Abstract
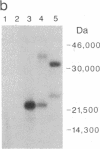
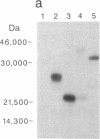
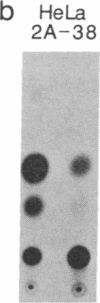
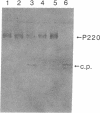
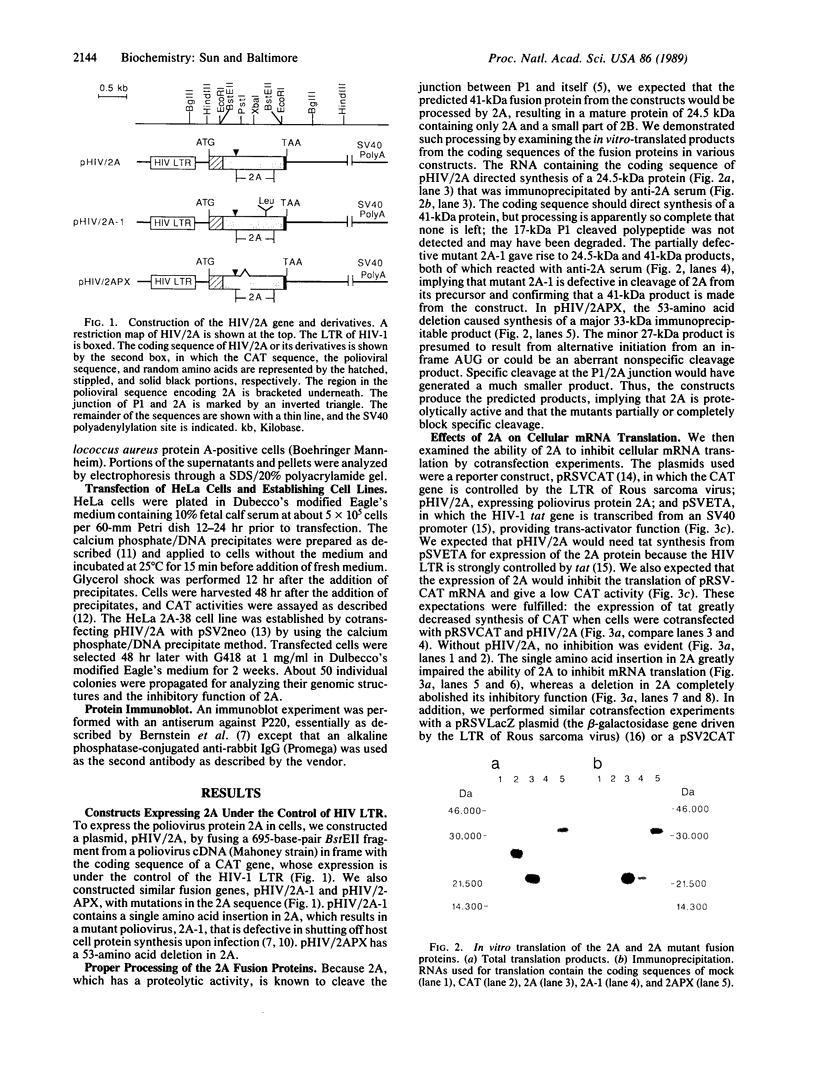
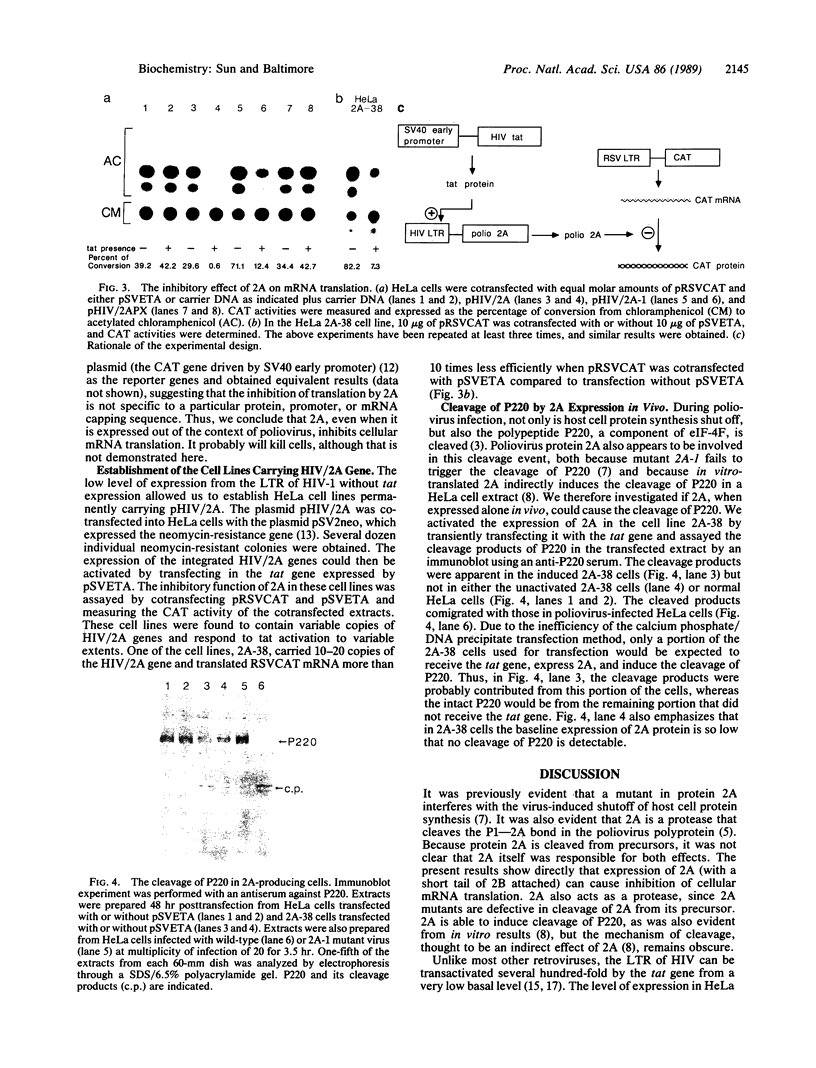
To study the effect of poliovirus protein 2A on cellular RNA translation, the tat control system of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was used. Protein 2A was expressed from a plasmid construct (pHIV/2A) incorporating the HIV long terminal repeat. Protein synthesis was measured by using chloramphenicol acetyltransferase as a reporter gene driven by the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. When HIV/2A was cotransfected with the reporter, addition of a tat-producing plasmid caused at least a 50-fold drop in chloramphenicol acetyltransferase synthesis. A HeLa cell line carrying HIV/2A was established. In it, tat expression caused more than a 10-fold drop in chloramphenicol acetyltransferase synthesis from the reporter plasmid. Furthermore, 2A induction by tat caused cleavage of the cellular translation factor P220, a part of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F. Thus protein 2A can, by itself, carry out the inhibition of cellular protein synthesis characteristic of a poliovirus infection. Also, the HIV tat activation provides a very effective method to control gene expression in mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein H. D., Sarnow P., Baltimore D. Genetic complementation among poliovirus mutants derived from an infectious cDNA clone. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1040–1049. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1040-1049.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Milburn S. C., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Hershey J. W. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis following poliovirus infection correlates with the proteolysis of a 220,000-dalton polypeptide associated with eucaryotic initiation factor 3 and a cap binding protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14806–14810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. mRNA cap binding proteins: essential factors for initiating translation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Arya S., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type III long terminal repeat. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.2981427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Lis J. T., Wu R. The positive and negative transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila Gapdh-2 gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):743–753. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]