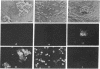
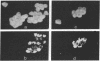
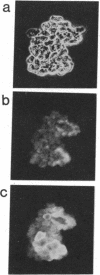
Abstract
Because the brain lacks a true lymphatic system, it is unclear how peripheral lymphocytes recognize foreign antigens present in the central nervous system. This report demonstrates that the choroid plexus, which constitutes the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier, is able to present foreign antigen to, and stimulate the proliferation of, peripheral helper T lymphocytes through an Ia-dependent, major histocompatibility complex-restricted mechanism. Furthermore, in vivo, choroid plexus epithelial cells have access to, and are capable of taking up, virus-sized particles injected elsewhere into the cerebrospinal fluid. Thus these data suggest that the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier may play a role in immunological communication between the central nervous system and periphery, a function relevant to the initiation of immunological responses to central nervous system infections and autoimmune processes and for the surveillance of tumor cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF
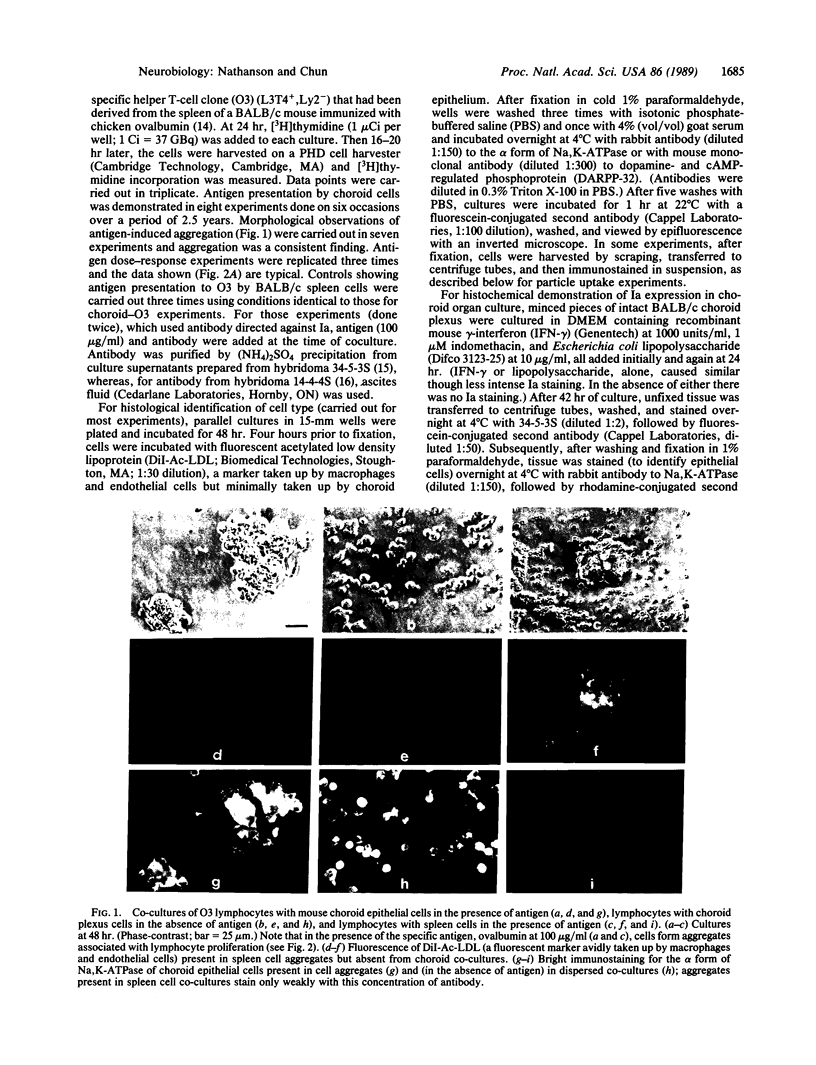


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abolarin M. O., Evans D. A., Tovey D. G., Ormerod W. E. Cryptic stage of sleeping-sickness trypanosome developing in choroid plexus epithelial cells. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Nov 13;285(6352):1380–1382. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6352.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abromson-Leeman S. R., Der Simonian H., Clabby M., Cantor H. Analysis of insulin-specific T cell clones. I. Strategy for production of clonotypic antibody. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3184–3188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Cole D. F. The role of the lymphatic system in drainage of cerebrospinal fluid and aqueous humour. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:353–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE F. C., SIMMONDS W. J. The removal of protein from the subarachnoid space. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1951 Jul;29(4):255–263. doi: 10.1038/icb.1951.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F., Cooper D. N., Milhorat T. H. Flow of cerebral interstitial fluid as indicated by the removal of extracellular markers from rat caudate nucleus. Exp Eye Res. 1977;25 (Suppl):461–473. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(77)80041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Fierz W., Wekerle H. Astrocytes present myelin basic protein to encephalitogenic T-cell lines. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):273–276. doi: 10.1038/307273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S., Sillcocks D., Rao A., Faas S., Cantor H. A subset of Ly-1 inducer T cell clones activates B cell proliferation but directly inhibits subsequent IgG secretion. J Exp Med. 1985 Apr 1;161(4):785–804. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.4.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Cole G. A., Monjan A. A., Nathanson N. Immunopathogenesis of acute central nervous system disease produced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. I. Cyclophosphamide-mediated induction by the virus-carrier state in adult mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):860–873. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Jablonski-Westrich D., Thiele H. G. Contact interaction between lymphocytes is a general event following activation and is mediated by LFA-1. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jul;16(7):847–850. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSUNEN T. U., WAKSMAN B. H., SAMUELSSON I. K. RADIOAUTOGRAPHIC STUDY OF CELLULAR MECHANISMS IN DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY. II. EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS IN THE RAT. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Jul;22:367–380. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196307000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koss M. N., Chernack W. J., Griswold W. R., McIntosh R. M. The choroid plexus in acute serum sickness. Morpholgic, ultrastructural, and immunohistologic studies. Arch Pathol. 1973 Nov;96(5):331–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Pathology of choroid plexus in spontaneous immune complex disease and chronic viral infections. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1974 May 27;363(1):21–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00432202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. Choroid plexus: target for systemic disease and pathway to the brain. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):231–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massa P. T., Dörries R., ter Meulen V. Viral particles induce Ia antigen expression on astrocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):543–546. doi: 10.1038/320543a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhorat T. H. Structure and function of the choroid plexus and other sites of cerebrospinal fluid formation. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;47:225–288. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson J. A. beta-Adrenergic-sensitive adenylate cyclase in choroid plexus: properties and cellular localization. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):199–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Neuronal phosphoproteins: physiological and clinical implications. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1357–1364. doi: 10.1126/science.6474180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N. M., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse major histocompatibility complex antigens. Transplantation. 1982 Sep;34(3):113–120. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198209000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peress N. S., Roxburgh V. A., Gelfand M. C. Binding sites for immune components in human choroid plexus. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Mar;24(3):520–526. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith Q. R., Johanson C. E., Woodbury D. M. Uptake of 36Cl and 22Na by the brain-cerebrospinal fluid system: comparison of the permeability of the blood-brain and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steardo L., Nathanson J. A. Brain barrier tissues: end organs for atriopeptins. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):470–473. doi: 10.1126/science.2879355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Wekerle H. Ia-restricted encephalitogenic T lymphocytes mediating EAE lyse autoantigen-presenting astrocytes. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):70–72. doi: 10.1038/320070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J., Gilkeson R. C. Two isozymes of the Na,K-ATPase have distinct antigenic determinants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):9016–9022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu M., Weiner H. L. Viral receptors on isolated murine and human ependymal cells. Science. 1982 Jan 22;215(4531):419–421. doi: 10.1126/science.6276976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traugott U., Raine C. S. Multiple sclerosis. Evidence for antigen presentation in situ by endothelial cells and astrocytes. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Jul;69(3):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. Mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):104–105. doi: 10.1038/318104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., Battye F., Schrader J. W. Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):688–691. doi: 10.1038/310688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Wellish M. C., Wolinsky J. S., Gilden D. Comparison of human cytomegalovirus growth in MRC-5 human fibroblasts, brain, and choroid plexus cells in vitro. J Med Virol. 1981;8(4):245–256. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B. Structural aspects of brain barriers, with special reference to the permeability of the cerebral endothelium and choroidal epithelium. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;65:117–191. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61960-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]