Abstract
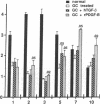
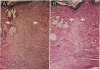
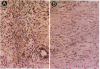
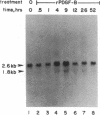
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) and the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) are potent mitogenic polypeptides which enhance rates of wound healing in experimental animals; in contrast, glucocorticoids inhibit wound repair. The potential of TGF-beta and PDGF to reverse this inhibition in healing was tested in methylprednisolone-treated rats with deficits in skin wound strength of 50%. Single applications of TGF-beta (10-40 pmol per wound, 0.25-1 micrograms) applied locally at the time of wounding fully reversed this deficit in a concentration-dependent and highly reproducible manner. Wounds in glucocorticoid-treated animals were characterized by a near total absence of neutrophils and macrophages and by a delayed influx and reduced density of fibroblasts; however, such wounds treated with TGF-beta showed significant increases in wound fibroblasts and in intracellular procollagen type I. PDGF did not reverse the deficit in wound breaking strength in glucocorticoid-treated rats; there were more fibroblasts in the PDGF-treated wounds, but these fibroblasts lacked the enhanced expression of procollagen type I found in TGF-beta-treated wounds. The wound macrophages, required for normal tissue repair, remained absent from both PDGF- and TGF-beta-treated wounds in glucocorticoid-treated animals. This result suggested that macrophages might normally act as an intermediate in the induction of procollagen synthesis in fibroblasts of PDGF-treated wounds and that TGF-beta might bypass the macrophage through its capacity to stimulate directly new synthesis of procollagen type I in fibroblasts. Whereas PDGF does not stimulate procollagen synthesis, in a rodent macrophage cell line, PDGF induced a highly significant, time-dependent enhancement of expression of TGF-beta.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assoian R. K., Fleurdelys B. E., Stevenson H. C., Miller P. J., Madtes D. K., Raines E. W., Ross R., Sporn M. B. Expression and secretion of type beta transforming growth factor by activated human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6020–6024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Cooper T. W., Huang J. S., Altman J., Deuel T. F. Stimulation of in vitro human skin collagenase expression by platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. K., Hoshi H., McKeehan W. L. Transforming growth factor type beta specifically stimulates synthesis of proteoglycan in human adult arterial smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5287–5291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. L., Rifas L., Shen V., Tong B., Pierce G., Deuel T., Peck W. A. J774A.1 macrophage cell line produces PDGF-like and non-PDGF-like growth factors for bone cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1987 Oct;2(5):467–474. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650020515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Goeddel D. V. The murine transforming growth factor-beta precursor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4377–4379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Huang J. S., Griffin G. L. Chemotaxis of monocytes and neutrophils to platelet-derived growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1046–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Tarver H. Effects of beta-carotene, vitamin A, and glucocorticoids on collagen synthesis in wounds. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Jul;137(3):936–938. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. P., Tarver H., Hunt T. K. Effects of vitamin A and glucocorticoids upon inflammation and collagen synthesis. Ann Surg. 1973 Feb;177(2):222–227. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197302000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Pencev D., Sodek J., Harvey A. K. Stimulation of granulation tissue formation by platelet-derived growth factor in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2323–2329. doi: 10.1172/JCI112243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. K., Knighton D. R., Thakral K. K., Goodson W. H., 3rd, Andrews W. S. Studies on inflammation and wound healing: angiogenesis and collagen synthesis stimulated in vivo by resident and activated wound macrophages. Surgery. 1984 Jul;96(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor J. A., Turner P. H., Nienhuis A. W. Beta Thalassemia: mutations which affect processing of the beta-Globin mRNA precursor. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90122-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence W. T., Norton J. A., Sporn M. B., Gorschboth C., Grotendorst G. R. The reversal of an Adriamycin induced healing impairment with chemoattractants and growth factors. Ann Surg. 1986 Feb;203(2):142–147. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198602000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibovich S. J., Ross R. The role of the macrophage in wound repair. A study with hydrocortisone and antimacrophage serum. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):71–100. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. W., Peacock E. E., Jr Studies on the biology of collagen during wound healing. I. Rate of collagen synthesis and deposition in cutaneous wounds of the rat. Surgery. 1968 Jul;64(1):288–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Whitehouse L. A., Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Crouch E. C., Stenmark K. R., Voelkel N. F. Smooth muscle-mediated connective tissue remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3603030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustoe T. A., Pierce G. F., Thomason A., Gramates P., Sporn M. B., Deuel T. F. Accelerated healing of incisional wounds in rats induced by transforming growth factor-beta. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1333–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2442813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson Y., Hammacher A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Possible positive autocrine feedback in the prereplicative phase of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):715–717. doi: 10.1038/328715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Kobayashi S., Bornstein P. Transforming growth factor beta increases mRNA for matrix proteins both in the presence and in the absence of changes in mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1105–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Mustoe T. A., Senior R. M., Reed J., Griffin G. L., Thomason A., Deuel T. F. In vivo incisional wound healing augmented by platelet-derived growth factor and recombinant c-sis gene homodimeric proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):974–987. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Stimulation of the chemotactic migration of human fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):251–256. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Gossage D., Kang A. H. Pretranslational regulation of type I collagen, fibronectin, and a 50-kilodalton noncollagenous extracellular protein by dexamethasone in rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4677–4684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Transforming growth factor-beta increases steady state levels of type I procollagen and fibronectin messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1285–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Huang J. S., Walz D. A., Deuel T. F. Chemotactic activity of platelet alpha granule proteins for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):382–385. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppä H., Grotendorst G., Seppä S., Schiffmann E., Martin G. R. Platelet-derived growth factor in chemotactic for fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):584–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull S., Cutroneo K. R. Glucocorticoids coordinately regulate procollagens type I and type III synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3364–3369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng D. Y., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Baehner R. L. Platelet-derived growth factor promotes human peripheral monocyte activation. Blood. 1985 Jul;66(1):179–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng D. Y., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Senior R. M., Boxer L. A., Baehner R. L. Platelet-derived growth factor promotes polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1123–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl S. M., Hunt D. A., Wakefield L. M., McCartney-Francis N., Wahl L. M., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor type beta induces monocyte chemotaxis and growth factor production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]