Abstract
The vascular endothelial growth factors VEGFA and VEGFC are crucial regulators of vascular development. They exert their effects by dimerization and activation of the cognate receptors VEGFR2 and VEGFR3. Here, we have used in situ proximity ligation to detect receptor complexes in intact endothelial cells. We show that both VEGFA and VEGFC potently induce formation of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. Receptor heterodimers were found in both developing blood vessels and immature lymphatic structures in embryoid bodies. We present evidence that heterodimers frequently localize to tip cell filopodia. Interestingly, in the presence of VEGFC, heterodimers were enriched in the leading tip cells as compared with trailing stalk cells of growing sprouts. Neutralization of VEGFR3 to prevent heterodimer formation in response to VEGFA decreased the extent of angiogenic sprouting. We conclude that VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers on angiogenic sprouts induced by VEGFA or VEGFC may serve to positively regulate angiogenic sprouting.
Keywords: angiogenic sprouting, embryoid body, heterodimer, proximity ligation, VEGF receptor
Introduction
The mammalian vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family includes VEGFA, VEGFB, VEGFC, VEGFD and placenta growth factor (PlGF). These ligands bind in an overlapping pattern to three different receptor tyrosine kinases denoted VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1), VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 (Olsson et al, 2006). Although the VEGFRs are not exclusively expressed on vascular cells, there is prominent expression and important function of VEGFR1 on hematopoietic and endothelial cells, of VEGFR2 on vascular endothelial cells and of VEGFR3 on vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs). The active VEGF/VEGFR signalling complexes also include co-receptors, such as heparan sulphate proteoglycans (Esko and Selleck, 2002) and neuropilins (Geretti et al, 2008).
The VEGFRs transduce their effects according to the consensus scheme for receptor tyrosine kinases. Binding of ligand leads to dimerization of receptors. This close apposition confers structural reorganization of the receptor intracellular domain and exposure of the kinase active site (Hubbard, 1999). Kinase activity catalyses the transfer of phosphate groups to tyrosine residues, which serve as substrates for the kinase. Such acceptor sites are found both on the partner in the dimer as well as on cytoplasmic signalling molecules. Tyrosine phosphorylation initiates signal transduction cascades, which ultimately become established as cellular responses such as survival, proliferation and motility.
Certain VEGF ligands bind to more than one VEGFR, potentially allowing receptors to form heterodimers in addition to homodimers. We have shown earlier that VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers are formed in cultured LECs in response to VEGFC (Dixelius et al, 2003). In accordance, processing of VEGFC during synthesis allows binding to both VEGFR2 and -3 (Joukov et al, 1997; Alitalo et al, 2005). Heterodimerization was accompanied by a loss of phosphorylation of C-terminal tyrosine residues in VEGFR3 (Dixelius et al, 2003). The underlying mechanism may involve different substrate specificities of the VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 kinases. Alternatively, VEGFR3 may undergo a conformational change when engaged in a heterodimer with VEGFR2, and thereby, certain acceptor sites become hidden or otherwise inaccessible. Thus, it is important to determine the composition of receptor complexes formed under different conditions, as this will be of consequence for the biological response.
Various sophisticated recombinant animal models have greatly aided our understanding of the biology of the VEGFRs. All three receptors are required for proper embryonic development. Gene inactivation of vegfr1 is lethal at E8.5–9 due to increased endothelial proliferation leading to obstruction of vessels (Fong et al, 1995, 1999). Inactivation of vegfr2 leads to arrest in endothelial differentiation, causing embryonic lethality at E8.5 (Shalaby et al, 1995). Inactivation of vegfr3 is lethal slightly later, at E10.5, due to the lack of remodelling of the vascular network (Dumont et al, 1998). In subsequent development, VEGFR3 is critical for lymphatic vessel function. Thus, during a restricted phase in early development, both VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 serve critical functions in the formation of the vascular tree.
A number of cell types co-express VEGFR2 and VEGFR3, potentially allowing formation of heterodimers. Expression of VEGFR3 is induced during angiogenic sprouting in the adult, both in physiological and pathological conditions (Tammela et al, 2008). In differentiating stem cell cultures, VEGFR3 is expressed by subpopulations of endothelial cells in growing vessels, some of which may transdifferentiate to become early lymphatic structures (Kreuger et al, 2006; Adams and Alitalo, 2007). In addition, VEGFR2 may be variably expressed by LECs (Petrova et al, 2002), and on collecting lymphatic vessels that otherwise are characterized by high expression levels of VEGFR3 (Saaristo et al, 2002).
Here, we investigate the function of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization in intact endothelial cells and angiogenic sprouts, using a newly developed in situ proximity ligation assay (in situ PLA) (Soderberg et al, 2006; Jarvius et al, 2007). This method is based on the use of oligonucleotide-conjugated antibodies, which when brought in close proximity by binding to epitopes on, for example, dimerized VEGFRs, allow a rolling-circle amplification detected by a fluorescently labelled probe. We show that endogenous unmanipulated VEGFRs form heterodimers in response to VEGFA or VEGFC. We present evidence that heterodimers are present on tip cell filopodia, and that neutralization of VEGFR3 to prevent heterodimer formation induced by VEGFA leads to a marked decrease in sprouting activity. It is concluded that VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers have a significant function in the positive regulation of angiogenic sprouting.
Results
Detection of VEGFC-induced VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in endothelial cells by immunoprecipitation
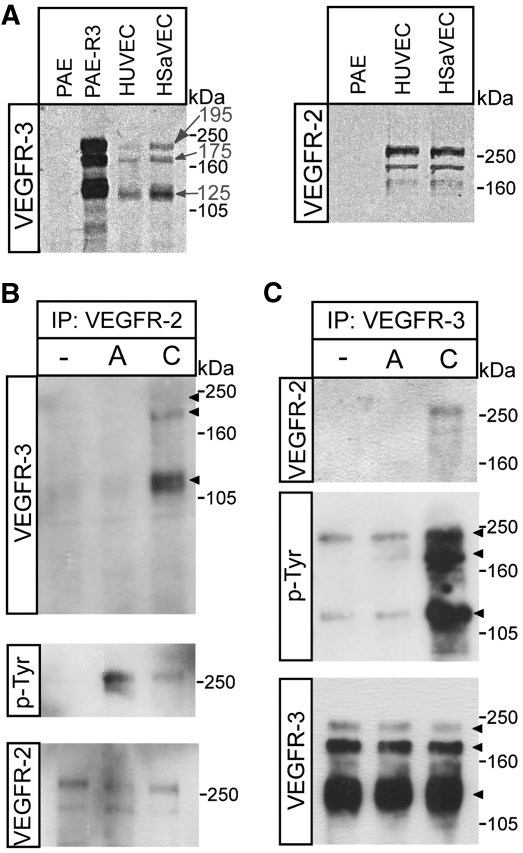
To study the induction of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers, we examined receptor expression in different endothelial cell cultures. On reducing gels, VEGFR3 migrates as three molecular weight species, 195, 175 and 125 kDa (Pajusola et al, 1994). The mature, cell surface expressed VEGFR2 appears as a 250 kDa band on immunoblots. Using porcine aortic endothelial (PAE) cells transfected to express VEGFR3 as control, we compared expression of receptors in primary human saphenous and umbilical vein-derived endothelial cells (HSaVECs and HUVECs). Both cell types co-expressed VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 (Figure 1A); we chose HSaVECs for further experimentation.
Figure 1.
Induction of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in co-expressing endothelial cells. (A) Total cell lysates derived from HUVECs, HSaVECS or PAE cells; either untransfected or expressing VEGFR3 were immunoblotted to detect VEGFR3 (left panel). After reduction of disulphide bridges, VEGFR3 migrates as three species of apparent mw 195, 175 and 125 kDa. PAE, HUVEC and HSaVEC lysates were also immunoblotted to detect VEGFR2, which migrates as two species around the 250 kDa marker (right panel). (B) HSaVEC lysates from cells treated or not with VEGFA or VEGFC for 8 min were used for immunoprecipitation (ip) of VEGFR2 followed by immunoblotting for VEGFR3 (upper panel) to detect receptor heterodimerization. This was followed by immunoblotting to detect phosphorylated VEGFR2 (middle panel) using the 4G10 mAb, and immunoblotting to show equal loading of VEGFR2 (lower panel). (C) Immunoprecipitation of VEGFR3 from HSaVECs treated as in (B) followed by immunoblotting to detect co-immunoprecipitation of VEGFR2 (upper panel), phosphorylation of VEGFR3 (middle panel) and VEGFR3 loading (lower panel).
Treatment of HSaVECs with processed VEGFC, followed by immunoprecipitation of VEGFR2 and immunoblotting for VEGFR3, showed complex formation between the receptors. Figure 1B displays the prominent 125 kDa band and the weaker 195–175 kDa VEGFR3 bands in the VEGFR2 immunoprecipitate. Heterodimers were not detected in response to VEGFA in this assay (Figure 1B, upper panel). The effect of VEGFA on VEGFR2 tyrosine phosphorylation was more prominent than that of VEGFC (Figure 1B, middle panel), in agreement with the data from earlier biochemical analyses, showing higher affinity of VEGFA than VEGFC, for binding to VEGFR2 (Joukov et al, 1997).
Similarly, treatment with VEGFC but not with VEGFA, allowed detection of the 250 kDa VEGFR2 band in immunoblots of VEGFR3 immunoprecipitates from HSaVECs (Figure 1C, upper panel). These data show that VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 form heterodimeric signalling complexes in primary cells in response to VEGFC.
in situ PLA reveals VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization in response to VEGFA or VEGFC
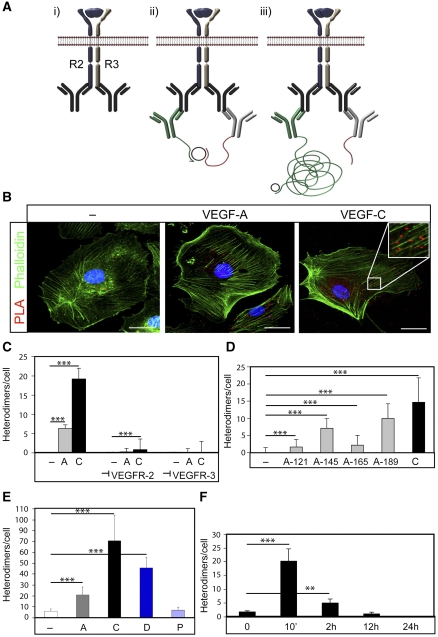
To demonstrate the formation of heterodimers in intact cells, we used in situ PLA (see schematic outline in Figure 2A). We used an experimental design where cells were incubated with VEGFA, VEGFC or vehicle for 8 min, fixed and then probed with primary antibodies raised in different species and directed towards the intracellular domains of VEGFR2 or VEGFR3. Antibodies against the intracellular domain were preferred, as they would not be disturbed by the ligand–receptor interaction. This was followed by incubation with two sets of secondary antibodies conjugated with oligonucleotide, unique for each type of secondary antibody. Ligation of the oligonucleotides by a bridging probe in a proximity-dependent manner, allows a rolling-circle amplification. Finally, this product is detected by complementary fluorescent probes. As shown in Figure 2B, treatment of HSaVECs with VEGFC induced formation of heterodimers in situ, distributed on the plasma membrane as well as in the cytoplasm. The number of heterodimers/cell increased 100-fold from basal, in response to VEGFC treatment (see quantification in Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
In situ PLA detection of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in intact HSaVECs. (A) Schematic outline of the in situ PLA strategy showing: (i) dimerized receptors (VEGFR2 in blue and VEGFR3 in grey) reacting with primary antibodies; (ii) close proximity of oligonucleotide-ligated secondary antibodies allows a rolling-circle amplification (RCA); (iii) detection of the RCA product by a fluorescently labelled probe. (B) Detection of heterodimers (in red) in HSaVECs treated with vehicle (–), VEGFA or VEGFC for 8 min on cells labelled with FITC-conjugated phalloidin (green). Inset in the VEGFC panel shows high magnification to clearly visualize the PLA spots representing heterodimers. Scale bar=10 μm. (C) Quantification of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in HSaVECs treated with vehicle (–), VEGFA (A) or VEGFC (C) in cells preincubated or not with neutralizing antibodies blocking ligand binding to VEGFR2 or VEGFR3. n=6. (D) Quantification of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in HSaVECs treated with different human VEGF isoforms (VEGFA121, 145, 165 or 189) or VEGFC for 8 min. n=6. (E) Quantification of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in response to VEGFA, VEGFC, VEGFD or PDGFB. Growth factors are indicated as A (VEGFA), C (VEGFC), D (VEGFD) and P (PDGFB). n=6. Note that a different batch of PLA probes was used in this analysis compared with other panels in the figure (see Materials and methods). (F) Turnover of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in HSaVECs. Cells were treated with VEGFC for different time periods from 10 min to 24 h and samples were processed for detection of in situ PLA signals. n=6. Asterisks in panels C–F indicate the degree of significance (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
Of note, VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization also increased significantly (25-fold) when cells were treated with VEGFA for 8 min (see Figure 2B and C). Therefore, despite the fact that VEGFA fails to induce receptor heterodimerization as detected by co-immunoprecipitation, VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers were induced by VEGFA in the in situ PLA.
To show the specificity of the reactions, we preincubated cells with antibodies previously shown to specifically neutralize either human VEGFR2; IMC-1121b (Zhu et al, 2003) or human VEGFR3; hF4-3C5 (Persaud et al, 2004), by binding to the ligand-binding part of the extracellular domains. As shown in Figure 2C, blocking with either of the neutralizing antibodies quenched the appearance of heterodimers to the level of basal heterodimerization recorded in unstimulated cells.
Different VEGFA isoforms (VEGFA121, 145, 165 and 189) were analysed for their ability to induce VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. Isoforms with a higher propensity for binding to heparan sulphate and extracellular matrix, that is VEGFA145 and VEGFA189 (Kawamura et al, 2008), induced heterodimers more efficiently than the relatively more soluble isoforms VEGFA121 and VEGFA165 (Figure 2D). In repeated experiments, however, VEGFC induced heterodimer formation more efficiently than any of the VEGFA isoforms.
Further, VEGFD also induced VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization, in agreement with that processed human VEGFD, but not mouse VEGFD, binds to VEGFR2 (Baldwin et al, 2001). The effect was less efficient than that of VEGFC but more prominent than that of VEGFA. To control for the specificity, we analysed the effect of PDGFB, which does not bind to either of the VEGF receptors. As shown in Figure 2E, VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers were not induced by PDGFB.
Binding of ligand induces internalization and degradation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Figure 2F shows HSaVECs treated with VEGFC for different time periods, followed by in situ PLA. Formation of heterodimers peaked at 10 min and the ligand-induced heterodimers remained detectable for up to 2 h. With prolonged incubations, the in situ PLA signals were lost, in agreement with the clearance of receptors. Combined, these data provide evidence that heterodimers are formed in a ligand-dependent and specific manner in intact cells.
Detection of homodimerization of VEGFRs by in situ PLA
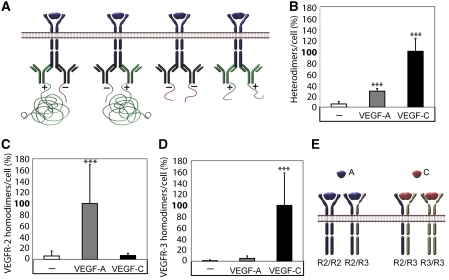
We next examined the pattern of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 homodimerization induced by VEGFA and VEGFC. For this purpose, monoclonal antibodies against either VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 were divided in pools, which were ligated with either a ‘plus' oligonucleotide or a ‘minus' oligonucleotide. The PLA reaction indicating for example VEGFR2 homodimers, would occur only as a result of close proximity of a plus-ligated antibody with a minus-ligated antibody, whereas pairs consisting of plus–plus or minus–minus ligated antibodies would not give rise to PLA signals (see Figure 3A for a schematic outline). Consequently, we could score only 50% of the actual homodimerization events, namely when antibodies combined in plus–minus and minus–plus constellations. Moreover, we could not directly compare the relative extent of receptor homo- and heterodimerization, as different combinations of antibodies had to be used to detect the different receptor complexes.
Figure 3.
VEGFR2/-3 homo- and heterodimers induced by VEGFA or VEGFC. (A) Schematic outline of primary antibody ligation with oligonucleotide plus and minus strands to detect VEGFR homodimers. Only pairing of antibodies with plus and minus strands allow initiation of the rolling-circle amplification. (B) VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization. HSaVECs were treated for 8 min with either VEGFA or VEGFC. Heterodimerization was 3–4-fold more efficiently induced by VEGFC. n=6. (C) VEGFR2 homodimers. Equal mixtures of VEGFR2 monoclonal antibodies ligated with plus and minus strands of oligonucleotides (as outlined in A) were used to detect VEGFR2 homodimers on HSaVECs treated for 8 min with VEGFA or VEGFC as above. n=6. (D) VEGFR3 homodimers. Equal mixtures of VEGFR3 monoclonal antibodies ligated with plus and minus strands of oligonucleotides were used to detect VEGFR3 homodimers on HSaVECs treated for 8 min with VEGFA or VEGFC. n=6. (E) Schematic outline of VEGFR homo- and heterodimerization induced by VEGFA or VEGFC. Note that the relative distribution of homodimers versus heterodimers cannot be accurately determined due to the inherent difference in affinity of different antibodies. Asterisks in panels B–D indicate the degree of significance (***P<0.001).
As shown in Figure 3B, VEGFA and VEGFC consistently induced heterodimers and VEGFC was about 3–4-fold more potent in this regard. VEGFR2 homodimers were induced only by VEGFA and not by VEGFC (Figure 3C). VEGFR3 homodimers were induced by VEGFC (Figure 3D). There was a slight tendency for VEGFA-induced VEGFR3 homodimerization, but still the effect was negligible compared with that of VEGFC. Figure 3E concludes on these results; VEGFA induces VEGFR2 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. VEGFC induces VEGFR3 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. Although no firm conclusions can be made as reasoned above, homodimers of VEGFR3 seemed to be roughly two-fold more frequent than heterodimers in VEGFC-treated cells. Moreover, homodimers of VEGFR2 were eight-fold more frequent than heterodimers in VEGFA-treated cells.
VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers are formed in blood and lymphatic endothelium in differentiating EBs
To identify the biological significance of VEGF receptor heterodimerization, we exploited the embryoid body (EB) model of angiogenesis (Jakobsson et al, 2007). In this model system, differentiating mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells efficiently form capillary structures in response to angiogenic growth factors. In the first set of experiments, EBs were cultured in the so-called two-dimensional (2D) setup, seeded onto tissue culture slides. The advantages of the 2D setup are that these cultures readily can be scaled up to allow for biochemical analyses, such as immunoprecipitation, and that the 2D setup also makes it feasible to analyse the relatively rare events whereby immature capillaries in EB cultures begin to transdifferentiate into early lymphatic structures (Kreuger et al, 2006).
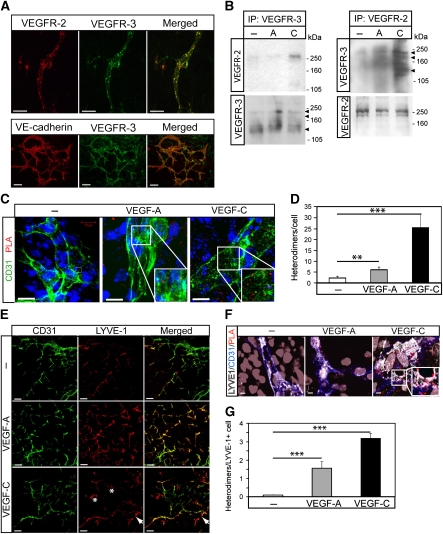
Figure 4A shows co-expression of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 in endothelial cells in vascular structures formed in 2D EBs differentiated for 12 days, when endothelial cells constitute about 5% of the total cellular pool (Magnusson et al, 2004). The vascular identity of the cells co-expressing VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 was validated by positive immunostaining for VE-cadherin (lower panel in Figure 4A). As shown in Figure 4B, left panel, immunoprecipitation/immunoblotting analyses demonstrated VEGFC-induced VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization in the EB model. Parallel VEGFR2 immunoprecipitation from VEGFA or VEGFC-treated EBs followed by immunoblotting for VEGFR3 (Figure 4B, right panel) showed VEGFC-, but also to some extent, VEGFA-induced receptor heterodimerization.
Figure 4.
Formation of vessel structures in differentiating 2D EBs involves both VEGFR2 and VEGFR3. (A) Expression of VEGFRs in 2D EB vascular structures. EBs differentiating in 2D cultures for 12 days in the presence of VEGFA shows vessel-like structures co-expressing VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 (upper panels; merged immunostainings to the right), or VE-cadherin and VEGFR3 (lower panels; merged immunostainings to the right). Scale bar=50 μm (upper), 100 μm (lower). (B) Complex formation between VEGFRs in 2D EBs. Left: Immunoprecipitation (ip) of VEGFR3 from day 12 EBs treated with vehicle (–) VEGFA (A) or VEGFC (C) for 15 min followed by immunoblotting for VEGFR2 (upper left panel). Immunoblotting for VEGFR3 (lower left panel) shows equal loading of VEGFR3. Right: Parallel aliquots of cell lysate were analysed by immunoprecipitation of VEGFR2 followed by immunoblotting for VEGFR3 (upper right panel). VEGFR2 immunoblotting (lower right panel) showed equal loading. (C) Heterodimers in CD31-positive cells. Formation of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers as detected by in situ PLA (red spots) on 2D EBs immunostained for CD31 (green), in response to vehicle (–), VEGFA or VEGFC. Scale bar=10 μm. (D) Quantification of PLA spots in CD31-positive cells as in C. n=8. (E) Identification of LYVE1-positive cells. EBs in 2D cultures were treated with VEGFA or VEGFC until day 12, and immunostained to detect expression of CD31 (green) and LYVE1 (red). Panels to the right show merged immunostainings. Lymphatic vascular structures expressing LYVE1 but not CD31 are indicated by arrows in the VEGFC-treated cultures. Single, rather than vessel-organized LYVE1-positive cells, are indicated by asterisk. Scale bar=100 μm. (F) Heterodimers in LYVE1-positive cells. EBs in 2D culture were treated as indicated above and processed for immunostaining to detect CD31 (blue) and LYVE1 (white), followed by in situ PLA to detect VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers (red). Scale bar=10 μm. (G) Quantification of PLA spots in LYVE1-positive cells as in (F). n=8. Asterisks in panels D and G indicate the degree of significance (**P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
We next used in situ PLA to examine VEGFR2/-3 heterodimer formation in intact 2D EBs. As shown in Figure 4C (quantification in Figure 4D), VEGFA and VEGFC induced heterodimers to an extent similar to that detected in the HSaVEC cultures (see Figure 2 for comparison). Occasional PLA signals were detected also in cells expressing low or non-detectable levels of CD31, prompting us to ask whether some of these cells could be LECs or progenitors thereof. We have shown earlier that differentiation of ES cells allows formation of lymphatic endothelial precursors that express lower levels of CD31, which can be identified by virtue of expression of lymphatic markers such as LYVE1 (Kreuger et al, 2006). As shown in Figure 4E, VEGFA-treated EB cultures contained LYVE1-positive cells that also expressed CD31. A certain fraction of the LYVE1-expressing cells lacked detectable CD31 expression (arrow in Figure 4E). LYVE1-positive cells with distinct morphology, possibly corresponding to monocytic CD45-positive cells, were also detected (asterisk in Figure 4E; see Kreuger et al, 2006). LYVE1-positive cells contained VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers, particularly in response to VEGFC, as shown using in situ PLA (Figure 4F; quantification in Figure 4G). The number of PLA signals/cell was lower in this analysis; this is in part likely due to that co-staining for LYVE1/CD31 together with PLA required additional washing steps and therefore, loss in sensitivity. However, the relationship between the different conditions (control, VEGFA, VEGFC) remained the same.
Tip cell filopodia assemble VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in response to VEGFA or VEGFC
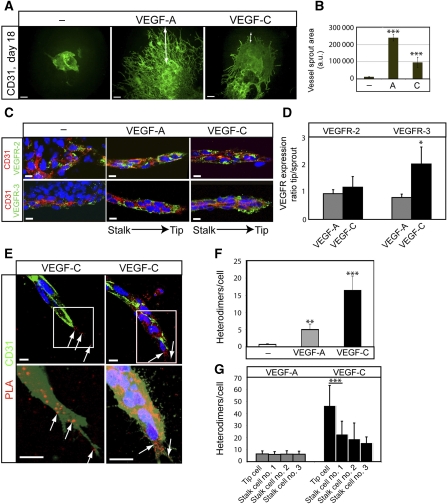
Next, the function of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in angiogenic sprouting was addressed. For this purpose, EBs were placed in a three-dimensional (3D) collagen I matrix that is permissive for the formation of high-quality angiogenic sprouts, shown to develop a complete basement membrane, to be luminized and covered by pericytes (Jakobsson et al, 2007; Jakobsson and Claesson-Welsh, 2008). As shown in Figure 5A, the 3D EB cultures treated with VEGFA displayed numerous sprouts extending from the core of the EB into the collagen I gel. Fewer and shorter sprouts were formed in cultures receiving VEGFC (see quantification in Figure 5B). Angiogenic sprouts were wrapped in a pericyte coat of NG2-positive cells both in VEGFA and VEGFC-treated cultures (Supplementary Figure S1).
Figure 5.
Heterodimers in angiogenic sprouts. (A) Angiogenic sprouting in response to VEGFA or VEGFC. EBs were cultured in 3D collagen matrix in the presence of VEGFA or VEGFC. Microphotographs were taken at day 18 on whole-mount fixed, CD31-immunostained samples. Scale bar=300 μm. (B) Quantification of total vascular area from the data in (A) based on five EBs per condition and expressed as fold induction ±s.d. (C) Expression of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 in angiogenic sprouts. Immunostaining for VEGFR2 (green; upper panels) and VEGFR3 (green; lower panels) on CD31-positive (red) angiogenic sprouts in 3D EBs treated with VEGFA or VEGFC. The orientation of the tip versus stalk is indicated. Scale bar=10 μm. (D) Quantification of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 expression in the tip cell region compared with entire angiogenic sprouts. n=4. (E) Location of heterodimers on VEGFC-induced angiogenic sprouts. Red spots represent PLA reactions in tip cells. Panels show PLA spots in CD31-positive angiogenic tip cell regions. Lower panels show saturation of CD31-positivity to better visualize the filopodia. Note that PLA spots are located on filopodia extending ahead of the tip cell. Scale bar=10 μm. (F) Quantification of in situ PLA detecting VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers in angiogenic sprouts in response to VEGFA or VEGFC in 3D EB cultures. n=8. (G) Quantification of heterodimers in tip and stalk cells. VEGFA-treated angiogenic sprouts contained heterodimers evenly distributed over the sprouts, whereas VEGFC-treated angiogenic sprouts showed accumulation of heterodimers in tip cells. n=8. Asterisks in panels B, D, F–G indicate degree of significance (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).
VEGFR2 expression was detected in CD31-positive endothelial cells throughout the angiogenic sprout to a similar extent in response to VEGFA and VEGFC (Figure 5C; quantification in Figure 5D). There was a tendency for reduced CD31 expression in the tip region of the sprout. VEGFR3 expression in CD31-positive cells was detected in both VEGFA and VEGFC-induced sprouts (Figure 5C). Interestingly, in the VEGFC-treated cultures, VEGFR3 expression was elevated in the tip region compared with the stalk region of the sprout (Figure 5D). In situ PLA signals representing VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization were detected in the 3D EB sprouts (Figure 5E; see quantification in Figure 5F). There was a low background in the untreated controls, and a similar relative degree of VEGFA- and VEGFC-induced heterodimerization as seen in monolayer cultures of HSaVECs and in 2D EBs. The heterodimer complexes were localized along the angiogenic sprouts both on the cell bodies and on the end of filopodia extending from the stalk and tip cells (Figure 5E, left). Note that the in situ PLA signals tended to coalesce into larger fluorescent clusters, indicating that the heterodimers were not evenly distributed over the plasma membrane. Heterodimers were more concentrated in the tip cells relative to the stalk cells (Figure 5E, right) in response to VEGFC, whereas VEGFA-treated sprouts displayed a more even heterodimer distribution (Figure 5G).
VEGFR3 blockade prevents heterodimer formation leading to reduced angiogenesis
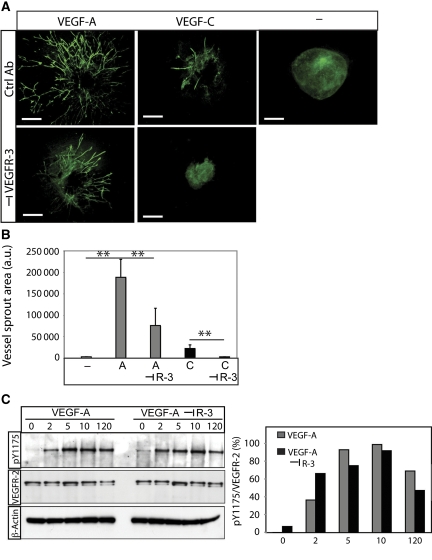
To study the function of heterodimerization in angiogenic sprouting, 3D EB cultures were treated with VEGFA in the presence and absence of neutralizing antibodies against mouse VEGFR3 (Pytowski et al, 2005) (Figure 6A; see quantification in Figure 6B). We avoided treating cultures with VEGFR2 neutralizing antibodies, as VEGFR2 is strictly required for differentiation of endothelial cells from precursor stages (Olsson et al, 2006). In accordance, we have shown earlier that VEGFR2 neutralization attenuates EB vascularization (Magnusson et al, 2004). The contribution of VEGFR2 to the different stages of endothelial cell development can therefore not readily be assessed by this approach.
Figure 6.
VEGFA-induced angiogenic sprouting is mediated by VEGFR2 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. (A) Effect of VEGFR3 neutralization. VEGFA- or VEGFC-induced EB cultures in 3D collagen were treated with or without antibodies neutralizing the function of VEGFR3. Scale bar=300 μm. (B) Quantification of sprouting area. Cultures treated with VEGFA or VEGFC in the absence or presence of neutralizing VEGFR3 antibodies as shown in panel (A) were quantified. n=5. Asterisks indicate degree of significance (**P<0.01). (C) Activation of VEGFR2. Immunoblotting for phosphorylated VEGFR2 (pY1175) from HSaVEC cultures treated with VEGFA in the presence and absence of neutralizing VEGFR3 antibodies, for different time periods (left panel). Middle panel shows blotting for VEGFR2 and lower panel shows equal loading of β-actin. Densitometric scanning (right panel) of bands showed no decrease in VEGFR2 activation by the VEGFR3 antibodies.
Figure 6A and B shows that VEGFA-induced angiogenic sprouting was significantly decreased by treatment with the VEGFR3-neutralizing antibody but not by a control IgG antibody. As shown in Figure 6C, the VEGFR3 neutralizing antibody did not block VEGFA-induced VEGFR2 phosphorylation. The transient increase in phosphorylated VEGFR2 level at the 2 min time point may be due to increased VEGFR2 homodimerization and more efficient phosphorylation under conditions when VEGFR3 is neutralized (compare VEGFR2 tyrosine phosphorylation in response to VEGFA and VEGFC in Figure 1B, middle panel). As VEGFA induces VEGFR2 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers but not VEGFR3 homodimers (Figure 3), these data indicate that the effect of the VEGFR3-neutralizing antibodies is to block formation of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. We thus conclude that VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization in this context serves to positively regulate sprouting angiogenesis.
Discussion
Molecular interactions such as dimerization of receptor tyrosine kinases are vital in cellular communication. We show herein that in situ PLA can successfully be used to detect native VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 homodimers as well as VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. Of note, detection of such native complexes cannot be done using co-immunoprecipitation methodology. In contrast to our recent in situ PLA study on epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor/Her2 homo- and heterodimerization, which occurs in the absence of ligand (Leuchowius et al, 2009), formation of VEGFR complexes was strictly ligand dependent. Using in situ PLA, we detected about 3–4-fold more heterocomplexes/cell in response to VEGFC as compared with VEGFA. The fold-induction of heterocomplexes compared with basal levels in unstimulated cells was about a 100-fold for VEGFC. The specificity of the methodology was validated (1) by the use of neutralizing anti-receptor antibodies, which block the ligand-binding site on the receptors; (2) by the use of an irrelevant ligand (PDGFB); and finally (3) by performing kinetic analyses that showed disappearance of the PLA spots with time, in conjunction with ligand-induced internalization of receptors.
Using in situ PLA, we made two novel and important discoveries concerning the composition of receptor complexes induced by VEGFA or VEGFC. First, VEGFC was able to induce formation of VEGFR3 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers, but not VEGFR2 homodimers. VEGFC has been shown to have the highest affinity for VEGFR3, but processed mouse VEGFC also binds to VEGFR2, although with lower affinity (Joukov et al, 1997) and theoretically, VEGFR2 homodimerization by VEGFC could therefore be anticipated. Indeed, VEGFC forms co-crystals with VEGFR2 immunoglobulin-like domains 2 and 3 (Leppänen et al, 2010). However, co-expression of VEGFR3 may block VEGFR2 homodimerization by VEGFC. Moreover, it is conceivable that the assembly and folding of the ligand-receptor complex is influenced by co-receptors such as neuropilins and proteoglycans. Thus, neuropilin2 has been shown to associate with VEGFR3 in a VEGFC-dependent manner (Karkkainen et al, 2001; Favier et al, 2006; Karpanen et al, 2006). The second important finding reported here is that VEGFA, which binds only to VEGFR2 and not to VEGFR3, induced VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers. In contrast, VEGFA did not induce co-immunoprecipitation of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 from monocultures of HSaVECs. A tendency for VEGFA-induced VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization was, however, detected by co-immunoprecipitation in the more complex 2D EB model (Figure 4B). VEGFA-induced heterodimeric complexes may be less stable than those induced by VEGFC as VEGFC binds directly to both VEGFR2 and VEGFR3, whereas VEGFA binds only to VEGFR2. Such loosely bonded heterodimers would more efficiently be detected by the PLA methodology, which does not require that complexes withstand the stress of detergent lysis and stringent wash protocols.
We used neutralizing antibodies to deduce the effects of the different VEGFR dimeric complexes in the EB model. VEGFR3-neutralizing antibodies, which bind to the ligand-binding site of VEGFR3 (Pytowski et al, 2005), blocked VEGFA-induced heterodimers although VEGFA fails to directly bind to VEGFR3. This indicates a scenario where dimerization is initiated by binding of ligand to one receptor molecule, rather than simultaneous bridging between two receptor molecules. Binding of ligand is likely to induce changes in the conformation of the extracellular domain, which in turn may trigger dimerization with the second receptor molecule. Binding of the neutralizing antibody to the second receptor molecule, in this case VEGFR3, may block dimerization either by steric hindrance or by locking the conformation of VEGFR3 in a state incompatible with dimerization. Interestingly, electron microscopical analysis of VEGFR2 homodimers show points of contacts between the receptor molecules involving Ig-like loop 7, which supports that receptor extracellular domain folding is modulated during the dimerization process (Ruch et al, 2007).
As it is likely that VEGFR3 neutralization of the VEGFA-induced sprouts was a result of blocking of heterodimers, we propose that both VEGFR2 homodimers and VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers contribute to angiogenic sprouting. As judged from the more modest response to VEGFC, compared with VEGFA, in angiogenic sprouting in the 3D EBs, VEGFR3 homodimers on the other hand may not contribute to sprouting. The extent of VEGFC-induced sprouting may very well be context dependent. We observed relatively efficient VEGFC-induced angiogenic sprouting compared with VEGFA, in adeno-associated virus-transduced muscle (Supplementary Figure S2). Overexpression of VEGFC in the mouse cornea, chorioallantoic membrane or mouse skin has previously been shown to induce blood vascular angiogenesis (Oh et al, 1997; Cao et al, 1998; Saaristo et al, 2002). Interestingly, VEGFC-induced blood vascular angiogenesis is negatively regulated by ongoing lymphangiogenesis and increases with increasing distance from the lymphangiogenic site (Benest et al, 2008). The extent of VEGFC-induced sprouting may be dependent on the concomitant production of VEGFA to drive essential aspects of vascular endothelial cell biology that VEGFC may complement but not replace. In vivo, simultaneous exposure of cells to VEGFA and VEGFC, in addition to many other growth modulatory factors, would be the expected scenario. In this context, it is interesting that EBs treated with a combination of VEGFA and VEGFC showed increased heterodimerization as detected by PLA, accompanied by a marked increase in vessel branching (Supplementary Figure S3). Ligand-dependent increase in commitment to the endothelial cells lineage and increased expression of receptors may contribute to this relative increase in receptor heterodimerization.
Our data agree excellently with those of Tammela et al (2008) who showed that VEGFR3 is upregulated during active angiogenesis and expressed on tip cells of angiogenic sprouts. Furthermore, there are previous indications in the literature that heterodimerization of VEGFRs may be of biological relevance. Goldman et al (2007) used receptor neutralizing antibodies to show cooperative signalling of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 in lymphatic migration and proliferation. VEGFR2 has been suggested to be required for VEGFC-induced differentiation of vascular progenitor cells (Suzuki et al, 2005). VEGFC, but not the VEGFR3-specific ligand VEGFC156S (Kirkin et al, 2001), induced differentiation of VEGFR3-expressing progenitors. On the other hand, Matsumura et al (2003) reported that VEGFR3 negatively regulates VEGFR2 in the maintenance of vascular integrity. We have previously shown that VEGFR3 heterodimerized to VEGFR2 does not become phosphorylated on two of its most C-terminal tyrosine phosphorylations sites (Dixelius et al, 2003). A similar scenario, with loss of specific tyrosine phosphorylation, may be true for VEGFR2 when dimerized with VEGFR3. However, as the VEGFC-induced VEGFR2 tyrosine phosphorylation is relatively weak (see Figure 1), it has not been technically feasible to determine VEGFR2 tyrosine phosphorylation pattern in response to VEGFC.
Taken together, it seems very likely that the molecular communication between VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 exerted via receptor heterodimerization is biologically relevant in angiogenesis and serves to modulate angiogenic sprouting. It is important to remember that receptor dimerization is guided not only by the growth factors but also by the availability of receptors whose expression levels may be highly plastic dependent on the physiological or pathological context. This is implied by our results using the 3D EB model (see Figure 5), where VEGFA-induced sprouts showed VEGFR3 expression throughout the length of the sprout. In contrast, VEGFC-induced sprouts showed higher expression of VEGFR3 and higher extent of VEGFR2/-3 heterodimerization in the tip. Therefore, the extent of heterodimerization is likely to vary with receptor expression level and be different during the various stages of the angiogenic process, and provide an additional avenue for cells to fine tune their responses to different VEGFs. Detailed studies on how homodimer versus heterodimer ratios impact proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation of endothelial cells will reveal the span of information that can be transmitted by VEGFA and VEGFC. It is for example an interesting possibility that signalling by VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers contribute to the early developmental function of VEGFR3 in vascular pruning (Dumont et al, 1998).
Materials and methods
Endothelial and ES cell culture
Primary human saphenous vein endothelial cells (HSaVECs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were purchased from Promocell (Heidelberg, Germany) and cultured on gelatin-coated dishes in endothelial cell basal medium supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and bullet kit (Promocell). Cells were used between passage 2 and 8. PAE cells overexpressing human VEGFR3 (PAE/VEGFR3) and wild-type controls were cultured on gelatin-coated dishes in F12 medium supplemented with 10% FBS (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA).
HSaVECs were treated with different growth factors as indicated. Typically, cells were seeded in eight-well chamber slides (5 × 104 per well), kept overnight in starvation medium and thereafter subjected to treatment for 8 min at 37°C, with the following human ligands: VEGFA121 (R&D), VEGFA165 (PeproTech), VEGFA145, VEGFA189 (both from Relia Tech GmbH, Braunschweig, Germany) all at 50 ng/ml. This concentration found to be close to saturating on a linear scale as determined by dose-response analyses (not shown). Effects were compared with those of VEGFC (in-house production), VEGFD (Vegenics Limited, Toorak, Australia), human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGFB; PeproTech), all given at 100 ng/ml. In some cases, pre-incubation on ice for 15 min with neutralizing antibodies against human VEGFR2 (IMC-1121b; 15 μg/ml; Zhu et al, 2003) or VEGFR3 (hF4-3C5; 15 μg/ml; Persaud et al, 2004) was performed.
The murine ES cell line R1 (Nagy et al, 1993) was routine cultured on a layer of mitomycin-C-arrested mouse embryonic fibroblasts in ES medium: DMEM-Glutamax supplemented with 15% FBS, 25 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 1.2 mM sodium pyruvate, 0.12% monothiolglycerol and 1000 U/ml recombinant leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF; Chemicon International, Temecula, CA) and passaged every second day. All medium components, except LIF, were from Invitrogen.
Differentiation of ES cells in 2D or 3D cultures were done essentially as described (Li et al, 2008). Briefly, on day 0, ES cells were resuspended in ES medium without LIF to induce differentiation. Cells were then aggregated in drops (1200 cells/drop) hanging from the lid of a non-adherent culture dish to form EBs. After 4 days, EBs were collected and seeded out individually on eight-well chamber glass slides (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ) for immunostaining or for proximity ligation, or in groups on 60 mm cell culture dishes for immunoprecipitation (ip) and western blot analyses. To score for 3D angiogenic sprouting, day 4 EBs were seeded into 12-well dishes, in groups of 8–10, on a layer of 0.6 ml of solidified collagen type I solution (Ham's F12 medium [Invitrogen], 5 mM NaOH, 20 mM HEPES, 0.117% NaHCO3, 1% Glutamax-1 [Invitrogen] and 1.5 mg/ml collagen type I (Cohesion Technologies Inc, Palo Alto, CA)). Immediately thereafter, a second layer of collagen solution was added on top. After 3 h, 1.2 ml of medium with or without indicated growth factors was added. EBs were maintained under normal growth conditions or supplemented with human VEGFA (50 ng/ml PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ), or human, processed VEGFC (100 ng/ml; produced in-house). When indicated, neutralizing anti-mouse VEGFR3 (31C1, 15 μg/ml; Pytowski et al, 2005) or isotype-matched control (15 μg/ml; Southern Biotech; Birmingham, AL) were added to the cultures.
Co-immunoprecipitation assay
Cultures grown in 60 mm dishes (5 × 105/dish), treated or not with growth factors and neutralizing antibodies as indicated, were lysed in Nonidet P-40 (NP-40) lysis buffer: 50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM PMSF, 5 μg/ml aprotinin, 5 μg/ml leupeptin, 100 μM Na3VO4, and 1% NP-40. Lysates were cleared by centrifugation and incubated on ice for 2 h with 1 μg of VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 antibodies. For immunoprecipitation of VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 from human cells (e.g. HSaVEC), sc505 or sc321 antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, Santa Cruz, CA) were used. The corresponding antibodies used for mouse cells (e.g. EBs) were AF644 for VEGFR2 or AF743 for VEGFR3 (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). Immunoprecipitates were collected using Protein G Sepharose and subjected to SDS–PAGE, followed by transfer to Hybond-C extra membranes (Amersham Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden). Membranes were incubated with antibodies directed against VEGFR2, VEGFR3 or phosphotyrosine (clone 4G10; Upstate Biotechnology Inc, Lake Placid, NY), followed by horse-radish perioxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Amersham Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden). In parallel, total cell lysates were analysed by immunoblotting for VEGFR2 phosphorylation (pY1175; Cell Signaling Technology Inc, Beverly MA) and β-actin content (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Immune reactivity was visualized using the enhanced chemiluminescence plus detection system (Amersham Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden). Assays were repeated three times and representative results are shown.
Immunofluorescent staining of EBs
EB cultures were washed twice in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. After permeabilization in 0.1% Triton X-100 and block with TNB (PerkinElmer Life Science) or Tris-buffered saline complemented with 3% bovine serum albumin and 0.1% Tween 20, antibodies against CD31, LYVE1, NG2 (Chemicon), VE-cadherin (R&D Systems), VEGFR2 (AF644) or VEGFR3 (sc321 or AF7431; R&D Systems) were applied. All samples were treated with Hoechst 33342 to visualize nuclei. Stained EBs were mounted on glass slides in Fluoromount-G (Southern Biotechnology, Birmingham, AL) and analysed by a Nikon Eclipse E1000 microscope with a Nikon Eclipse DXM 1200 camera (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) or an LSM 510 META confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
Quantification of CD31-positive vascular area was done on × 4 objective micrographs using the Easy Image Analysis 2000 software (Tekno Optik, Huddinge, Sweden). Five-10 EBs per condition were examined and the results are shown in arbitrary units±s.d. Quantification of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 expression along vascular sprouts in 3D EBs was performed on four EBs per condition and repeated three independent times.
in situ proximity ligation assay (in situ PLA)
Cultures, treated as indicated, were immediately fixed in 4% PFA on ice for 30 min and thereafter subjected to in situ PLA using Duolink Detection kit (Olink Bioscience, Uppsala, Sweden) according to the manufacturer's instructions for Duolink Blocking solution and Detection protocol. Briefly, slides were blocked, incubated with antibodies directed against VEGFR2 (sc-6251) and VEGFR3 (sc321; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and thereafter incubated with PLA probes, which are secondary antibodies (anti-mouse and anti-rabbit) conjugated to unique oligonucleotides. Note that different commercial batches of secondary antibodies varied slightly in their capacity to detect VEGFR2/-3 heterodimers so that the absolute but not relative numbers of receptor complexes were different (see Figure 2C compared with Figure 2E).
When indicated, primary antibodies were converted to PLA probes by conjugation to 5′thiolated oligonucleotides as described earlier (Soderberg et al, 2006). Briefly, 50 μg monoclonal antibody (anti-VEGFR2, sc-6251 from Santa Cruz or anti-VEGFR3, MAB743 from R&D) were treated with 30-fold excess of sulfo-SMCC (sulfosuccinimidyl 4-[N-maleimidomethyl]cyclohexane-1-carboxylate), Pierce Biotechnology (Rockford, Il). Unreacted sulfo-SMCC was removed by gel filtration. Freshly reduced thiolated oligonucleotides were added at a ratio of 1:4 (antibody:oligonucleotide) and coupled overnight. The PLA probes were then purified by gel filtration, removing unreacted antibodies and oligonucleotides.
Circularization and ligation of the oligonucleotides was followed by an amplification step. The products were detected by a complementary fluorescently labelled probe. Slides were mounted using Vectashield (Vector Laboratories Inc, Burlingame, CA) and evaluated using an LSM 510 META confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss). Z-stack micrographs taken with the 40 × /63 × objectives were obtained. The number of heterodimers, visualized as bright fluorescent signals, was counted in 10–15 fields/well. n (number of wells) =6 for HSaVEC analyses, and n (number of individual EBs) =8 for EB analyses. Representative results are shown from experiments repeated at least three times. Cell images obtained were exported using the AxioVision software (Carl Zeiss) in TIF format for further analysis and determination of heterodimers/cell in Blob-Finder image analysis software (Version 2.5), which has been developed by the Centre for Image Analysis, Uppsala University. Quantifications are given as mean+s.d.
Statistical evaluation
Statistical analyses were performed using Student t-test and P-values <0.05 were considered significant. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants to Lena Claesson-Welsh from the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Swedish Research Council and the EU frame work program Lymphangiogenomics, LSHG.CT2004-503573. Ola Söderberg was supported by grants from the Wallenberg Foundation, by the EU FP6 project ‘ENLIGHT', and by the Swedish Cancer Foundation. Johan Kreuger was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research.
Footnotes
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Adams RH, Alitalo K (2007) Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 464–478 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV (2005) Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 438: 946–953 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin ME, Catimel B, Nice EC, Roufail S, Hall NE, Stenvers KL, Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K, Stacker SA, Achen MG (2001) The specificity of receptor binding by vascular endothelial growth factor-d is different in mouse and man. J Biol Chem 276: 19166–19171 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benest AV, Harper SJ, Herttuala SY, Alitalo K, Bates DO (2008) VEGF-C induced angiogenesis preferentially occurs at a distance from lymphangiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 78: 315–323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y, Linden P, Farnebo J, Cao R, Eriksson A, Kumar V, Qi JH, Claesson-Welsh L, Alitalo K (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 14389–14394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixelius J, Makinen T, Wirzenius M, Karkkainen MJ, Wernstedt C, Alitalo K, Claesson-Welsh L (2003) Ligand-induced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) heterodimerization with VEGFR-2 in primary lymphatic endothelial cells regulates tyrosine phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem 278: 40973–40979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont DJ, Jussila L, Taipale J, Lymboussaki A, Mustonen T, Pajusola K, Breitman M, Alitalo K (1998) Cardiovascular failure in mouse embryos deficient in VEGF receptor-3. Science 282: 946–949 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esko JD, Selleck SB (2002) Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu Rev Biochem 71: 435–471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favier B, Alam A, Barron P, Bonnin J, Laboudie P, Fons P, Mandron M, Herault JP, Neufeld G, Savi P, Herbert JM, Bono F (2006) Neuropilin-2 interacts with VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 and promotes human endothelial cell survival and migration. Blood 108: 1243–1250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M, Breitman ML (1995) Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376: 66–70 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong GH, Zhang L, Bryce DM, Peng J (1999) Increased hemangioblast commitment, not vascular disorganization, is the primary defect in flt-1 knock-out mice. Development 126: 3015–3025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geretti E, Shimizu A, Klagsbrun M (2008) Neuropilin structure governs VEGF and semaphorin binding and regulates angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 11: 31–39 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J, Rutkowski JM, Shields JD, Pasquier MC, Cui Y, Schmokel HG, Willey S, Hicklin DJ, Pytowski B, Swartz MA (2007) Cooperative and redundant roles of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 signaling in adult lymphangiogenesis. FASEB J 21: 1003–1012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard SR (1999) Structural analysis of receptor tyrosine kinases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 71: 343–358 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson L, Claesson-Welsh L (2008) Vascular basement membrane components in angiogenesis—an act of balance. Scientific World J 8: 1246–1249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson L, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2007) Building blood vessels—stem cell models in vascular biology. J Cell Biol 177: 751–755 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvius M, Paulsson J, Weibrecht I, Leuchowius KJ, Andersson AC, Wahlby C, Gullberg M, Botling J, Sjoblom T, Markova B, Ostman A, Landegren U, Soderberg O (2007) In situ detection of phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta using a generalized proximity ligation method. Mol Cell Proteomics 6: 1500–1509 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joukov V, Sorsa T, Kumar V, Jeltsch M, Claesson-Welsh L, Cao Y, Saksela O, Kalkkinen N, Alitalo K (1997) Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity of VEGF-C. EMBO J 16: 3898–3911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkkainen MJ, Saaristo A, Jussila L, Karila KA, Lawrence EC, Pajusola K, Bueler H, Eichmann A, Kauppinen R, Kettunen MI, Yla-Herttuala S, Finegold DN, Ferrell RE, Alitalo K (2001) A model for gene therapy of human hereditary lymphedema. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 12677–12682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpanen T, Heckman CA, Keskitalo S, Jeltsch M, Ollila H, Neufeld G, Tamagnone L, Alitalo K (2006) Functional interaction of VEGF-C and VEGF-D with neuropilin receptors. FASEB J 20: 1462–1472 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura H, Li X, Harper SJ, Bates DO, Claesson-Welsh L (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A165b is a weak in vitro agonist for VEGF receptor-2 due to lack of coreceptor binding and deficient regulation of kinase activity. Cancer Res 68: 4683–4692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkin V, Mazitschek R, Krishnan J, Steffen A, Waltenberger J, Pepper MS, Giannis A, Sleeman JP (2001) Characterization of indolinones which preferentially inhibit VEGF-C- and VEGF-D-induced activation of VEGFR-3 rather than VEGFR-2. Eur J Biochem 268: 5530–5540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuger J, Nilsson I, Kerjaschki D, Petrova T, Alitalo K, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) Early lymph vessel development from embryonic stem cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26: 1073–1078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppänen VM, Prota AE, Jeltsch M, Anisimov A, Kalkkinen N, Strandin T, Lankinen H, Goldman A, Ballmer-Hofer K, Alitalo K (2010) Structural determinants of growth factor binding and specificity by VEGF receptor-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107: 2425–2430 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuchowius KJ, Weibrecht I, Landegren U, Gedda L, Soderberg O (2009) Flow cytometric in situ proximity ligation analyses of protein interactions and post-translational modification of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. Cytometry A 75: 833–839 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X, Claesson-Welsh L, Shibuya M (2008) VEGF receptor signal transduction. Methods Enzymol 443: 261–284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson P, Rolny C, Jakobsson L, Wikner C, Wu Y, Hicklin DJ, Claesson-Welsh L (2004) Deregulation of Flk-1/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in fibroblast growth factor receptor-1-deficient vascular stem cell development. J Cell Sci 117 (Part 8): 1513–1523 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura K, Hirashima M, Ogawa M, Kubo H, Hisatsune H, Kondo N, Nishikawa S, Chiba T (2003) Modulation of VEGFR-2-mediated endothelial-cell activity by VEGF-C/VEGFR-3. Blood 101: 1367–1374 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A, Rossant J, Nagy R, Abramow-Newerly W, Roder JC (1993) Derivation of completely cell culture-derived mice from early-passage embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8424–8428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh SJ, Jeltsch MM, Birkenhager R, McCarthy JE, Weich HA, Christ B, Alitalo K, Wilting J (1997) VEGF and VEGF-C: specific induction of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the differentiated avian chorioallantoic membrane. Dev Biol 188: 96–109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 359–371 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajusola K, Aprelikova O, Pelicci G, Weich H, Claesson-Welsh L, Alitalo K (1994) Signalling properties of FLT4, a proteolytically processed receptor tyrosine kinase related to two VEGF receptors. Oncogene 9: 3545–3555 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persaud K, Tille JC, Liu M, Zhu Z, Jimenez X, Pereira DS, Miao HQ, Brennan LA, Witte L, Pepper MS, Pytowski B (2004) Involvement of the VEGF receptor 3 in tubular morphogenesis demonstrated with a human anti-human VEGFR-3 monoclonal antibody that antagonizes receptor activation by VEGF-C. J Cell Sci 117 (Part 13): 2745–2756 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrova TV, Makinen T, Makela TP, Saarela J, Virtanen I, Ferrell RE, Finegold DN, Kerjaschki D, Yla-Herttuala S, Alitalo K (2002) Lymphatic endothelial reprogramming of vascular endothelial cells by the Prox-1 homeobox transcription factor. EMBO J 21: 4593–4599 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytowski B, Goldman J, Persaud K, Wu Y, Witte L, Hicklin DJ, Skobe M, Boardman KC, Swartz MA (2005) Complete and specific inhibition of adult lymphatic regeneration by a novel VEGFR-3 neutralizing antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 97: 14–21 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruch C, Skiniotis G, Steinmetz MO, Walz T, Ballmer-Hofer K (2007) Structure of a VEGF-VEGF receptor complex determined by electron microscopy. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14: 249–250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saaristo A, Veikkola T, Enholm B, Hytonen M, Arola J, Pajusola K, Turunen P, Jeltsch M, Karkkainen MJ, Kerjaschki D, Bueler H, Yla-Herttuala S, Alitalo K (2002) Adenoviral VEGF-C overexpression induces blood vessel enlargement, tortuosity, and leakiness but no sprouting angiogenesis in the skin or mucous membranes. FASEB J 16: 1041–1049 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby F, Rossant J, Yamaguchi TP, Gertsenstein M, Wu XF, Breitman ML, Schuh AC (1995) Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376: 62–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderberg O, Gullberg M, Jarvius M, Ridderstrale K, Leuchowius KJ, Jarvius J, Wester K, Hydbring P, Bahram F, Larsson LG, Landegren U (2006) Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nat Methods 3: 995–1000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H, Watabe T, Kato M, Miyazawa K, Miyazono K (2005) Roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling in differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived vascular progenitor cells into endothelial cells. Blood 105: 2372–2379 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tammela T, Zarkada G, Wallgard E, Murtomaki A, Suchting S, Wirzenius M, Waltari M, Hellstrom M, Schomber T, Peltonen R, Freitas C, Duarte A, Isoniemi H, Laakkonen P, Christofori G, Yla-Herttuala S, Shibuya M, Pytowski B, Eichmann A, Betsholtz C et al. (2008) Blocking VEGFR-3 suppresses angiogenic sprouting and vascular network formation. Nature 454: 656–660 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Hattori K, Zhang H, Jimenez X, Ludwig DL, Dias S, Kussie P, Koo H, Kim HJ, Lu D, Liu M, Tejada R, Friedrich M, Bohlen P, Witte L, Rafii S (2003) Inhibition of human leukemia in an animal model with human antibodies directed against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Correlation between antibody affinity and biological activity. Leukemia 17: 604–611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.