Abstract
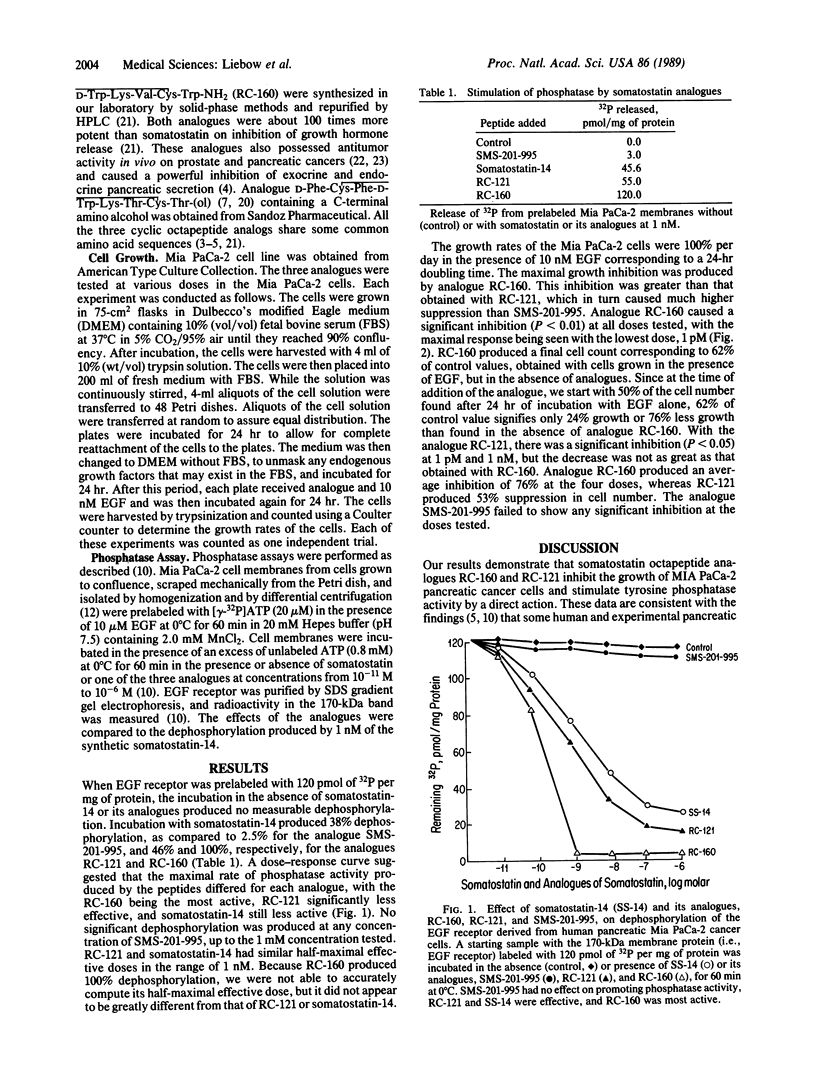
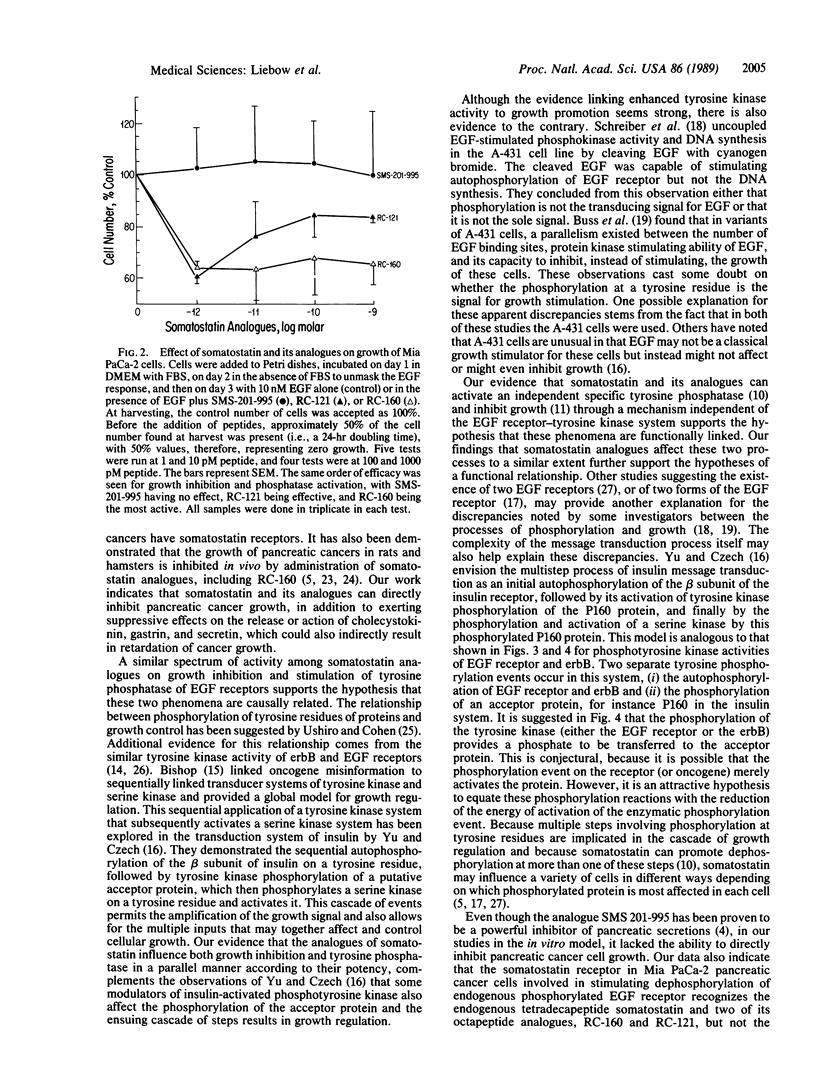
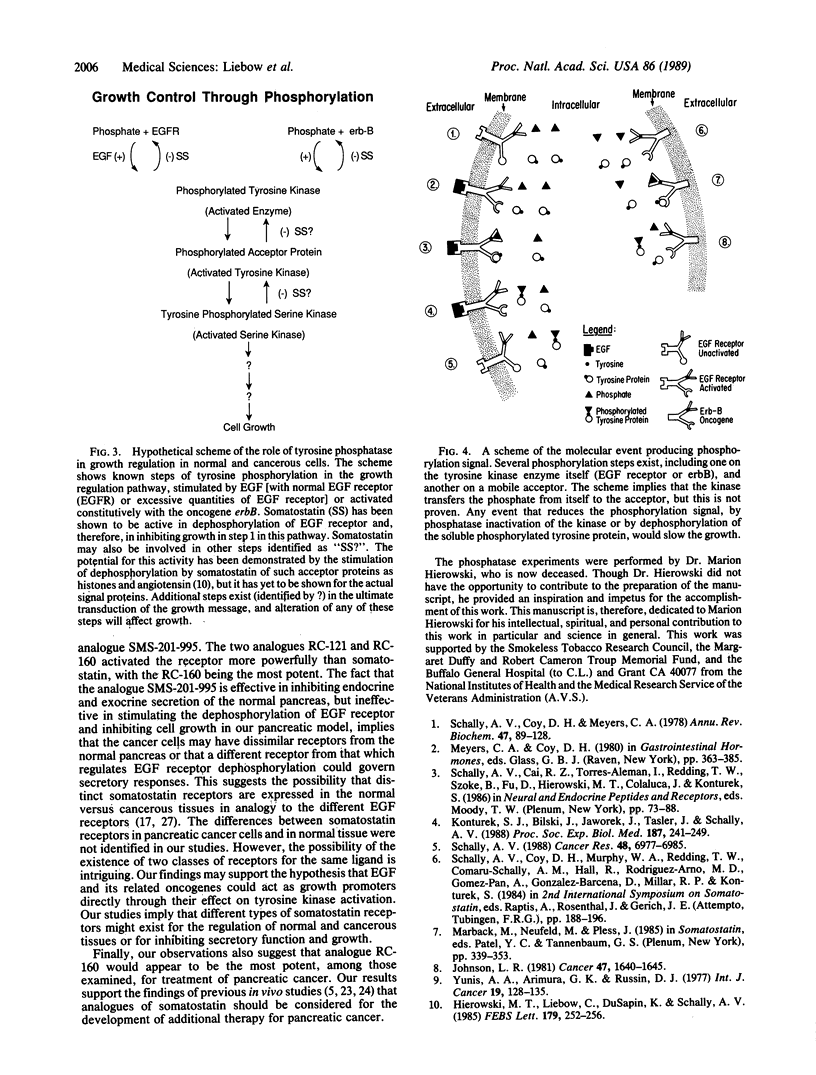
Several analogues of somatostatin were examined in the Mia PaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cell line for their ability to promote tyrosine phosphatase activity affecting the receptors for the epidermal growth factor. The inhibition of growth of the Mia PaCa-2 cells in culture was also evaluated to determine the mechanism of action of somatostatin analogues and their relative effectiveness in inhibiting cancer growth. Of the analogues tested D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys-Trp-NH2 (RC-160) caused the greatest stimulation of tyrosine phosphatase activity. Analogue D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Lys-Val-Cys-Thr-NH2 (RC-121) had less effect but was more potent than somatostatin-14. Analogue D-Phe-Cys-Phe-D-Trp-Lys-Thr-Cys-Thr(ol) (SMS 201-995) produced no significant dephosphorylation. The analogues displayed the same order of activity in assays on growth inhibition of Mia PaCa-2 cells in cultures. Analogue (SMS-201-995) caused virtually no tyrosine phosphatase stimulation or growth inhibition in this cancer cell line, although it possesses a much higher antisecretory activity than somatostatin-14 in normal tissues. These observations indicate that somatostatin and some of its analogues can act as growth inhibitors in cancer cells through the activation of tyrosine phosphatase. These data reinforce the view that somatostatin analogue RC-160 and related compounds could be used for treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Sudo C., Ogawara H., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: a 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1644–1646. doi: 10.1126/science.3012781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Briner U., Doepfner W., Haller R., Huguenin R., Marbach P., Petcher T. J., Pless SMS 201-995: a very potent and selective octapeptide analogue of somatostatin with prolonged action. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 13;31(11):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Kudlow J. E., Lazar C. S., Gill G. N. Altered epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated protein kinase activity in variant A431 cells with altered growth responses to EGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F. Mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation and high-affinity binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai R. Z., Szoke B., Lu R., Fu D., Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Synthesis and biological activity of highly potent octapeptide analogs of somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierowski M. T., Liebow C., du Sapin K., Schally A. V. Stimulation by somatostatin of dephosphorylation of membrane proteins in pancreatic cancer MIA PaCa-2 cell line. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 7;179(2):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80529-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. R. Effects of gastrointestinal hormones on pancreatic growth. Cancer. 1981 Mar 15;47(6 Suppl):1640–1645. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810315)47:6+<1640::aid-cncr2820471430>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Bilski J., Jaworek J., Tasler J., Schally A. V. Comparison of somatostatin and its highly potent hexa- and octapeptide analogs on exocrine and endocrine pancreatic secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1988 Feb;187(2):241–249. doi: 10.3181/00379727-187-42661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebow C., Hierowski M., duSapin K. Hormonal control of pancreatic cancer growth. Pancreas. 1986;1(1):44–48. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198601000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding T. W., Schally A. V. Inhibition of growth of pancreatic carcinomas in animal models by analogs of hypothalamic hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):248–252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Coy D. H., Meyers C. A. Hypothalamic regulatory hormones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:89–128. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V. Oncological applications of somatostatin analogues. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 15;48(24 Pt 1):6977–6985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schally A. V., Redding T. W. Somatostatin analogs as adjuncts to agonists of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in the treatment of experimental prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7275–7279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Transforming growth factor-alpha: a more potent angiogenic mediator than epidermal growth factor. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1250–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.2422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. A non-mitogenic analogue of epidermal growth factor enhances the phosphorylation of endogenous membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 30;101(2):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91290-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis A. A., Arimura G. K., Russin D. J. Human pancreatic carcinoma (MIA PaCa-2) in continuous culture: sensitivity to asparaginase. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jan;19(1):128–135. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalatnai A., Schally A. V. Responsiveness of the hamster pancreatic cancer to treatment with microcapsules of D-Trp-6-LH-RH and somatostatin analog RC-160. Histological evidence of improvement. Int J Pancreatol. 1989 Mar;4(2):149–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02931317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


