Abstract
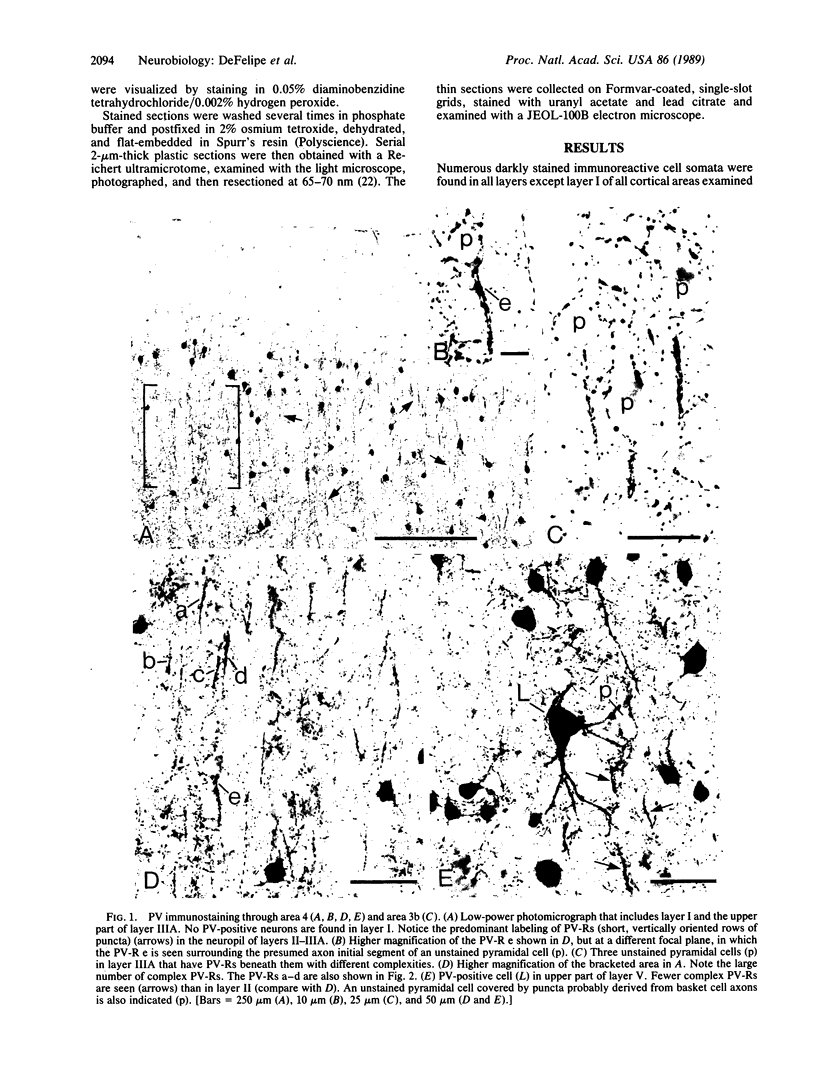
Antibodies directed against the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin label a subpopulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid-releasing neurons in the cerebral cortex that is thought to have particular metabolic and physiological properties. The chandelier cell is a well-characterized morphological type of gamma-aminobutyric acid-releasing cortical interneuron, the axon of which possesses very distinctive terminal portions located around the initial axon segments of pyramidal cells. In the pre- and postcentral gyri of the monkey, we found that these distinctive terminal portions of chandelier cell axons were immunocytochemically stained for parvalbumin in a manner that reveals their complete structure. The chandelier cell axons were identified light-microscopically as short, vertically oriented rows of parvalbumin-positive puncta (PV-Rs). The PV-Rs varied in both length and complexity and were located beneath unstained pyramidal cells. PV-Rs were very numerous in layers II-III, where most pyramidal cells appeared to have a PV-R beneath them. Fewer PV-Rs were found in deeper layers, and in layer VI PV-Rs were rare. With EM all PV-Rs could be seen to form multiple synaptic contacts of the symmetrical type on the initial segments of pyramidal cell axons. Parvalbumin immunoreactivity can therefore be used as a reliable marker for chandelier cell axons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelipe J., Fairén A. A type of basket cell in superficial layers of the cat visual cortex. A Golgi-electron microscope study. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 22;244(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90898-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Jones E. G. A correlative electron microscopic study of basket cells and large GABAergic neurons in the monkey sensory-motor cortex. Neuroscience. 1986 Apr;17(4):991–1009. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Schmechel D. Variability in the terminations of GABAergic chandelier cell axons on initial segments of pyramidal cell axons in the monkey sensory-motor cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jan 15;231(3):364–384. doi: 10.1002/cne.902310307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demeulemeester H., Vandesande F., Orban G. A., Brandon C., Vanderhaeghen J. J. Heterogeneity of GABAergic cells in cat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Mar;8(3):988–1000. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-03-00988.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairén A., Valverde F. A specialized type of neuron in the visual cortex of cat: a Golgi and electron microscope study of chandelier cells. J Comp Neurol. 1980 Dec 15;194(4):761–779. doi: 10.1002/cne.901940405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Martin K. A., Smith A. D., Somogyi P. Glutamate decarboxylase-immunoreactive terminals of Golgi-impregnated axoaxonic cells and of presumed basket cells in synaptic contact with pyramidal neurons of the cat's visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Dec 10;221(3):263–278. doi: 10.1002/cne.902210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., DeFelipe J., Schmechel D., Brandon C., Emson P. C. Neuropeptide-containing neurons of the cerebral cortex are also GABAergic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6526–6530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Maggio J. E. A study of tachykinin-immunoreactive neurons in monkey cerebral cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Apr;8(4):1206–1224. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01206.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G. Varieties and distribution of non-pyramidal cells in the somatic sensory cortex of the squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Mar 15;160(2):205–267. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T., Heizmann C. W., Tateishi K., Hamaoka Y., Hama K. An aspect of the organizational principle of the gamma-aminobutyric acidergic system in the cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 21;409(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90732-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Lu S. M., Schmechel D. E. Glutamic acid decarboxylase and somatostatin immunoreactivities in rat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Feb 15;244(3):369–383. doi: 10.1002/cne.902440309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin-Padilla M. Origin of the pericellular baskets of the pyramidal cells of the human motor cortex: a Golgi study. Brain Res. 1969 Aug;14(3):633–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Proskauer C. C., Ribak C. E. Chandelier cells in rat visual cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Apr 20;206(4):397–416. doi: 10.1002/cne.902060408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribak C. E. Axon terminals of GABAergic chandelier cells are lost at epileptic foci. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 11;326(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Vickrey B. G., Fitzpatrick D., Elde R. P. GABAergic neurons of mammalian cerebral cortex: widespread subclass defined by somatostatin content. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Jun 29;47(3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90518-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P. A specific 'axo-axonal' interneuron in the visual cortex of the rat. Brain Res. 1977 Nov 11;136(2):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90808-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Freund T. F., Cowey A. The axo-axonic interneuron in the cerebral cortex of the rat, cat and monkey. Neuroscience. 1982;7(11):2577–2607. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., Smith A. D., Nunzi M. G., Gorio A., Wu J. Y. Different populations of GABAergic neurons in the visual cortex and hippocampus of cat contain somatostatin- or cholecystokinin-immunoreactive material. J Neurosci. 1984 Oct;4(10):2590–2603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-10-02590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentágothai J. The 'module-concept' in cerebral cortex architecture. Brain Res. 1975 Sep 23;95(2-3):475–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde F. Short axon neuronal subsystems in the visual cortex of the monkey. Int J Neurosci. 1971 Feb;1(3):181–197. doi: 10.3109/00207457109146970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]