Abstract
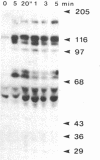
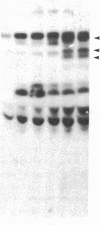
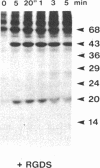
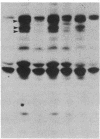
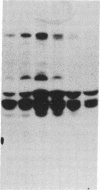
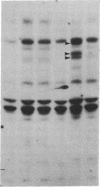
We have previously shown that a number of platelet proteins become phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in response to platelet-activating agents. Here we present two lines of evidence implicating a platelet integrin, glycoprotein IIb-IIIa, in the regulation of a specific subset of these tyrosine phosphorylations. (i) Two peptides that inhibit the binding of fibrinogen and other ligands to gpIIb-IIIa, Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser and His-His-Leu-Gly-Gly-Ala-Lys-Gln-Ala-Gly-Asp-Val, also inhibited the thrombin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of this subset of proteins. The tetrapeptide Arg-Gly-Glu-Ser, which does not inhibit fibrinogen binding, did not inhibit thrombin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation. (ii) Platelets lacking gpIIb-IIIa (from a subject with Glanzmann thrombasthenia) did not undergo this subset of tyrosine phosphorylation in response to thrombin, although other serine, threonine, and tyrosine phosphorylations proceeded normally. These findings suggest a role for tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation in integrin-mediated cell-matrix recognition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basler K., Hafen E. Control of photoreceptor cell fate by the sevenless protein requires a functional tyrosine kinase domain. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr J. G., Dreyfuss G., Penman S., Buchanan J. M. Association of the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus with cytoskeletal structures of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3484–3488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Peerschke E. I., Scudder L. E., Sullivan C. A. A murine monoclonal antibody that completely blocks the binding of fibrinogen to platelets produces a thrombasthenic-like state in normal platelets and binds to glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):325–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI110973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Charo I. F., Phillips D. R. Human and bovine endothelial cells synthesize membrane proteins similar to human platelet glycoproteins IIb and IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10893–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Lo S. S., Phillips D. R. Protein sequence of endothelial glycoprotein IIIa derived from a cDNA clone. Identity with platelet glycoprotein IIIa and similarity to "integrin". J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3936–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Reynolds C. C., Phillips D. R. Calcium-dependent proteolysis occurs during platelet aggregation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9973–9981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. E., Rohrschneider L. R. Common features of the yes and src gene products defined by peptide-specific antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.539-546.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. Association of p60src with Triton X-100-resistant cellular structure correlates with morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2312–2316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harfenist E. J., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Effects of the cell adhesion peptide, Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser, on responses of washed platelets from humans, rabbits, and rats. Blood. 1988 Jan;71(1):132–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Cowan J. F., Yamada K. M., Santoro S. A. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor substrates by a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Crouse C., Takada Y., Sonnenberg A. Multiple very late antigen (VLA) heterodimers on platelets. Evidence for distinct VLA-2, VLA-5 (fibronectin receptor), and VLA-6 structures. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7660–7665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R., Horwitz A., Buck C., Rohrschneider L. Phosphorylation of the fibronectin receptor complex in cells transformed by oncogenes that encode tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg W. M., McEver R. P., Phillips D. R., Shuman M. A., Bainton D. F. The platelet fibrinogen receptor: an immunogold-surface replica study of agonist-induced ligand binding and receptor clustering. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1655–1663. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunicki T. J., Nugent D. J., Staats S. J., Orchekowski R. P., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G. The human fibroblast class II extracellular matrix receptor mediates platelet adhesion to collagen and is identical to the platelet glycoprotein Ia-IIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4516–4519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Wasenius V. M., Salvén P., Saraste M. Transforming and membrane proteins. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):388–388. doi: 10.1038/334388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A., Pasquale E. B., Wang J. Y., Singer S. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins are concentrated in focal adhesions and intercellular junctions in normal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6576–6580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parise L. V., Phillips D. R. Reconstitution of the purified platelet fibrinogen receptor. Fibrinogen binding properties of the glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10698–10707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowicz R. S., Orchekowski R. P., Nugent D. J., Yamada K. Y., Kunicki T. J. Glycoprotein Ic-IIa functions as an activation-independent fibronectin receptor on human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1359–1364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Specific and saturable binding of plasma fibronectin to thrombin-stimulated human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9477–9482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Srouji A. H., Meyer D., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Evidence that three adhesive proteins interact with a common recognition site on activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5388–5391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Eisman R., Heidenreich R., Silver S. M., Vilaire G., Surrey S., Schwartz E., Bennett J. S. Structure of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb. Homology to the alpha subunits of the vitronectin and fibronectin membrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8476–8482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Ruoslahti E. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa: member of a family of Arg-Gly-Asp--specific adhesion receptors. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.2420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R., Najita L. M. Detection of the v-abl gene product at cell-substratum contact sites in Abelson murine leukemia virus-transformed fibroblasts. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):547–552. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.547-552.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Modderman P. W., Hogervorst F. Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):487–489. doi: 10.1038/336487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyers M., Rachubinski R. A., Stewart M. I., Varrichio A. M., Shorr R. G., Haslam R. J., Harley C. B. Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):470–473. doi: 10.1038/333470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigo C. Effect of C-reactive protein on platelet-activating factor-induced platelet aggregation and membrane stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3418–3422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. W., Tallant E. A., McManus M. C. Human platelet calmodulin-binding proteins: identification and Ca2+-dependent proteolysis upon platelet activation. Biochemistry. 1987 May 19;26(10):2766–2773. doi: 10.1021/bi00384a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]