Abstract
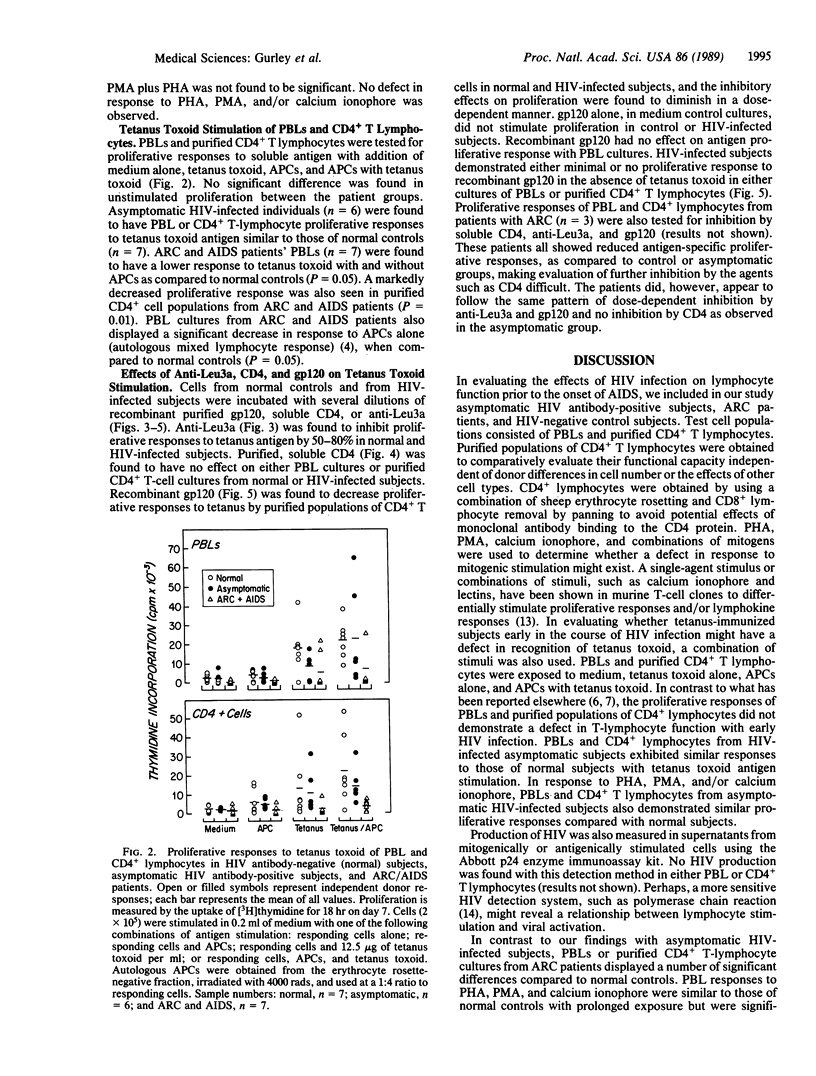
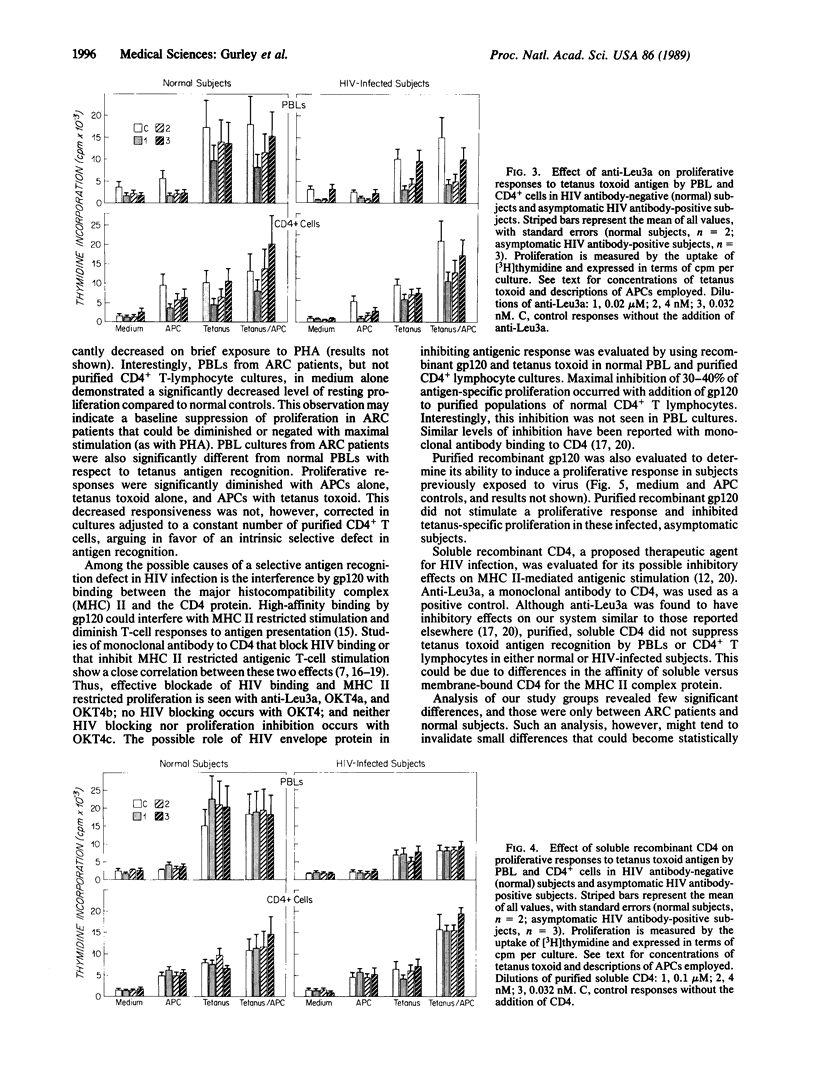
The pathogenesis of cellular immune deficiency following human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection could result from quantitative and/or qualitative dysfunction of the CD4+ lymphocyte population. To better characterize the T-cell response to soluble antigen with HIV infection, we have isolated peripheral blood lymphocytes and purified populations of CD4+ lymphocytes from healthy HIV antibody-positive subjects, patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)-related complex (ARC), and healthy HIV antibody-negative controls. T-lymphocyte function was determined by proliferative response to lectin (phytohemagglutinin), phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), calcium ionophore, purified recombinant HIV envelope gp120, tetanus toxoid antigen, and tetanus toxoid antigen in the presence of recombinant gp120 or purified recombinant soluble CD4. PBLs and CD4+ lymphocytes from asymptomatic HIV-infected subjects responded equally well to lectin, PMA, and/or calcium ionophore and to tetanus toxoid as cells from uninfected control subjects. The cells that proliferated in response to a soluble antigenic stimulus did not respond to gp120. Cells from subjects with ARC had a selective antigen recognition defect independent of the number of CD4+ lymphocytes. Recombinant gp120 inhibited CD4+ lymphocyte proliferation to antigenic stimulus by 30-40%. Recombinant soluble CD4, a proposed therapeutic for HIV, had no effect on T-cell response to antigen. A selective antigen recognition response was not compromised early in HIV infection but was compromised in subjects with ARC. Inhibition of proliferation to tetanus toxoid by gp120 suggests that HIV may affect major histocompatibility complex II restricted antigen recognition independent of CD4+ cell loss.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddison W. E., Rao P. E., Talle M. A., Goldstein G., Shaw S. Possible involvement of the T4 molecule in T cell recognition of class II HLA antigens: evidence from studies of proliferative responses to SB antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):152–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Glickman E., Evans R. L. Antibodies to membrane structures that distinguish suppressor/cytotoxic and helper T lymphocyte subpopulations block the mixed leukocyte reaction in man. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):193–198. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D., Maddon P., Sekaly R., Talle M. A., Godfrey M., Long E., Goldstein G., Chess L., Axel R., Kappler J. Functional interaction between human T-cell protein CD4 and the major histocompatibility complex HLA-DR antigen. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):626–629. doi: 10.1038/328626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi J. V., Fahey J. L., Smith D. C., Hultin L. E., Cheng H. L., Mitsuyasu R. T., Detels R. Early effects of HIV on CD4 lymphocytes in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 1;138(11):3725–3730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb M. S., Schroff R., Schanker H. M., Weisman J. D., Fan P. T., Wolf R. A., Saxon A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and mucosal candidiasis in previously healthy homosexual men: evidence of a new acquired cellular immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1425–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Safai B. Deficient autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in Kaposi's sarcoma associated with deficiency of Leu-3+ responder T cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):296–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI110769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckford S. E., Gelmann E. P., Agnor C. L., Jacobson S., Zinn S., Matis L. A. Distinct signals are required for proliferation and lymphokine gene expression in murine T cell clones. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3652–3663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussey R. E., Richardson N. E., Kowalski M., Brown N. R., Chang H. C., Siliciano R. F., Dorfman T., Walker B., Sodroski J., Reinherz E. L. A soluble CD4 protein selectively inhibits HIV replication and syncytium formation. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):78–81. doi: 10.1038/331078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B. The regulation of intracellular signals during lymphocyte activation. Immunol Today. 1988 Jan;9(1):17–18. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Greene W. C. Sequential expression of genes involved in human T lymphocyte growth and differentiation. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1593–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Depper J. M., Greene W. C., Whalen G., Waldmann T. A., Fauci A. S. Qualitative analysis of immune function in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for a selective defect in soluble antigen recognition. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):79–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Groopman J. E., Fennie C. W., Benz P. M., Capon D. J., Dowbenko D. J., Nakamura G. R., Nunes W. M., Renz M. E., Berman P. W. Neutralization of the AIDS retrovirus by antibodies to a recombinant envelope glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.3014647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linette G. P., Hartzman R. J., Ledbetter J. A., June C. H. HIV-1-infected T cells show a selective signaling defect after perturbation of CD3/antigen receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.2899908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Lasane F., Popovic M., Arthur L. O., Robey W. G., Blattner W. A., Newman M. J. HTLV-III large envelope protein (gp120) suppresses PHA-induced lymphocyte blastogenesis. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2640–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Michelis M. A., Greene J. B., Onorato I., Stouwe R. A., Holzman R. S., Wormser G., Brettman L., Lange M., Murray H. W. An outbreak of community-acquired Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: initial manifestation of cellular immune dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1431–1438. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Kwok S., Mitchell S. W., Mack D. H., Sninsky J. J., Krebs J. W., Feorino P., Warfield D., Schochetman G. DNA amplification for direct detection of HIV-1 in DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3336784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Dalgleish A. G., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1120–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.2430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Weiss R. A. The CD4 antigen: physiological ligand and HIV receptor. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):631–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Bernstein D. C., Tung K. S., Via C. S., Redfield R., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C. A model for the selective loss of major histocompatibility complex self-restricted T cell immune responses during the development of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2514–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegal F. P., Lopez C., Hammer G. S., Brown A. E., Kornfeld S. J., Gold J., Hassett J., Hirschman S. Z., Cunningham-Rundles C., Adelsberg B. R. Severe acquired immunodeficiency in male homosexuals, manifested by chronic perianal ulcerative herpes simplex lesions. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1439–1444. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Byrn R. A., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Groopman J. E., Capon D. J. Blocking of HIV-1 infectivity by a soluble, secreted form of the CD4 antigen. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1704–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.3500514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]