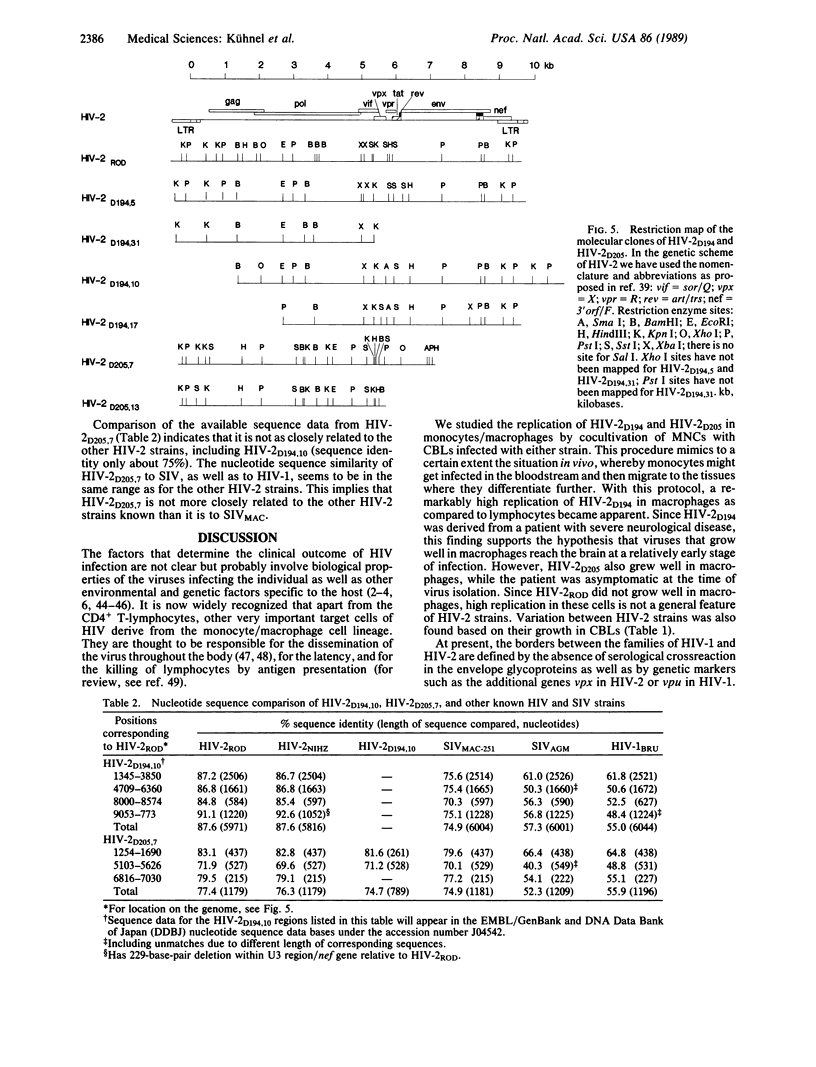
Abstract
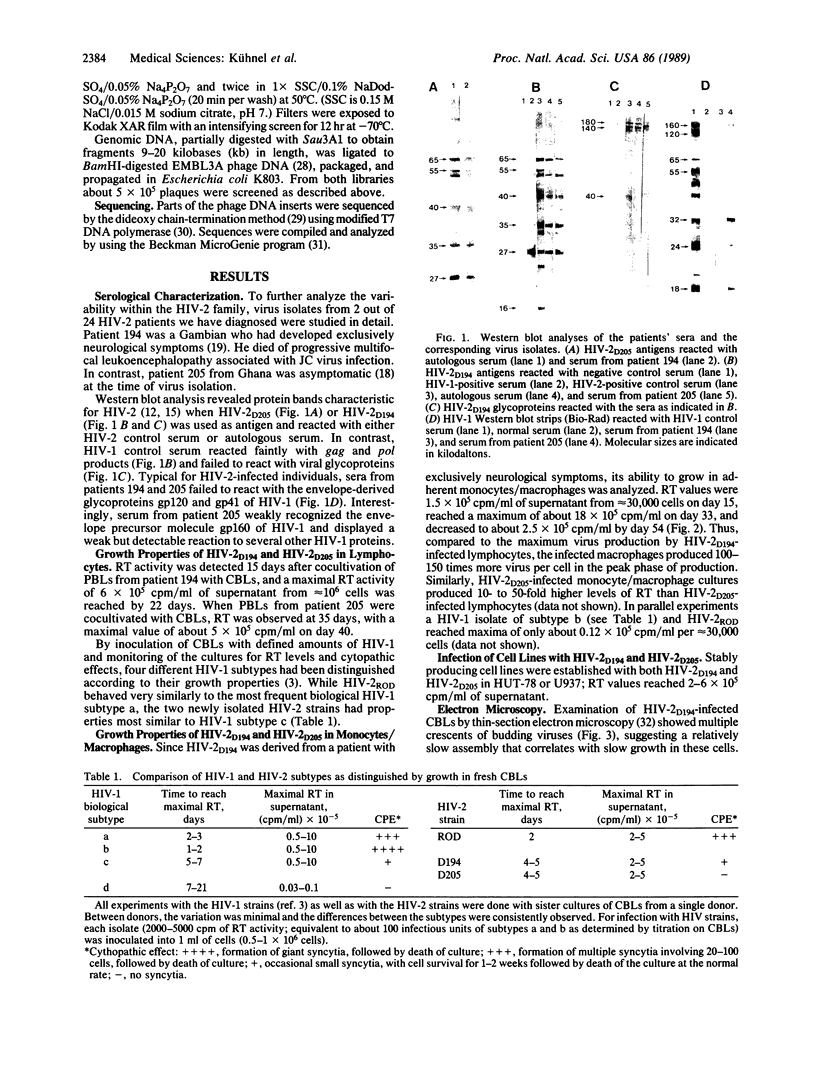
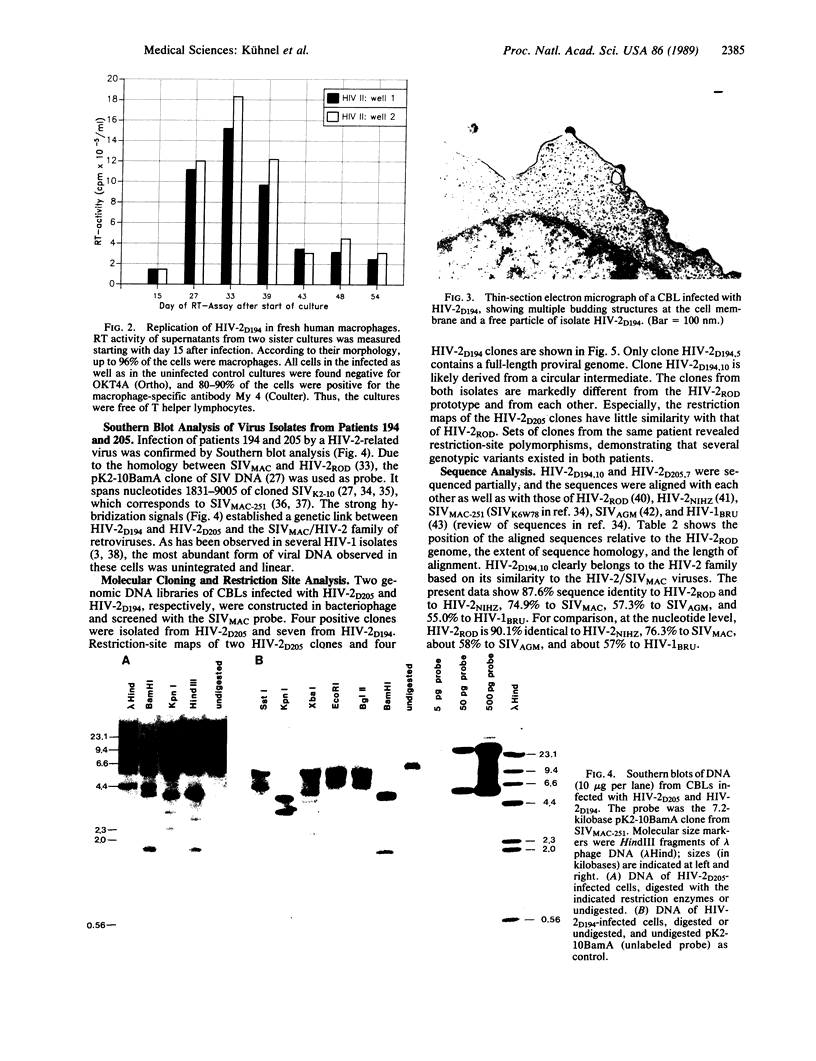
Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2)-related viruses were isolated from a Gambian dying of exclusively neurological disease (HIV-2D194) and from an asymptomatic Ghanian (HIV-2D205). Both strains exhibited properties of HIV-1 biological subtype c: they grew slowly and induced few or no syncytia but eventually produced high levels of particle-associated reverse transcriptase in cultures of fresh peripheral blood lymphocytes, and they established stable infection of T-lymphoma (HUT-78) and monocytic (U937) cell lines. Each produced even higher levels of reverse transcriptase when fresh human monocytes/macrophages were used as target cells. The viruses were molecularly cloned after a single passage in culture, in order to minimize in vitro selection of subtypes present in vivo. Restriction-site analysis showed heterogeneity within each isolate. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a portion of the HIV-2D194 genome revealed that it is a member of the prototypic HIV-2 family, displaying 13% divergence versus HIV-2ROD and HIV-2NIHZ, as compared to 9% divergence between HIV-2ROD and HIV-2NIHZ. In contrast, HIV-2D205 is the most highly divergent HIV-2 strain yet described: it is equidistant in relation between the known HIV-2 strains and the simian immunodeficiency virus isolates from rhesus macaque monkeys (23-25% divergence).
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alizon M., Montagnier L. Genetic variability in human immunodeficiency viruses. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;511:376–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb36266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Picht J., Löhr G. W. Primary cultures of human blood-born macrophages grown on hydrophobic teflon membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Feb 11;56(3):295–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(83)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun-Vezinet F., Rey M. A., Katlama C., Girard P. M., Roulot D., Yeni P., Lenoble L., Clavel F., Alizon M., Gadelle S. Lymphadenopathy-associated virus type 2 in AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Clinical and virological features in four patients. Lancet. 1987 Jan 17;1(8525):128–132. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91967-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guyader M., Guétard D., Sallé M., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Molecular cloning and polymorphism of the human immune deficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):691–695. doi: 10.1038/324691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavel F., Guétard D., Brun-Vézinet F., Chamaret S., Rey M. A., Santos-Ferreira M. O., Laurent A. G., Dauguet C., Katlama C., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a new human retrovirus from West African patients with AIDS. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2425430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellrodt A., Barre-Sinoussi F., Le Bras P., Nugeyre M. T., Palazzo L., Rey F., Brun-Vezinet F., Rouzioux C., Segond P., Caquet R. Isolation of human T-lymphotropic retrovirus (LAV) from Zairian married couple, one with AIDS, one with prodromes. Lancet. 1984 Jun 23;1(8391):1383–1385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91877-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., McHugh T. M., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Differential ability of human immunodeficiency virus isolates to productively infect human cells. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3415–3418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. A., Moreau J., Odehouri K., Legg H., Barboza A., Cheng-Mayer C., Levy J. A. Characterization of a noncytopathic HIV-2 strain with unusual effects on CD4 expression. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1522–1525. doi: 10.1126/science.2836951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Gurgo C., Guo H. G., Gallo R. C., Collalti E., Fargnoli K. A., Hall L. F., Wong-Staal F., Reitz M. S., Jr Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus and its relationship to the human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):539–543. doi: 10.1038/328539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R., Wong-Staal F., Montagnier L., Haseltine W. A., Yoshida M. HIV/HTLV gene nomenclature. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):504–504. doi: 10.1038/333504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Carney D. N., Bunn P. A., Russell E. K., Jaffe E. S., Schechter G. P., Guccion J. G. Mitogen requirements for the in vitro propagation of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Arya S. K., Popovic M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Molecular cloning and characterization of the HTLV-III virus associated with AIDS. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):166–169. doi: 10.1038/312166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Taylor M. E., Redfield R. R., Markham P. D., Salahuddin S. Z., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Parks E. S., Parks W. P. Genetic variation in HTLV-III/LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1548–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.3012778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch V., Riedel N., Kornfeld H., Kanki P. J., Essex M., Mullins J. I. Cross-reactivity to human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus and molecular cloning of simian T-cell lymphotropic virus type III from African green monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9754–9758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Kaplan J. C., Rackauskas I. E., Gurney M. E. Second conserved domain of gp120 is important for HIV infectivity and antibody neutralization. Science. 1988 Feb 26;239(4843):1021–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2830667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer J. M., Schulz T. F., Hengster P., Larcher C., Zangerle R., Kofler H., Fritsch P., Wachter H., Dierich M. P. Comparison of Western blot (immunoblot) based on recombinant-derived p41 with conventional tests for serodiagnosis of human immunodeficiency virus infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):116–120. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.116-120.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsen J., Diemer N. H., Gaub J., Brun B., Helweg-Larsen S. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient without other clinical manifestations of AIDS. Acta Neurol Scand. 1987 Mar;75(3):209–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1987.tb07919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki P. J., Barin F., M'Boup S., Allan J. S., Romet-Lemonne J. L., Marlink R., McLane M. F., Lee T. H., Arbeille B., Denis F. New human T-lymphotropic retrovirus related to simian T-lymphotropic virus type III (STLV-IIIAGM). Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):238–243. doi: 10.1126/science.3006256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H. W., 3rd, Li Y., Naidu Y. M., Butler C. V., Ochs M. F., Jaenel G., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Comparison of simian immunodeficiency virus isolates. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):619–622. doi: 10.1038/331619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L. I., Lee S. W., Kappes J. C., Parkin J. S., Decker D., Hoxie J. A., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. West African HIV-2-related human retrovirus with attenuated cytopathicity. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1525–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.3375832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Riedel N., Viglianti G. A., Hirsch V., Mullins J. I. Cloning of HTLV-4 and its relation to simian and human immunodeficiency viruses. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):610–613. doi: 10.1038/326610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedrig M., Rabanus J. P., L'Age Stehr J., Gelderblom H. R., Pauli G. Monoclonal antibodies directed against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gag proteins with specificity for conserved epitopes in HIV-1, HIV-2 and simian immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):2109–2114. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D. HIV persistence in monocytes leads to pathogenesis and AIDS. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90310-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Korn L. J. A comprehensive sequence analysis program for the IBM personal computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):581–599. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):790–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rácz P., Tenner-Rácz K., Kahl C., Feller A. C., Kern P., Dietrich M. Spectrum of morphologic changes of lymph nodes from patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complexes. Prog Allergy. 1986;37:81–181. doi: 10.1159/000318442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Becker W. B., Helm E. B., Brodt R., Fischer H., Henco K., Brede H. D. Isolation of variants of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with ARC or AIDS. J Med Virol. 1986 Aug;19(4):335–344. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890190406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saag M. S., Hahn B. H., Gibbons J., Li Y., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Shaw G. M. Extensive variation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in vivo. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):440–444. doi: 10.1038/334440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., de Goede R. E., Al B. J., Winkel I. N., Gruters R. A., Cuypers H. T., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Differential syncytium-inducing capacity of human immunodeficiency virus isolates: frequent detection of syncytium-inducing isolates in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2026–2032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2026-2032.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Markham P., Redfield R., Gallo R. C. Genomic diversity of human T-lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III). Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):759–762. doi: 10.1126/science.2992084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury J. F., Franchini G., Reitz M., Collalti E., Starcich B., Hall L., Fargnoli K., Jagodzinski L., Guo H. G., Laure F. Genetic variability between isolates of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 is comparable to the variability among HIV type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5941–5945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Briesen H., Becker W. B., Henco K., Helm E. B., Gelderblom H. R., Brede H. D., Rübsamen-Waigmann H. Isolation frequency and growth properties of HIV-variants: multiple simultaneous variants in a patient demonstrated by molecular cloning. J Med Virol. 1987 Sep;23(1):51–66. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890230107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]