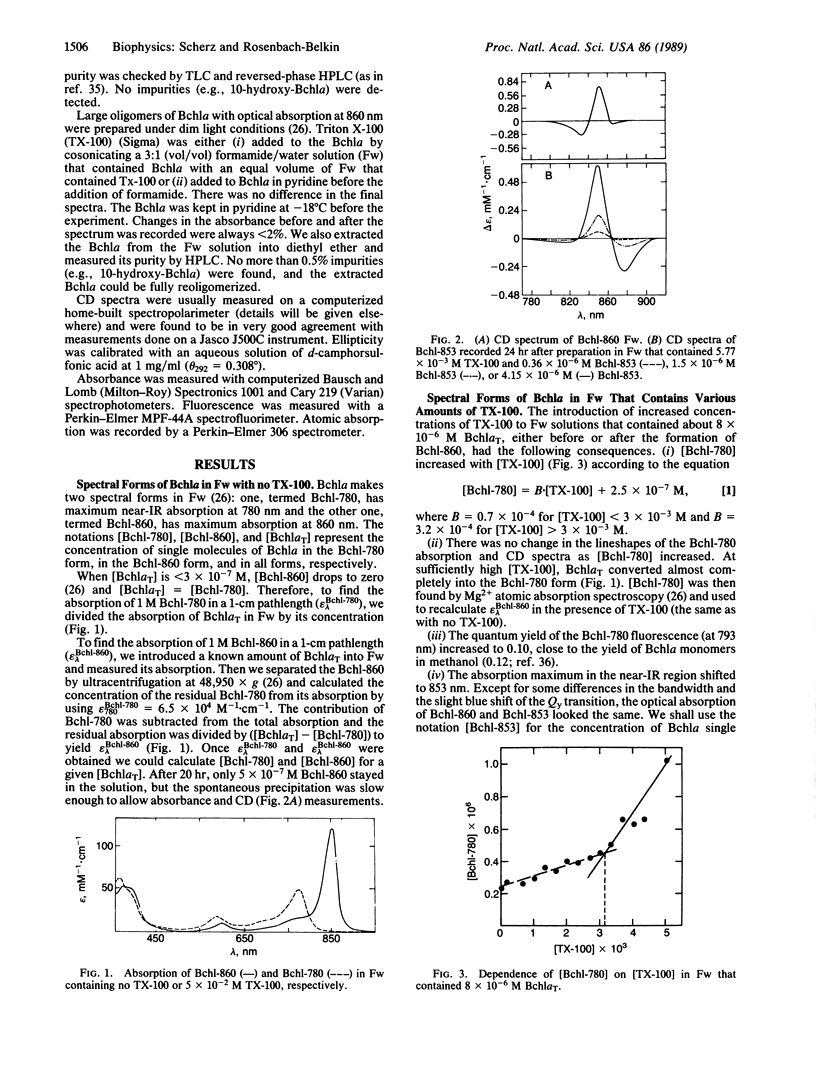
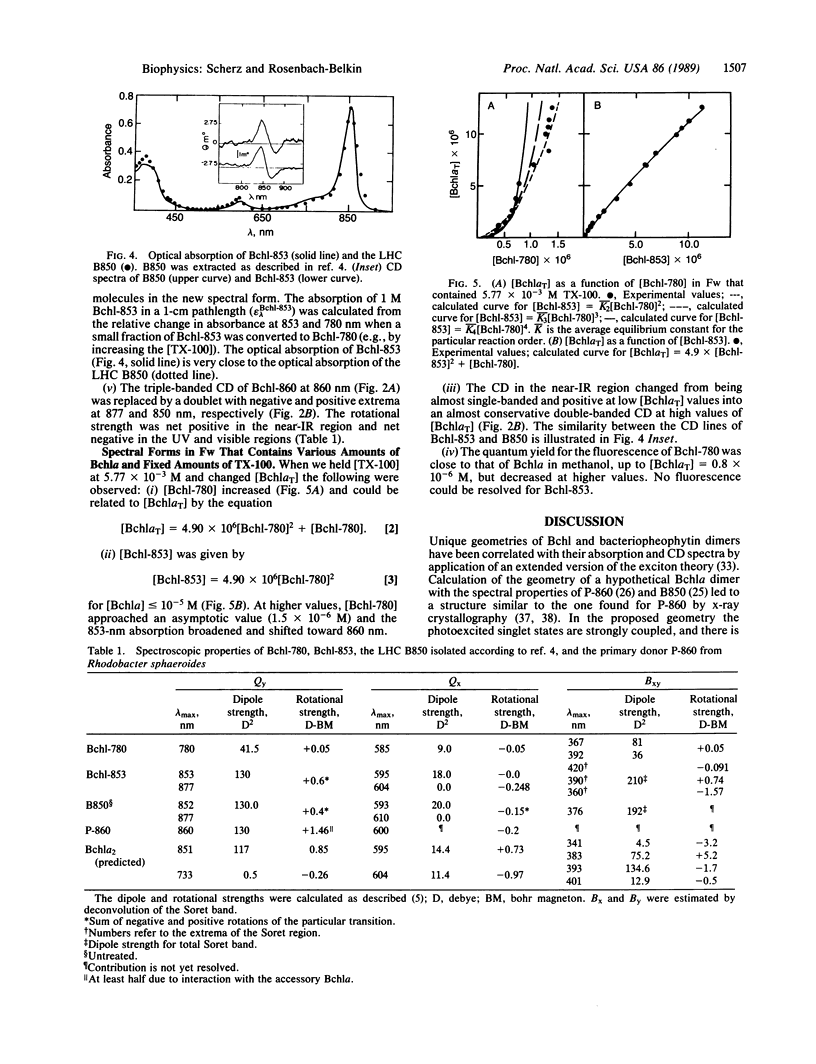
Dimers of bacteriochlorophyll a (Bchla) with optical absorption maximum at 853 nm and a nonconservative circular dichroism spectrum are formed in a solution of formamide/water that contains micelles of Triton X-100. The apparent equilibrium constant and the corresponding Gibbs energy change for the Bchl self-organization are 4.9 × 106 M-1 and -9.2 kcal/mol, respectively. The experimental absorption and circular dichroism spectra of the in vitro Bchl dimer (termed Bchl-853) are similar to the spectra of the bacterial light-harvesting complex B850 and the primary electron donor P-860 and probably point to a common structural motif. Indeed, simulation of the dimers' spectra (optical absorption and circular dichroism), achieved by using an extended version of the exciton theory, suggests the same geometry as recently elucidated for P-860 by x-ray diffraction crystallography. The proposed geometry is predicted to have the minimum energy in the gas phase. In conclusion, the spectral properties of the bathochromically shifted forms of Bchla are likely a result of strong dipolar interactions in self-organized structures of Bchls.
Keywords: photosynthesis, light-harvesting complexes, chromophore-protein organization, exciton theory
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. P., Feher G., Yeates T. O., Komiya H., Rees D. C. Structure of the reaction center from Rhodobacter sphaeroides R-26: the cofactors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5730–5734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballschmiter K., Katz J. J. Chlorophyll-chlorophyll and chlorophyll-water interactions in the solid state. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):307–327. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballschmiter K., Truesdell K., Katz J. J. Aggregation of chlorophyll in nonpolar solvents from molecular weight measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Sep 2;184(3):604–613. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., Petsko G. A. Aromatic-aromatic interaction: a mechanism of protein structure stabilization. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.3892686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Tiede D., Tang J., Smith U., Norris J., Schiffer M. Structure of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26 reaction center. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80870-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J., Honig B. Charged amino acids as spectroscopic determinants for chlorophyll in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4959–4962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein J., Scheer H. Long-wavelength-absorbing forms of bacteriochlorophyll a in solutions of Triton X-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2231–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. J., Norris J. R., Shipman L. L. Models for reaction-center and antenna chlorophyll. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1976 Jun 7;(28):16–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratky C., Dunitz J. D. Ordered aggregation states of chlorophyll a and some derivatives. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 25;113(2):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafferty C. N., Bolt J., Sauer K., Clayton R. K. Photooxidation of antenna bacteriochlorophyll in chromatophores from carotenoidless mutant Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides and the attendant loss of dimeric exciton interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4429–4432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer K., Austin L. A. Bacteriochlorophyll-protein complexes from the light-harvesting antenna of photosynthetic bacteria. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):2011–2019. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theiler R., Suter F., Wiemken V., Zuber H. The light-harvesting polypeptides of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26.1. I. Isolation, purification and sequence analyses. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Jul;365(7):703–719. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1984.365.2.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theiler R., Zuber H. The light-harvesting polypeptides of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides R-26.1. II. Conformational analyses by attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy and the possible molecular structure of the hydrophobic domain of the B 850 complex. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1984 Jul;365(7):721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Smith G. M., Thomas T. B., Feldmann R. J. Electronic distributions within protein phenylalanine aromatic rings are reflected by the three-dimensional oxygen atom environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornber J. P., Cogdell R. J., Pierson B. K., Seftor R. E. Pigment-protein complexes of purple photosynthetic bacteria: an overview. J Cell Biochem. 1983;23(1-4):159–169. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240230113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L., Michalski T. J., Katz J. J. Small-angle neutron scattering studies of chlorophyll micelles: Models for bacterial antenna chlorophyll. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3791–3795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedgar S., Barenholz Y., Cooper V. G. Molecular weight, shape and structure of mixed micelles of Triton X-100 and sphingomyelin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 21;363(1):98–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


