Abstract
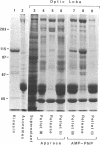
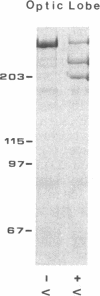
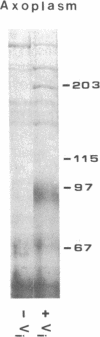
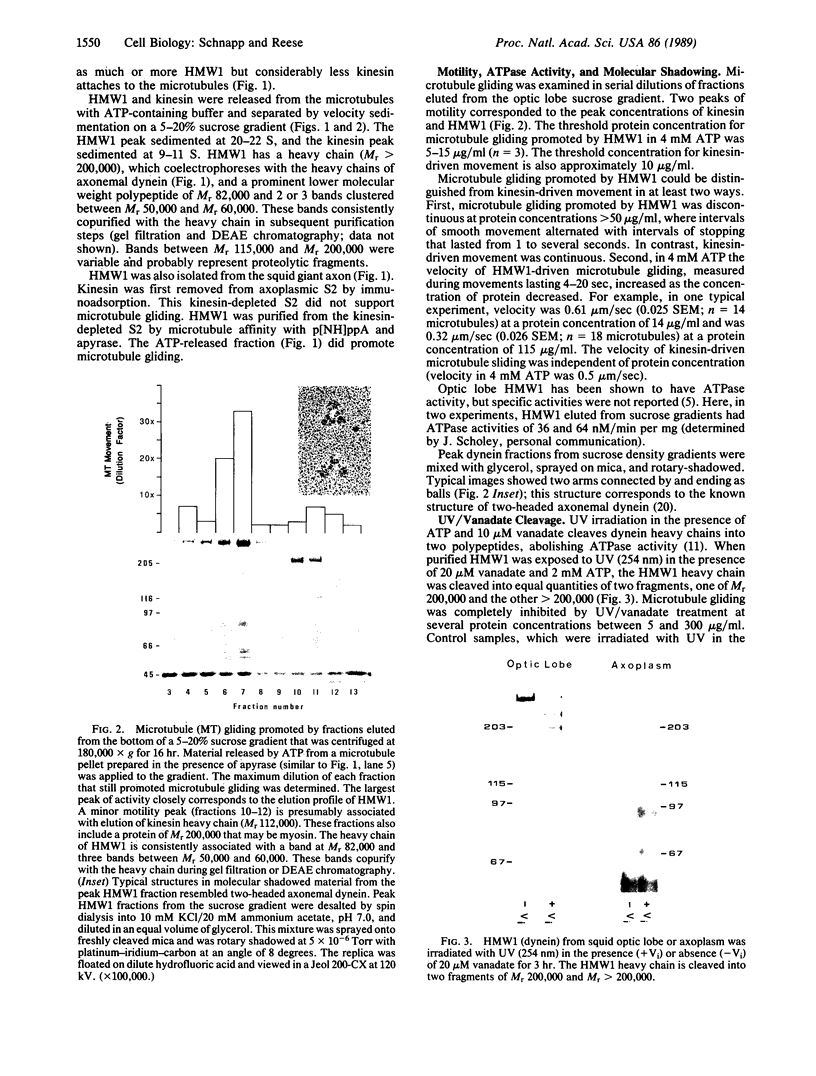
Vesicular organelles in axons of nerve cells are transported along microtubules either toward their plus ends (fast anterograde transport) or toward their minus ends (retrograde transport). Two microtubule-based motors were previously identified by examining plastic beads induced to move along microtubules by cytosol fractions from the squid giant axon: (i) an anterograde motor, kinesin, and (ii) a retrograde motor, which is characterized here. The retrograde motor, a cytosolic protein previously termed HMW1, was purified from optic lobes and extruded axoplasm by nucleotide-dependent microtubule affinity and release; microtubule gliding was used as the assay of motor activity. The following properties of the retrograde motor suggest that it is cytoplasmic dynein: (i) sedimentation at 20-22 S with a heavy chain of Mr greater than 200,000 that coelectrophoreses with the alpha and beta subunits of axonemal dynein, (ii) cleavage by UV irradiation in the presence of ATP and vanadate, and (iii) a molecular structure resembling two-headed dynein from axonemes. Furthermore, bead movement toward the minus end of microtubules was blocked when axoplasmic supernatants were treated with UV/vanadate. Treatment of axoplasmic supernatant with UV/vanadate also blocks the retrograde movement of purified organelles in vitro without changing the number of anterograde moving organelles, indicating that dynein interacts specifically with a subgroup of organelles programmed to move toward the cell body. However, purified optic lobe dynein, like purified kinesin, does not by itself promote the movement of purified organelles along microtubules, suggesting that additional axoplasmic factors are necessary for retrograde as well as anterograde transport.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Euteneuer U., Koonce M. P., Pfister K. K., Schliwa M. An ATPase with properties expected for the organelle motor of the giant amoeba, Reticulomyxa. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):176–178. doi: 10.1038/332176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons I. R., Cosson M. P., Evans J. A., Gibbons B. H., Houck B., Martinson K. H., Sale W. S., Tang W. J. Potent inhibition of dynein adenosinetriphosphatase and of the motility of cilia and sperm flagella by vanadate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodno C. C. Myosin active-site trapping with vanadate ion. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):116–123. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Landers J. M., Hamborg M. A. Polarity orientation of axonal microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):661–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Eiford A., Ow R. A., Gibbons I. R. Specific cleavage of dynein heavy chains by ultraviolet irradiation in the presence of ATP and vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2337–2342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye R. J., Porter M. E., Scholey J. M., McIntosh J. R. Identification of a microtubule-based cytoplasmic motor in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Isolation of mammalian centrosomes. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:261–268. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Shpetner H. S., Vallee R. B. MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1273–1282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paschal B. M., Vallee R. B. Retrograde transport by the microtubule-associated protein MAP 1C. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):181–183. doi: 10.1038/330181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale W. S., Goodenough U. W., Heuser J. E. The substructure of isolated and in situ outer dynein arms of sea urchin sperm flagella. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1400–1412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sale W. S., Satir P. Direction of active sliding of microtubules in Tetrahymena cilia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2045–2049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Vale R. D., Sheetz M. P., Reese T. S. Single microtubules from squid axoplasm support bidirectional movement of organelles. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J. Viewing single microtubules by video light microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1986;134:561–573. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)34121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. The role of kinesin and other soluble factors in organelle movement along microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1785–1792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. The movement of membranous organelles in axons. Electron microscopic identification of anterogradely and retrogradely transported organelles. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):513–530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Identification of a novel force-generating protein, kinesin, involved in microtubule-based motility. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80099-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Schnapp B. J., Mitchison T., Steuer E., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Different axoplasmic proteins generate movement in opposite directions along microtubules in vitro. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):623–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90234-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Movement of organelles along filaments dissociated from the axoplasm of the squid giant axon. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Schnapp B. J., Reese T. S., Sheetz M. P. Organelle, bead, and microtubule translocations promoted by soluble factors from the squid giant axon. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]