Abstract
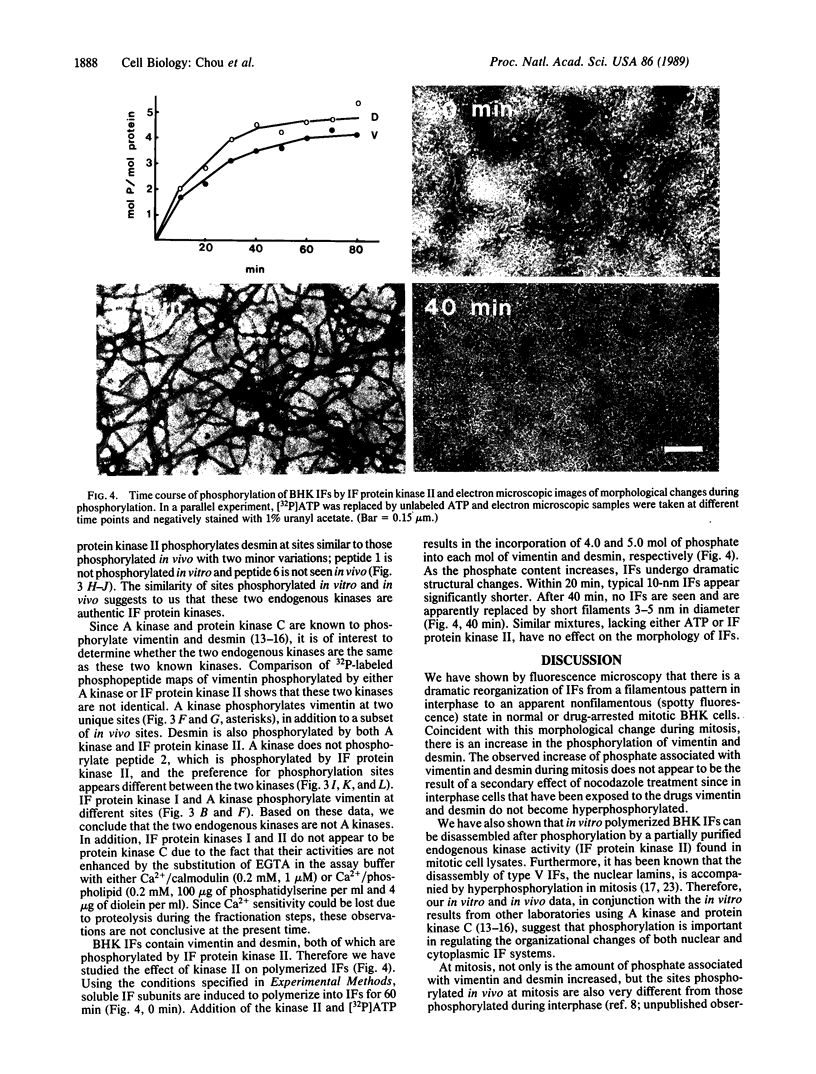
As baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells enter mitosis, networks of intermediate filaments (IFs) are transformed into cytoplasmic aggregates of protofilaments. Coincident with this morphological change, the phosphate content of vimentin increases from 0.3 mol of Pi per mol of protein in interphase to 1.9 mol of Pi per mol of protein in mitosis. A similar increase in phosphate content is observed with desmin, from 0.5 mol of Pi per mol of protein to 1.5 mol of Pi per mol of protein. Fractionation of mitotic cell lysates by hydroxylapatite column chromatography reveals the presence of two IF protein kinase activities, designated as IF protein kinase I and IF protein kinase II. Comparison of two-dimensional 32P-labeled phosphopeptide maps of vimentin and desmin phosphorylated in vivo in mitosis, and in vitro using partially purified kinase fractions, reveals extensive similarity in the two sets of phosphorylation sites. Phosphorylation of in vitro polymerized IFs by IF protein kinase II induces complete disassembly as determined by negative-stain electron microscopy. The results support the idea that the disassembly of IFs in mitosis is regulated by the phosphorylation of its subunit proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubin J. E., Osborn M., Franke W. W., Weber K. Intermediate filaments of the vimentin-type and the cytokeratin-type are distributed differently during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):149–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90340-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J., Celis A. Phosphorylation of keratin and vimentin polypeptides in normal and transformed mitotic human epithelial amnion cells: behavior of keratin and vimentin filaments during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1429–1434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase-induced vimentin filament disassembly involves modification of the N-terminal domain of intermediate filament subunits. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81306-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. An alteration in the phosphorylation of vimentin-type intermediate filaments is associated with mitosis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Peptide mapping of phosphorylated vimentin. Evidence for a site-specific alteration in mitotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5372–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The intermediate-filament proteins vimentin and desmin are phosphorylated in specific domains. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;46(1):152–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner C., Traut R. R., Mason D. T., Wikman-Coffelt J. Quantification of Coomassie Blue stained proteins in polyacrylamide gels based on analyses of eluted dye. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Analysis of desmin and vimentin phosphopeptides in cultured avian myogenic cells and their modulation by 8-bromo-adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6912–6916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. The synthesis and distribution of desmin and vimentin during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Phosphorylation of desmin in vitro inhibits formation of intermediate filaments; identification of three kinase A sites in the aminoterminal head domain. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B., Kupfer H., Eshhar Z., Geiger B. Reorganization of arrays of prekeratin filaments during mitosis. Immunofluorescence microscopy with multiclonal and monoclonal prekeratin antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Gonda Y., Matsuyama M., Nishizawa K., Nishi Y., Sato C. Intermediate filament reconstitution in vitro. The role of phosphorylation on the assembly-disassembly of desmin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5970–5978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman A. E., Yang H. Y., Goldman R. D. The organizational fate of intermediate filament networks in two epithelial cell types during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):93–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Goodman S. L., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Disruption of the keratin filament network during epithelial cell division. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviano Y., Gerace L. Phosphorylation of the nuclear lamins during interphase and mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):624–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Broek L., Egberts W. V., Ramaekers F., Bloemendal H. Characterization of the hamster desmin gene: expression and formation of desmin filaments in nonmuscle cells after gene transfer. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starger J. M., Brown W. E., Goldman A. E., Goldman R. D. Biochemical and immunological analysis of rapidly purified 10-nm filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):93–109. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Keratin filament disruption in interphase and mitotic cells--how is it induced? Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;43(1):35–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Li Y., Roe B. A., Paterson B. M., Sax C. M. The chicken vimentin gene. Nucleotide sequence, regulatory elements, and comparison to the hamster gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8112–8120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]