Abstract
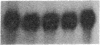
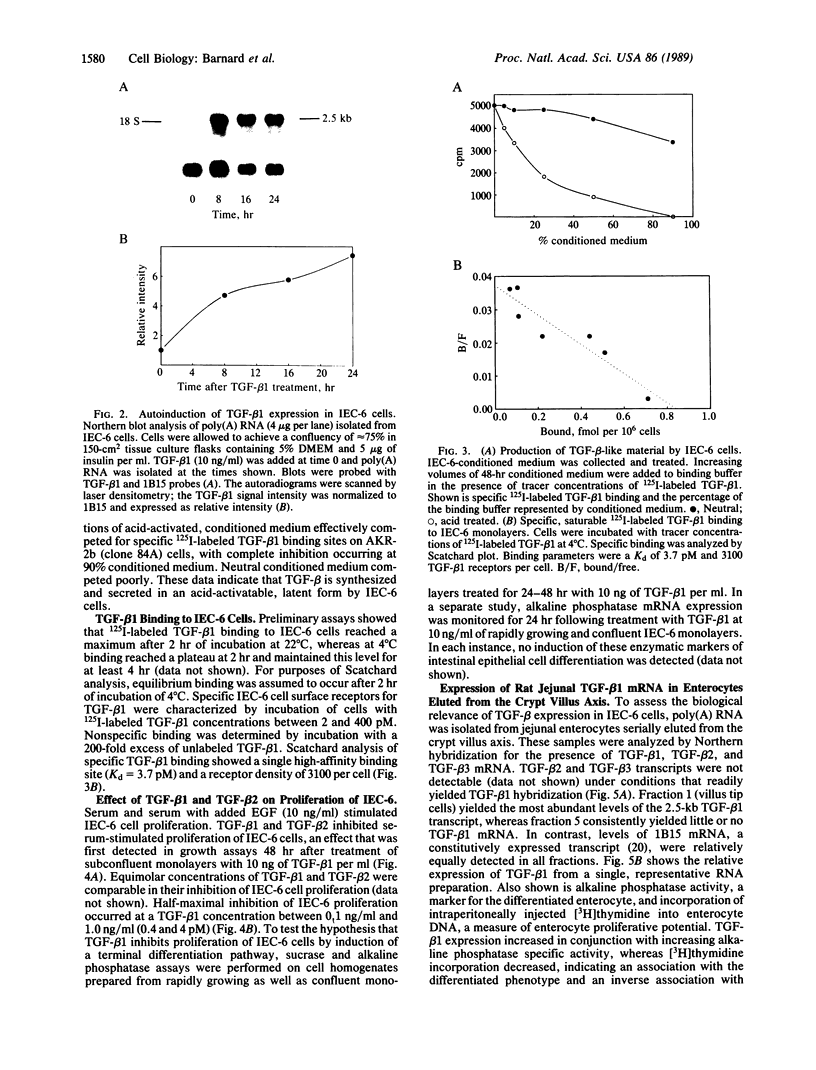
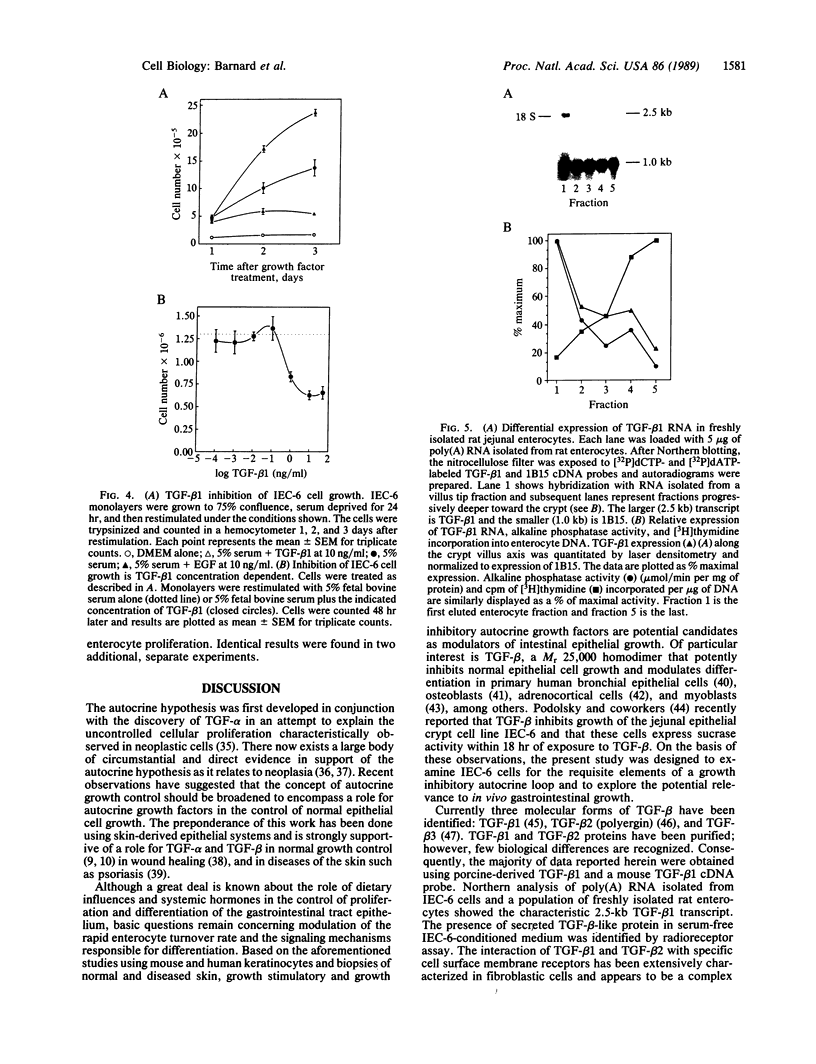
A nontransformed rat jejunal crypt cell line (IEC-6) expresses transforming growth factor type beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) mRNA, secretes latent 125I-labeled TGF-beta 1 competing activity into culture medium, and binds 125I-labeled TGF-beta 1 to specific, high-affinity (Kd = 3.7 pM) cell surface receptors. IEC-6 cell growth is markedly inhibited by TGF-beta 1 and TGF-beta 2 with half-maximal inhibition occurring between 0.1 and 1.0 ng of TGF-beta 1 per ml. TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition is not associated with the appearance of biochemical markers of enterocyte differentiation such as alkaline phosphatase expression and sucrase activity. TGF-beta 1 (10 ng/ml) increases steady-state levels of its own mRNA expression within 8 hr of treatment of rapidly growing IEC-6 cells. In freshly isolated rat jejunal enterocytes that are sequentially eluted from the crypt villus axis, TGF-beta 1 mRNA expression is most abundant in terminally differentiated villus tip cells and least abundant in the less differentiated, mitotically active crypt cells. We conclude that TGF-beta 1 is an autoregulated growth inhibitor in IEC-6 cells that potentially functions in an autocrine manner. In the rat jejunal epithelium, TGF-beta 1 expression is most prominently localized to the villus tip--i.e., the region of the crypt villus unit that is characterized by the terminally differentiated phenotype. These data suggest that TGF-beta 1 may function in coordination of the rapid cell turnover typical for the intestinal epithelium.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J., Fee F., Balmain A. Localized production of TGF-beta mRNA in tumour promoter-stimulated mouse epidermis. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):363–365. doi: 10.1038/331363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrandon Y., Green H. Cell migration is essential for sustained growth of keratinocyte colonies: the roles of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1131–1137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheifetz S., Like B., Massagué J. Cellular distribution of type I and type II receptors for transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9972–9978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Leblond C. P. Origin, differentiation and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine. I. Columnar cell. Am J Anat. 1974 Dec;141(4):461–479. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001410403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Derynck R., Wilcox J. N., Bringman T. S., Goustin A. S., Moses H. L., Pittelkow M. R. Production and auto-induction of transforming growth factor-alpha in human keratinocytes. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):817–820. doi: 10.1038/328817a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Production of transforming growth factors by human colon cancer lines. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1164–1169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Sipes N. J., Bascom C. C., Graves-Deal R., Pennington C. Y., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Growth modulation of mouse keratinocytes by transforming growth factors. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1596–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson P. E., Forss-Petter S., Brow M. A., Calavetta L., Douglass J., Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. p1B15: a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin. DNA. 1988 May;7(4):261–267. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. The murine transforming growth factor-beta precursor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4377–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Lindquist P. B., Lee A., Wen D., Tamm J., Graycar J. L., Rhee L., Mason A. J., Miller D. A., Coffey R. J. A new type of transforming growth factor-beta, TGF-beta 3. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3737–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Roberts A. B., Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta. A very potent inhibitor of myoblast differentiation, identical to the differentiation inhibitor secreted by Buffalo rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16509–16513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frolik C. A., Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Sporn M. B. Characterization of a membrane receptor for transforming growth factor-beta in normal rat kidney fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10995–11000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Armour R., Baldwin J. H., Maldonado F., Spiess J., Holley R. W. Amino acid sequence of the BSC-1 cell growth inhibitor (polyergin) deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):79–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. D., Cairnie A. B. Changes in intestinal cell kinetics in the small intestine of lactating mice. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1975 Mar;8(2):135–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1975.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta M., Baird A. Differential effects of transforming growth factor type beta on the growth and function of adrenocortical cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7795–7799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Leof E. B., Lyons R. M., Coffey R. J., Jr, Moses H. L. Transforming growth factors and control of neoplastic cell growth. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Feb;33(2):95–107. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240330204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurokowa M., Lynch K., Podolsky D. K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: transforming growth factor beta inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):775–782. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Pircher R., Jullien P. Conversion of a high molecular weight latent beta-TGF from chicken embryo fibroblasts into a low molecular weight active beta-TGF under acidic conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):1026–1034. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madisen L., Webb N. R., Rose T. M., Marquardt H., Ikeda T., Twardzik D., Seyedin S., Purchio A. F. Transforming growth factor-beta 2: cDNA cloning and sequence analysis. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):1–8. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J. Subunit structure of a high-affinity receptor for type beta-transforming growth factor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked glycosylated receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7059–7066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui T., Wakefield L. M., Lechner J. F., LaVeck M. A., Sporn M. B., Harris C. C. Type beta transforming growth factor is the primary differentiation-inducing serum factor for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2438–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Hanson W., Schedl H. P., Osborne J. W. Proliferation rate and transit time of mucosal cells in small intestine of the diabetic rat. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1326–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Pierce G. F., Thomason A., Gramates P., Sporn M. B., Deuel T. F. Accelerated healing of incisional wounds in rats induced by transforming growth factor-beta. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1333–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2442813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Rodan G. A. Type beta transforming growth factor (TGF beta) regulation of alkaline phosphatase expression and other phenotype-related mRNAs in osteoblastic rat osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Dec;133(3):426–437. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovitt C. E., Strauss A. W., Alpers D. H., Chou J. Y., Boime I. Expression of different-sized placental alkaline phosphatase mRNAs in placenta and choriocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson Y., Hammacher A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Possible positive autocrine feedback in the prereplicative phase of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):715–717. doi: 10.1038/328715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Childs C. B., Volkenant M. E., Moses H. L. Differential effects of epidermal growth factor, transforming growth factor, and insulin on DNA and protein synthesis and morphology in serum-free cultures of AKR-2B cells. Cancer Res. 1984 Feb;44(2):710–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Pittelkow M. R., Wille J. J., Jr, Scott R. E., Moses H. L. Reversible inhibition of normal human prokeratinocyte proliferation by type beta transforming growth factor-growth inhibitor in serum-free medium. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):2068–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trier J. S., Browning T. H. Epithelial-cell renewal in cultured duodenal biopsies in celiac sprue. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 3;283(23):1245–1250. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012032832302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Hansen P., Iwata K. K., Pieler C., Foulkes J. G. Identification of another member of the transforming growth factor type beta gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4715–4719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]