Abstract
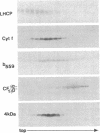
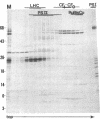
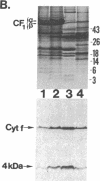
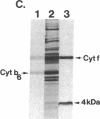
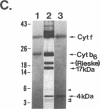
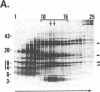
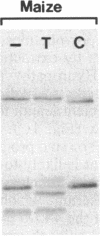
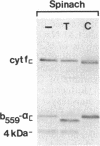
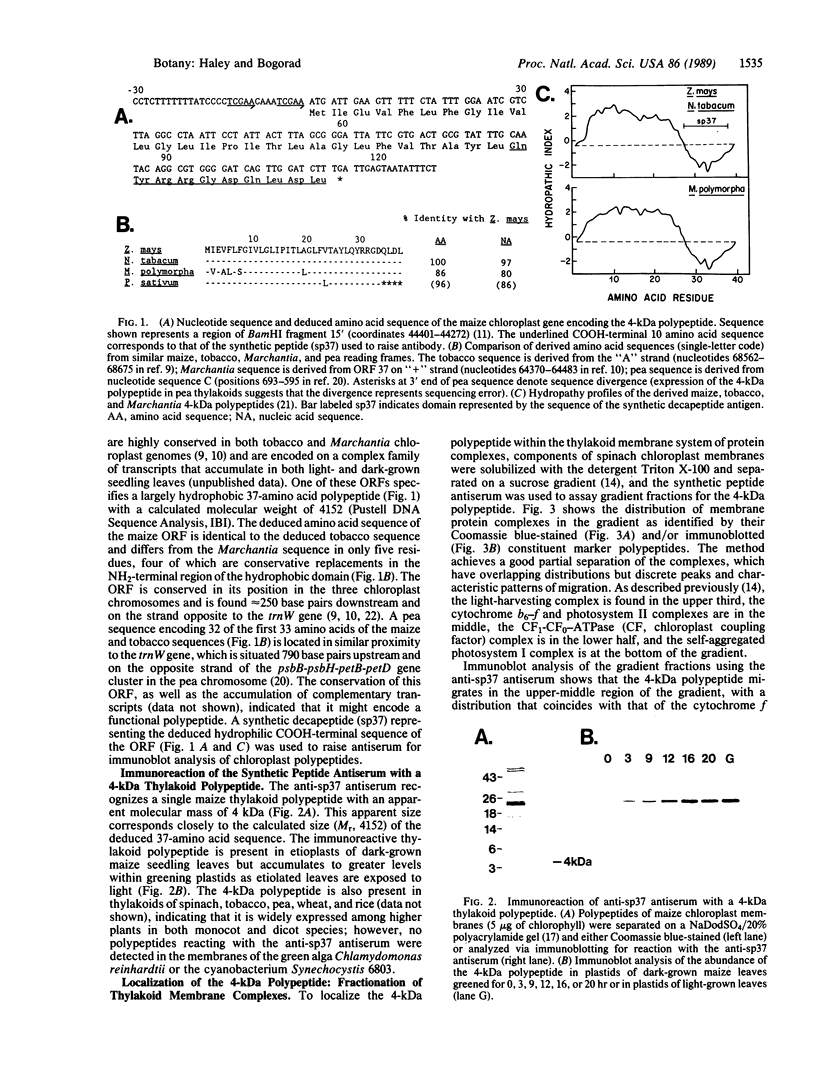
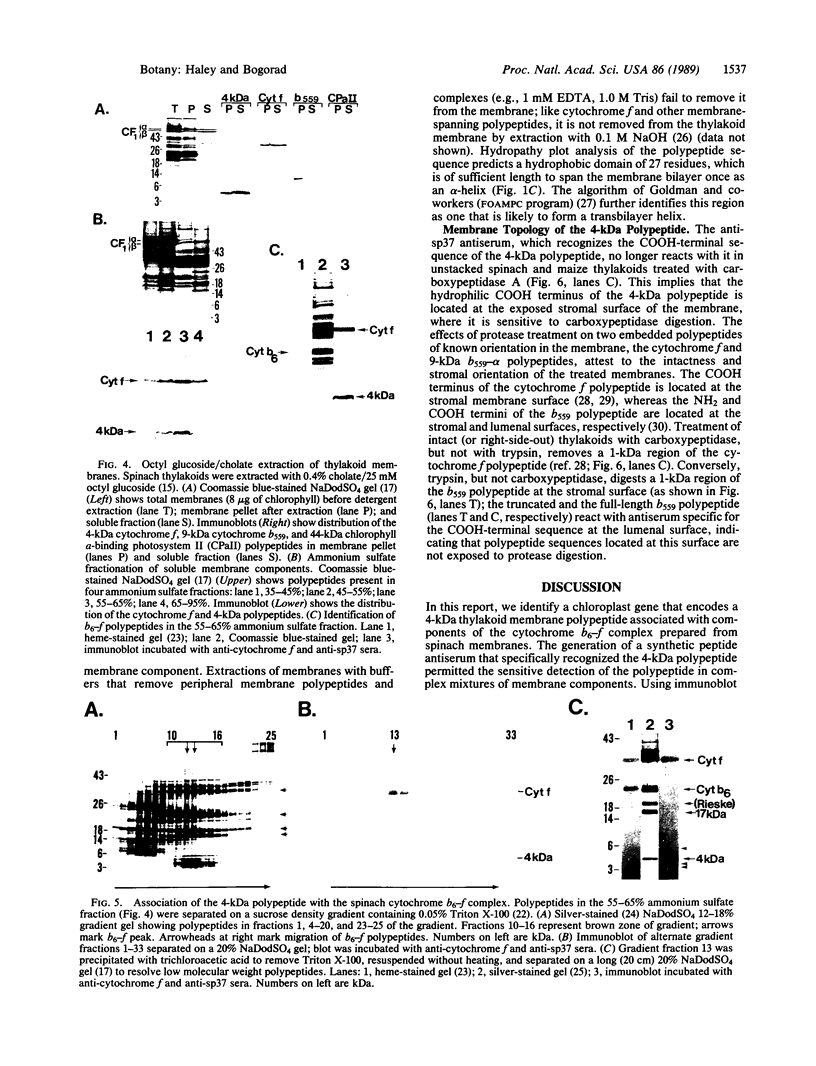
Four polypeptides, three of which are chloroplast-encoded, have been shown to be associated with the thylakoid membrane cytochrome b6-f complex. In this report, the gene for a fifth polypeptide, which copurifies with the b6-f complex, is identified through the use of an antibody generated against a synthetic decapeptide predicted from a maize chloroplast DNA sequence. The deduced 37-amino acid sequence of the immunoreactive 4-kDa polypeptide is 100% and 86% conserved in the respective similar open reading frames encoded by Nicotiana tabacum and Marchantia chloroplast DNA. The 4-kDa polypeptide is present in both etioplasts and chloroplasts of maize and is found as well in spinach, tobacco, pea, wheat, and rice thylakoids. Similar to the other subunits of the b6-f complex, it is intrinsic to the membrane, and its hydrophilic COOH terminus is located at the stromal thylakoid surface. We propose to call the 4-kDa polypeptide "subunit 5" and the chloroplast gene that encodes it the petE gene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt J., Westhoff P., Sears B. B., Nelson N., Hurt E., Hauska G., Herrmann R. G. Genes and transcripts for the polypeptides of the cytochrome b6/f complex from spinach thylakoid membranes. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):979–986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E., Daldal F. Primary structure of the bc1 complex of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Nucleotide sequence of the pet operon encoding the Rieske cytochrome b, and cytochrome c1 apoproteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K. A proton motive force transducer and its role in proton pumps, proton engines, tobacco mosaic virus assembly and hemoglobin allosterism. J Theor Biol. 1982 Jul 7;97(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(82)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A., Goldman A. Identifying nonpolar transbilayer helices in amino acid sequences of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:321–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish L. E., Kück U., Bogorad L. Two partially homologous adjacent light-inducible maize chloroplast genes encoding polypeptides of the P700 chlorophyll a-protein complex of photosystem I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1413–1421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian G. G., Moss R. L., Greaser M. Improved methodology for analysis and quantitation of proteins on one-dimensional silver-stained slab gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Hurt E., Gabellini N., Lockau W. Comparative aspects of quinol-cytochrome c/plastocyanin oxidoreductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 15;726(2):97–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E., Hauska G. Identification of the polypeptides in the cytochrome b6/f complex from spinach chloroplasts with redox-center-carrying subunits. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1982 Dec;14(5-6):405–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00743067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmbeck J., Stummann B. M., Henningsen K. W. Sequence of two regions of pea chloroplast DNA, one with the genes rps14, trnfM and trnG-GCC, and one with the genes trnP-UGG and trnW-CCA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3630–3630. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukens J. H., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequence containing the maize chloroplast proline (UGG) and tryptophan (CCA) tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 10;16(11):5192–5192. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.11.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips A. L., Gray J. C. Isolation and characterization of a cytochrome b-f complex from pea chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre R. T., Cheniae G. M. Studies on the reconstitution of o(2)-evolution of chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1084–1095. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tae G. S., Black M. T., Cramer W. A., Vallon O., Bogorad L. Thylakoid membrane protein topography: transmembrane orientation of the chloroplast cytochrome b-559 psbE gene product. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9075–9080. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. E., Ryan D., Levin W. An improved staining procedure for the detection of the peroxidase activity of cytochrome P-450 on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widger W. R., Cramer W. A., Herrmann R. G., Trebst A. Sequence homology and structural similarity between cytochrome b of mitochondrial complex III and the chloroplast b6-f complex: position of the cytochrome b hemes in the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey D. L., Auffret A. D., Gray J. C. Structure and topology of cytochrome f in pea chloroplast membranes. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]