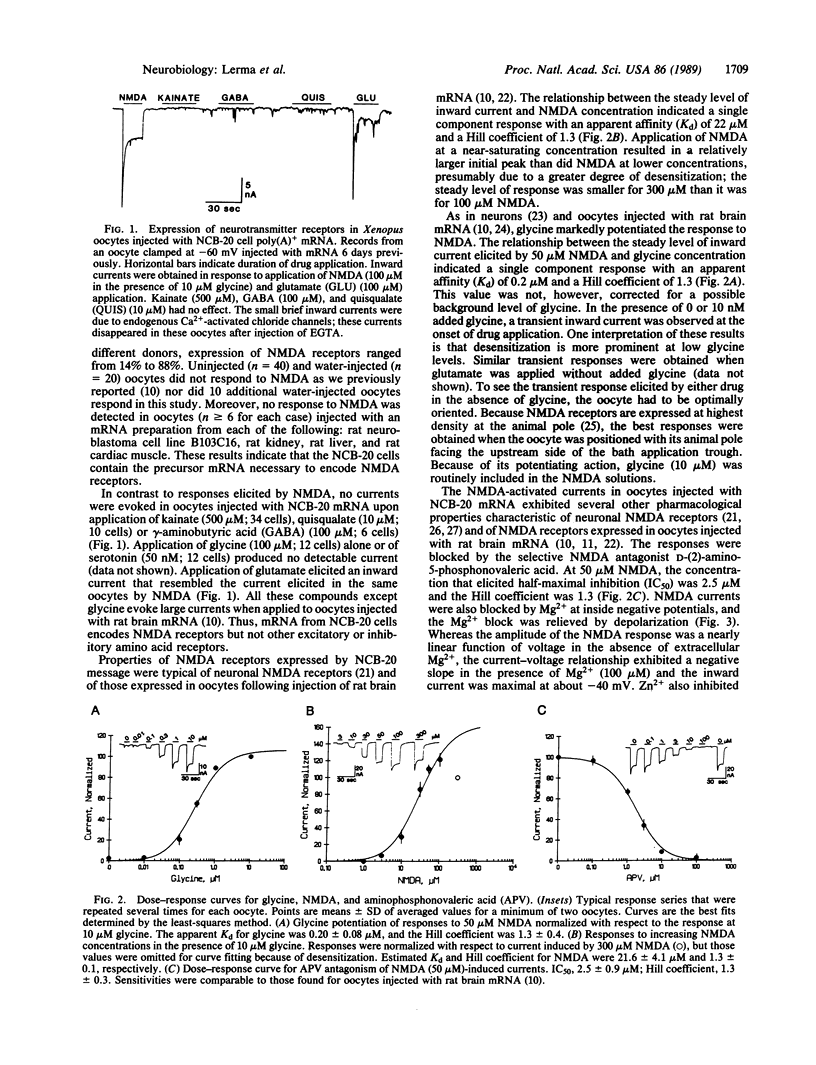
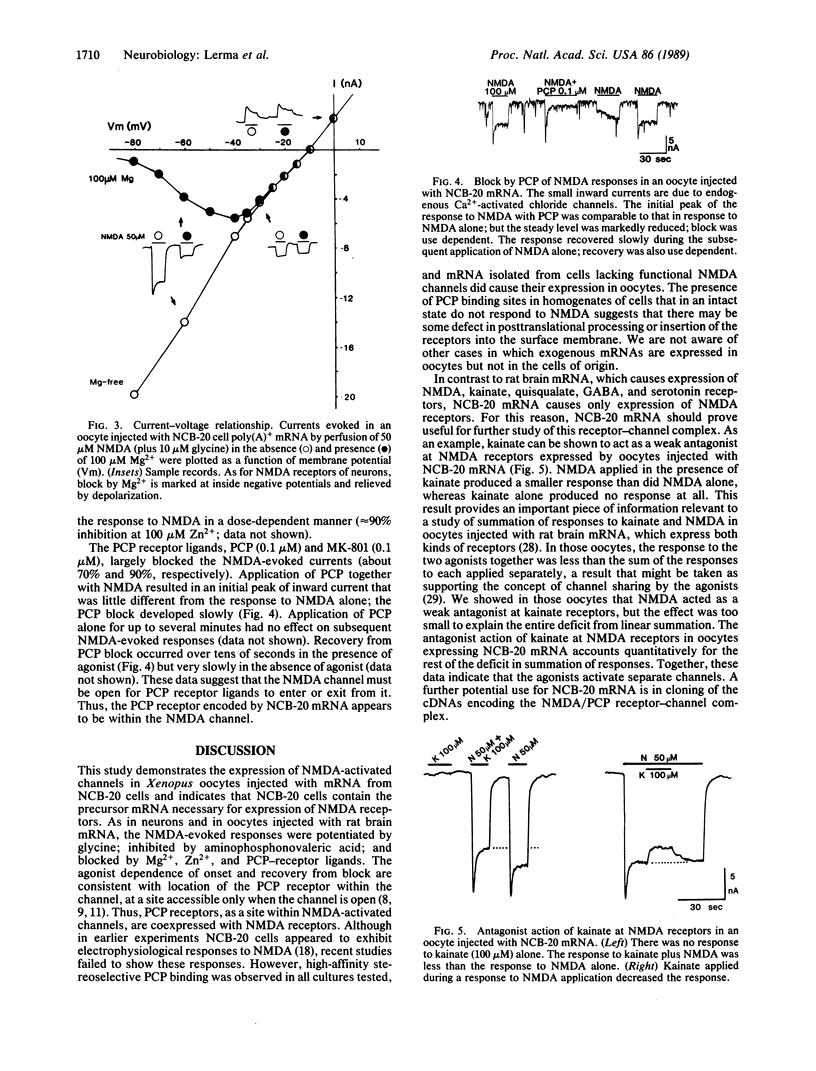
Abstract
The mouse neuroblastoma--Chinese hamster brain hybrid cell line NCB-20 is the only clonal cell line in which binding studies indicate the presence of phencyclidine (PCP) receptors. We report here that Xenopus oocytes injected with NCB-20 cell poly(A)+ RNA express N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-activated channels and that these channels include the PCP receptor site. In injected oocytes, NMDA application evoked a partially desensitizing inward current that was potentiated by glycine, blocked by the competitive antagonist D-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid, blocked by Mg2+ and by Zn2+, and blocked in a use-dependent manner by the PCP receptor ligands PCP and MK-801. There was little or no response to kainate or quisqualate (agonists of the other excitatory amino acid receptors), to gamma-aminobutyric acid (an inhibitory transmitter), or to glycine (an inhibitory transmitter as well as an allosteric potentiator of NMDA channels). Thus, NMDA/PCP receptors expressed from NCB-20 cell mRNA exhibit properties similar to those of the neuronal receptors. The absence of expression of other excitatory amino acid receptors in this system makes it particularly useful for study of NMDA-evoked responses without interference from responses mediated by other receptors. Moreover, NCB-20 mRNA may be an appropriate starting material for cloning the cDNA(s) encoding the NMDA/PCP-receptor complex.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry S. C., Dawkins S. L., Lodge D. Comparison of sigma- and kappa-opiate receptor ligands as excitatory amino acid antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolino M., Vicini S., Mazzetta J., Costa E. Phencyclidine and glycine modulate NMDA-activated high conductance cationic channels by acting at different sites. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):351–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90534-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Snutch T. P., Lübbert H., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Expression and modulation of voltage-gated calcium channels after RNA injection in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1147–1150. doi: 10.1126/science.2418503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Acidic amino acid binding sites in mammalian neuronal membranes: their characteristics and relationship to synaptic receptors. Brain Res. 1984 May;319(2):103–164. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Medzihradsky F., Woods J. H., Dahlstrom P. J. Stereospecific binding of 3H-phencyclidine in brain membranes. Life Sci. 1982 Jun 21;30(25):2147–2154. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes B. A., Balster R. L. Anticonvulsant properties of phencyclidine-like drugs in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 29;117(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman S. G. Phencyclidine-like discriminative effects of opioids in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Sep;214(3):614–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey C. R., Miljkovic Z., MacDonald J. F. Ketamine and phencyclidine cause a voltage-dependent block of responses to L-aspartic acid. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 24;61(1-2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Bean B. P. Block of N-methyl-D-aspartate-activated current by the anticonvulsant MK-801: selective binding to open channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1307–1311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. W., Dingledine R. Requirement for glycine in activation of NMDA-receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):835–837. doi: 10.1126/science.2841759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner L., Lerma J., Zukin R. S., Bennett M. V. Coexpression of N-methyl-D-aspartate and phencyclidine receptors in Xenopus oocytes injected with rat brain mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3250–3254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushner L., Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Characterization of opioid, sigma, and phencyclidine receptors in the neuroblastoma-brain hybrid cell line NCB-20. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;34(5):689–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Miljkovic Z., Pennefather P. Use-dependent block of excitatory amino acid currents in cultured neurons by ketamine. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):251–266. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Mixed-agonist action of excitatory amino acids on mouse spinal cord neurones under voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:29–53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sircar R., Rappaport M., Nichtenhauser R., Zukin S. R. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801: a potent and specific ligand of the brain phencyclidine/sigma-receptor. Brain Res. 1987 Dec 1;435(1-2):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91606-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdoorn T. A., Dingledine R. Excitatory amino acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: agonist pharmacology. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):298–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kartalovski B., Geneste P., Kamenka J. M., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidine ("angel dust") with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



