Abstract
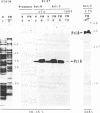
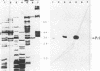
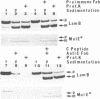
Genetic evidence indicates that the PrlA (SecY) protein of Escherichia coli functions as a membrane integrated signal sequence receptor in protein "export"--i.e., in protein translocation across (or integration into) the plasma membrane. We have raised antibodies in rabbits against two synthetic peptides representing the hydrophilic N- or C-terminal region of PrlA. Using these antibodies as probes in cell fractionation experiments, we confirm that PrlA is an integral membrane protein of the plasma membrane of E. coli. Fab fragments prepared from each of the two antisera specifically inhibit protein export by interfering with the binding of preproteins to the plasma membrane. Inhibition of preprotein binding and export by Fab fragments was shown in a cell-free translocation system: precursors for LamB (an integral membrane protein) and for a truncated form of MalE (a periplasmic protein) were first synthesized in a membrane-depleted E. coli-derived cell-free translocation system followed by posttranslational incubation with inverted vesicles derived from the plasma membrane of E. coli. Our data thus indicate that the N and C termini of PrlA are exposed to the cytoplasm. We discuss the possibility that the transmembrane segments of PrlA could be arranged in the lipid bilayer in a cylindrical fashion, thereby delimiting a protein conducting channel, with a signal sequence binding domain represented, at least in part, by the N and C termini of PrlA. Such a channel would also contain a "stop-transfer" sequence binding domain that in response to a stop-transfer sequence would open the cylindrical channel to the lipid bilayer and permit displacement of the polypeptide from the channel to the lipid bilayer, resulting in membrane integration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. Overproduction, isolation and determination of the amino-terminal sequence of the SecY protein, a membrane protein involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):263–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. The SecY membrane component of the bacterial protein export machinery: analysis by new electrophoretic methods for integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3351–3356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. Topology analysis of the SecY protein, an integral membrane protein involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3465–3470. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02670.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli K12. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:101–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerretti D. P., Dean D., Davis G. R., Bedwell D. M., Nomura M. The spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: sequence and cotranscription of the ribosomal protein genes and a protein export gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2599–2616. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Localization and processing of outer membrane and periplasmic proteins in Escherichia coli strains harboring export-specific suppressor mutations. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5852–5860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fandl J. P., Tai P. C. Biochemical evidence for the secY24 defect in Escherichia coli protein translocation and its suppression by soluble cytoplasmic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7448–7452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K. Identification of the secY (prlA) gene product involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00330964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Wittekind M., Nomura M., Shiba K., Yura T., Miura A., Nashimoto H. A temperature-sensitive mutant of E. coli exhibiting slow processing of exported proteins. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):789–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marglin A., Merrifield R. B. Chemical synthesis of peptides and proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:841–866. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.004205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Protein composition of the cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):890–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.890-901.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiba K., Ito K., Yura T., Cerretti D. P. A defined mutation in the protein export gene within the spc ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of a new temperature-sensitive secY mutant. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):631–635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz J., Silhavy T. J., Berman M. L., Fiil N., Emr S. D. A previously unidentified gene in the spc operon of Escherichia coli K12 specifies a component of the protein export machinery. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Uses of lac fusions for the study of biological problems. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):398–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.398-418.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Hunt J. F., Blobel G. In vitro synthesized bacterial outer membrane protein is integrated into bacterial inner membranes but translocated across microsomal membranes. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):71–73. doi: 10.1038/323071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]