Abstract
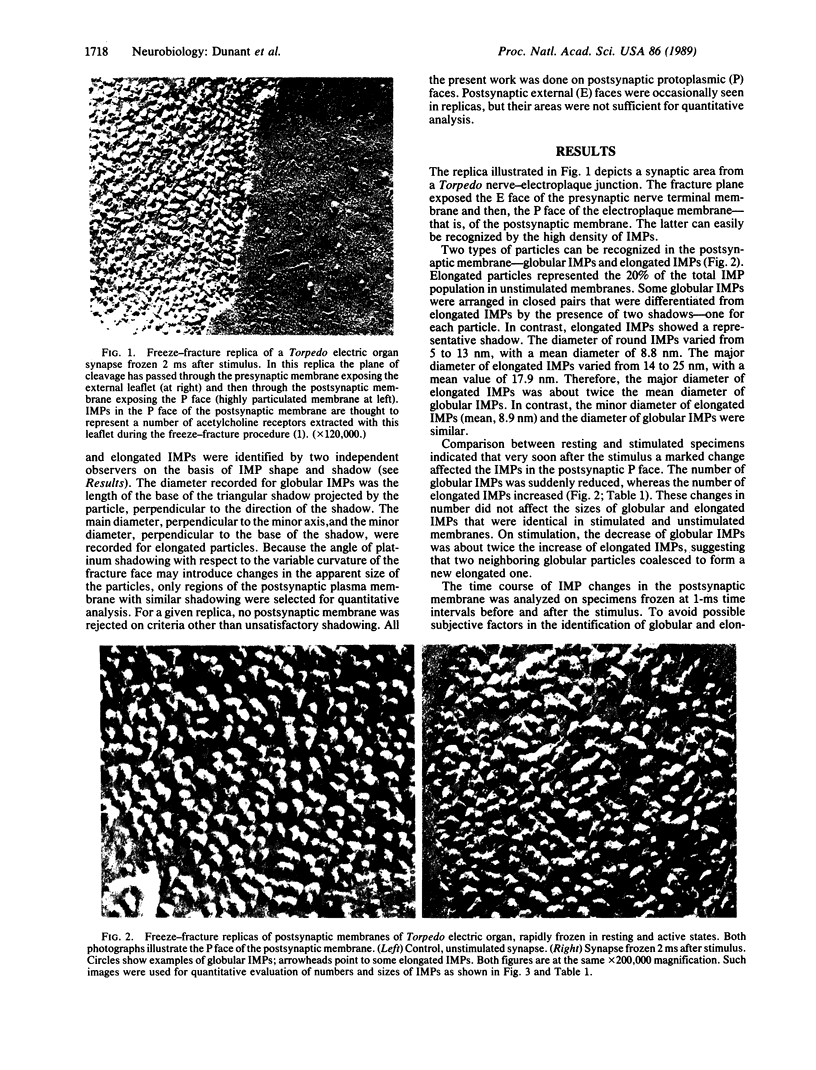
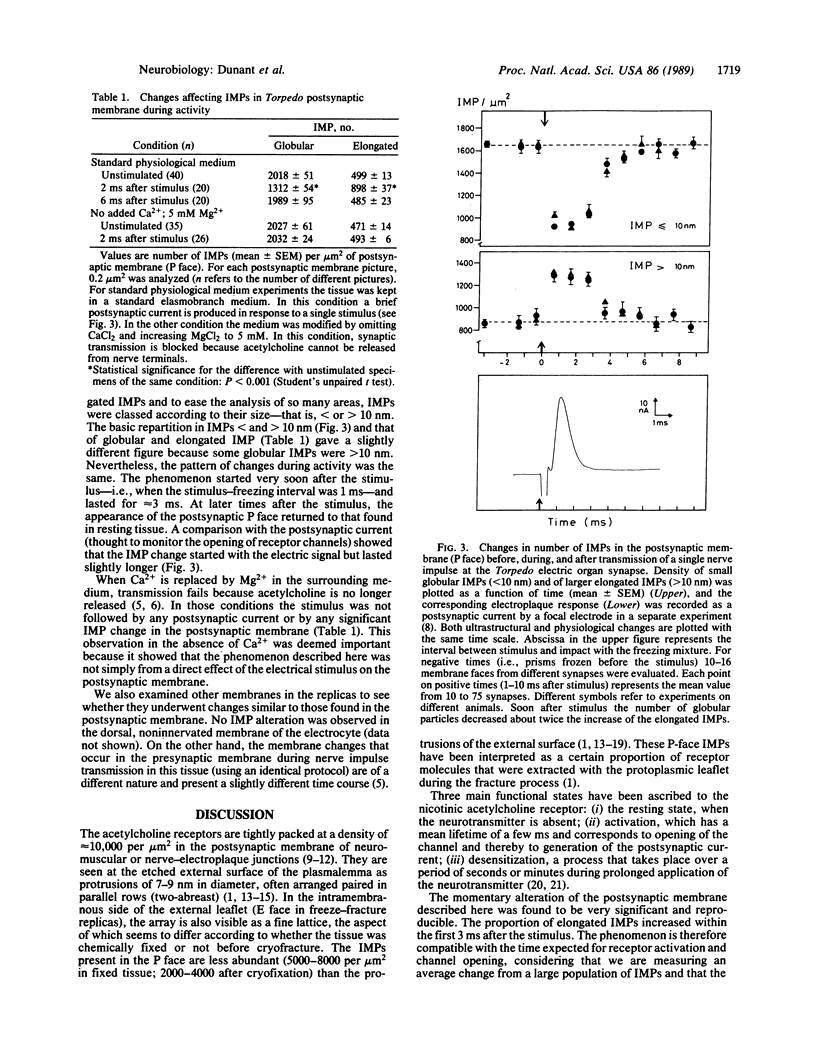
Transmission of a nerve impulse at neuromuscular and other synapses is an extremely brief event. By using rapid-freezing and cryofracture techniques in the electric organ of Torpedo, synaptic transmission was found to be accompanied by significant changes affecting the postsynaptic membrane for a few milliseconds. In the replicas, the protoplasmic leaflet of this membrane was seen to contain intramembrane particles (IMPs) of two different forms, globular and elongated. Globular IMPs had a mean diameter of 8.8 nm; they were the most frequently found (80% in unstimulated specimens). Elongated IMPs had a major diameter of 17.9 nm, about twice that of globular IMPs. Transmission of a single nerve impulse was accompanied by a marked decrease in the number of globular IMPs and by an increase in the number of elongated IMPs, as if there were a coalescence of two adjacent round particles to form an elongated one. These changes started soon after the electrical stimulus and lasted for approximately 3 ms. IMPs in the postsynaptic protoplasmic face are thought to correspond to a certain proportion of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that were extracted with this leaflet during the fracture process. The phenomenon described here reflects an abrupt change in the membrane, probably linked to activation of the acetylcholine nicotinic receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T., Baerwald R., Potter L. T. Postsynaptic membranes in the electric tissue of Narcine: II. A freeze-fracture study of nicotinic receptor molecules. Tissue Cell. 1977;9(4):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(77)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brisson A., Unwin P. N. Tubular crystals of acetylcholine receptor. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1202–1211. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Benedetti E. L. A morphological study of the cholinergic receptor protein from Torpedo marmorata in its membrane environment and in its detergent-extracted purified form. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:313–337. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Chemouilli P. Acetylcholine receptor: an allosteric protein. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1335–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.6382611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clementi F., Conti-Tronconi B., Peluchetti D., Morgutti M. Effect of denervation on the organization of the postsynaptic membrane of the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 6;90(1):133–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90687-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunant Y., Muller D. Quantal release of acetylcholine evoked by focal depolarization at the Torpedo nerve-electroplaque junction. J Physiol. 1986 Oct;379:461–478. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Segura L. M., Muller D., Dunant Y. Increase in the number of presynaptic large intramembrane particles during synaptic transmission at the Torpedo nerve-electroplaque junction. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):63–79. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Segura L. M., Perrelet A. Postsynaptic membrane domains in the molecular layer of the cerebellum: a correlation between presynaptic inputs and postsynaptic plasma membrane organization. Brain Res. 1984 Nov 12;321(2):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Ros J. M., Farach M. C., Martinez-Carrion M. Ligand-induced effects at regions of acetylcholine receptor accessible to membrane lipids. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3807–3811. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grohovaz F., Limbrick A. R., Miledi R. Acetylcholine receptors at the rat neuromuscular junction as revealed by deep etching. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 May 22;215(1199):147–154. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Salpeter S. R. Organization of acetylcholine receptors in quick-frozen, deep-etched, and rotary-replicated Torpedo postsynaptic membrane. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):150–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Heuser J. E. Internal and external differentiations of the postsynaptic membrane at the neuromuscular junction. J Neurocytol. 1982 Jun;11(3):487–510. doi: 10.1007/BF01257990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Garcia-Segura L. M., Parducz A., Dunant Y. Brief occurrence of a population of presynaptic intramembrane particles coincides with transmission of a nerve impulse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Perrelet A., Dunant Y. A peculiar substructure in the postsynaptic membrane of Torpedo electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Feb;71(2):307–310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Changeux J. P. Nicotinic receptor of acetylcholine: structure of an oligomeric integral membrane protein. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1162–1239. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter C. W., Barnard E. A. The density of cholinergic receptors at the endplate postsynaptic membrane: ultrastructural studies in two mammalian species. J Membr Biol. 1975;20(1-2):31–49. doi: 10.1007/BF01870626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluth J. Synaptic membrane structure in Torpedo electric organ. J Neurocytol. 1975 Dec;4(6):697–712. doi: 10.1007/BF01181631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Loring R. H. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in vertebrate muscle: properties, distribution and neural control. Prog Neurobiol. 1985;25(4):297–325. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(85)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin N., Toyoshima C., Kubalek E. Arrangement of the acetylcholine receptor subunits in the resting and desensitized states, determined by cryoelectron microscopy of crystallized Torpedo postsynaptic membranes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1123–1138. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]