Abstract
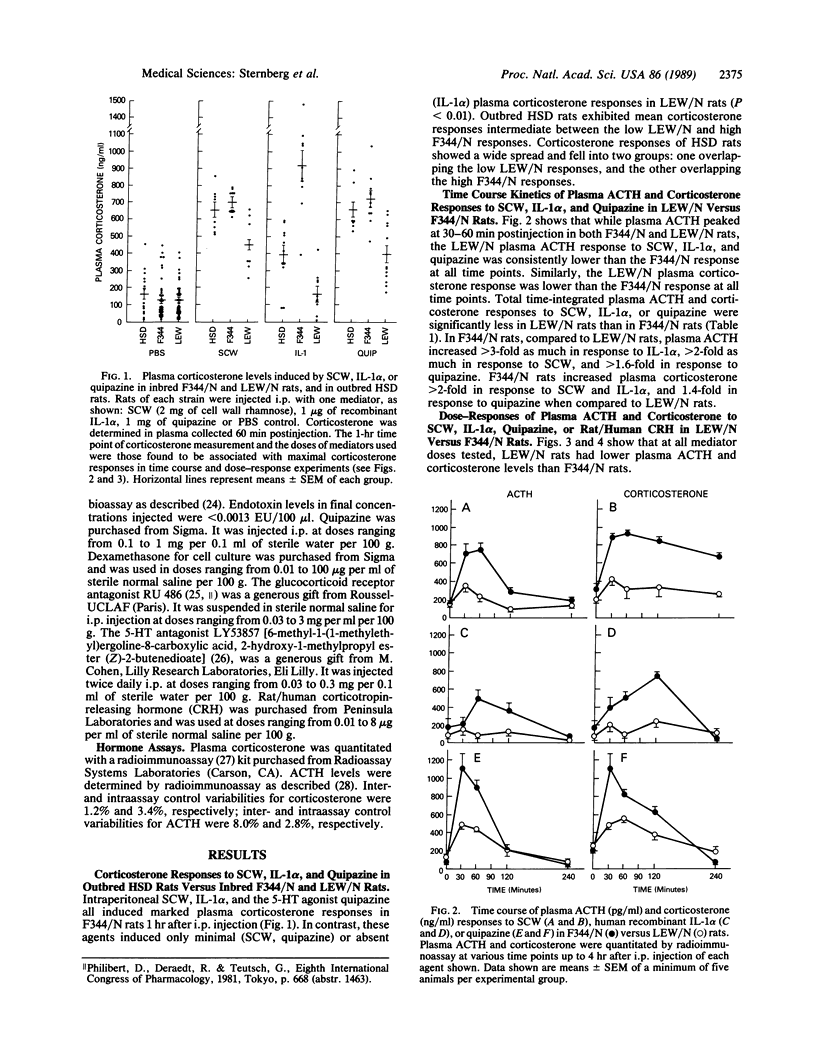
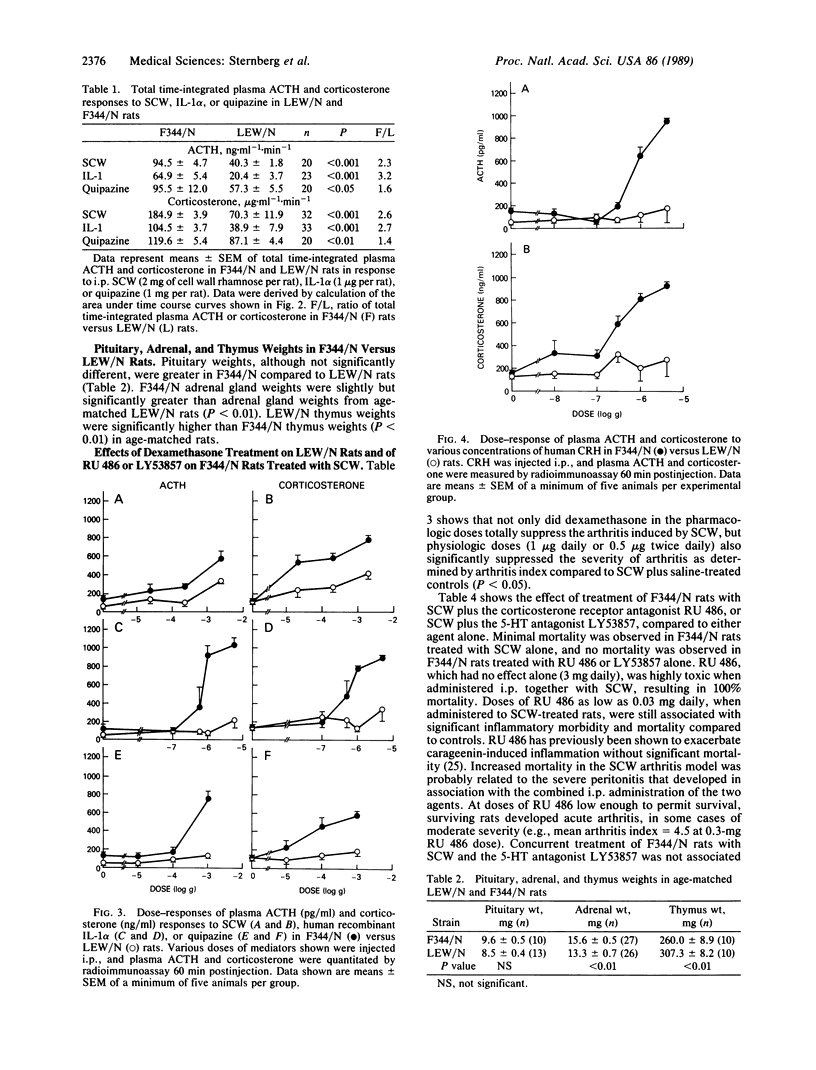
Inbred Lewis (LEW/N) female rats develop an arthritis in response to group A streptococcal cell wall peptidoglycan polysaccharide (SCW), which mimics human rheumatoid arthritis. Histocompatible Fischer (F344/N) rats do not develop arthritis in response to the same SCW stimulus. To evaluate this difference in inflammatory reactivity, we examined the function of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and its ability to modulate the development of the inflammatory response in LEW/N and F344/N rats. We have found that, in contrast to F344/N rats, LEW/N rats had markedly impaired plasma corticotropin and corticosterone responses to SCW, recombinant human interleukin 1 alpha, the serotonin agonist quipazine, and synthetic rat/human corticotropin-releasing hormone. LEW/N rats also had smaller adrenal glands and larger thymuses. Replacement doses of dexamethasone decreased the severity of LEW/N rats' SCW-induced arthritis. Conversely, treatment of F344/N rats with the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist RU 486 or the serotonin antagonist LY53857 was associated with development of severe inflammatory disease, including arthritis, in response to SCW. These findings support the concept that susceptibility of LEW/N rats to SCW arthritis is related to defective HPA axis responsiveness to inflammatory and other stress mediators and that resistance of F344/N rats to SCW arthritis is regulated by an intact HPA axis-immune system feedback loop.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Wilder R. L. Variable severity and Ia antigen expression in streptococcal-cell-wall-induced hepatic granulomas in rats. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):674–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.674-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beraud E., Reshef T., Vandenbark A. A., Offner H., Friz R., Chou C. H., Bernard D., Cohen I. R. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by T lymphocyte lines: genotype of antigen-presenting cells influences immunodominant epitope of basic protein. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):511–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenbosch F., van Oers J., del Rey A., Tilders F., Besedovsky H. Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2443979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Beach J. E., Holaday J. W., Smallridge R. C., Fein H. G. Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2821620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspi R. R., Roberge F. G., McAllister C. G., el-Saied M., Kuwabara T., Gery I., Hanna E., Nussenblatt R. B. T cell lines mediating experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in the rat. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A., Hall T. R., Harvey S. Serotoninergic regulation of corticosterone secretion in domestic fowl. J Endocrinol. 1987 May;113(2):159–165. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1130159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Cutler G. B., Jr, Sauer M., Simons S. S., Jr, Loriaux D. L. Development of glucocorticoid antagonists. Pharmacol Ther. 1983;20(2):263–281. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(83)90041-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Schulte H. M., Oldfield E. H., Gold P. W., Cutler G. B., Jr, Loriaux D. L. The corticotropin-releasing factor stimulation test. An aid in the evaluation of patients with Cushing's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. L., Fuller R. W., Kurz K. D. LY53857, a selective and potent serotonergic (5-HT2) receptor antagonist, does not lower blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Nov;227(2):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupps T. R., Fauci A. S. Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:133–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Thorp R. B., Maddox P. A., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in F344 and LEW rats: evolution of lesions and lung lymphoid cell populations. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):720–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.720-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Kilian P. L., Ruff M. R., Hill J. M., Pert C. B. Visualization and characterization of interleukin 1 receptors in brain. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):459–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W. Serotonergic stimulation of pituitary-adrenocortical function in rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1981 Feb;32(2):118–127. doi: 10.1159/000123142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs D. M., Vale W. Effect of the serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine on corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin secretion into hypophysial portal blood. Brain Res. 1983 Nov 28;280(1):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., DeWitt C. W. Genetic control of collagen-induced arthritis in rats: the immune response to type II collagen among susceptible and resistant strains and evidence for multiple gene control. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. A., Ruder H. J., Brown K. S., Lipsett M. B. A radioimmunoassay for plasma corticosterone. Steroids. 1972 Dec;20(6):681–695. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(72)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. L., Yu D. T. Development of an experimental animal model for reactive arthritis induced by Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):721–726. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.721-726.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. C., Di Renzo G., Beckford U., Gillham B., Jones M. T. Role of serotonin in the control of secretion of corticotrophin releasing factor. J Endocrinol. 1982 May;93(2):151–160. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0930151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian P. L., Kaffka K. L., Stern A. S., Woehle D., Benjamin W. R., Dechiara T. M., Gubler U., Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Lomedico P. T. Interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta bind to the same receptor on T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4509–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Kohashi Y., Takahashi T., Ozawa A., Shigematsu N. Suppressive effect of Escherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):547–553. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. L., Henson P. M. Mediators of inflammation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:335–359. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laue L., Kawai S., Brandon D. D., Brightwell D., Barnes K., Knazek R. A., Loriaux D. L., Chrousos G. P. Receptor-mediated effects of glucocorticoids on inflammation: enhancement of the inflammatory response with a glucocorticoid antagonist. J Steroid Biochem. 1988 Jun;29(6):591–598. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(88)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Lactobacillus casei cell wall-induced arthritis in rats: cell wall fragment distribution and persistence in chronic arthritis-susceptible LEW/N and -resistant F344/N rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):939–942. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Guyre P. M., Holbrook N. J. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984 Winter;5(1):25–44. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Ruff M. R., Weber R. J., Herkenham M. Neuropeptides and their receptors: a psychosomatic network. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2 Suppl):820s–826s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Unanue E. R. Corticosteroids inhibit murine macrophage Ia expression and interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1803–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinedi E., Negro-Vilar A. Serotonin and adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) release: direct effects at the anterior pituitary level and potentiation of arginine vasopressin-induced ACTH release. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1217–1223. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Trial J., Parker C. W. Effect of serotonin on murine macrophages: suppression of Ia expression by serotonin and its reversal by 5-HT2 serotonergic receptor antagonists. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):276–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara A., Gottschall P. E., Dahl R. R., Arimura A. Interleukin-1 stimulates ACTH release by an indirect action which requires endogenous corticotropin releasing factor. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1580–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Hansen C. Thymus-dependent and -independent regulation of Ia antigen expression in situ by cells in the synovium of rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Differences in site and intensity of expression in euthymic, athymic, and cyclosporin A-treated LEW and F344 rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI112933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L. Proinflammatory microbial products as etiologic agents of inflammatory arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):293–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Smith E. M., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Fuller G. M., Blalock J. E. Corticotropin-releasing activity of monokines. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1035–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2997929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



