Abstract
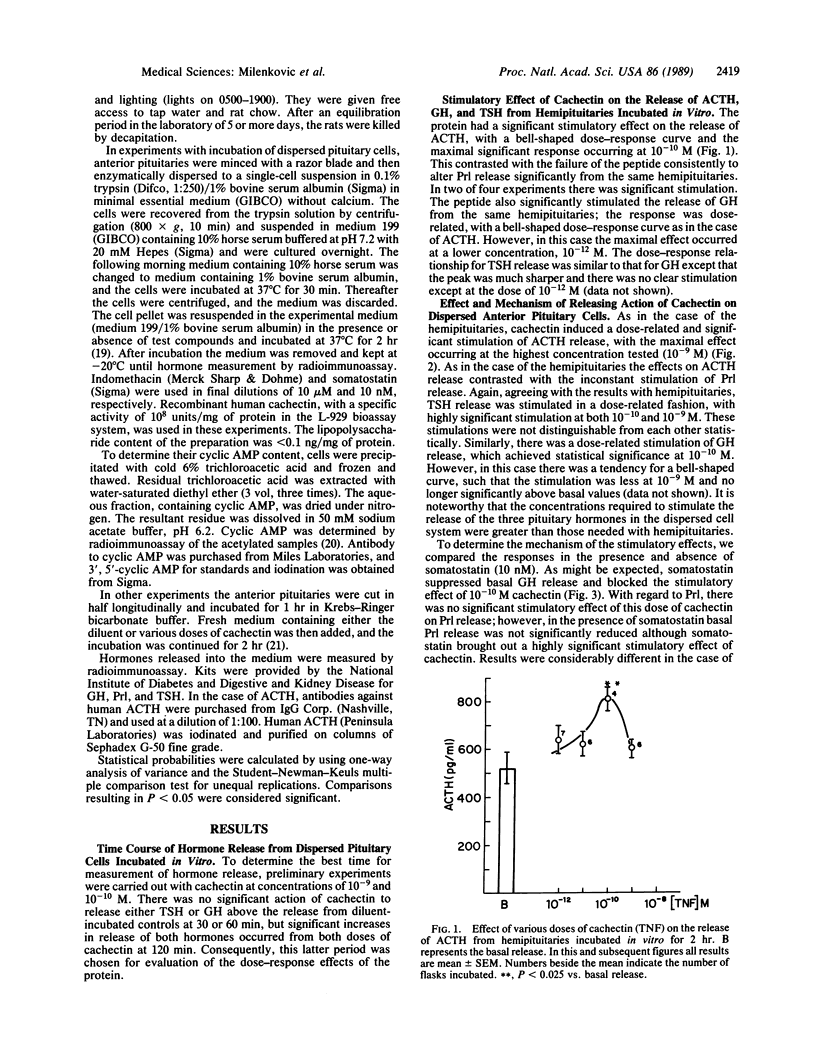
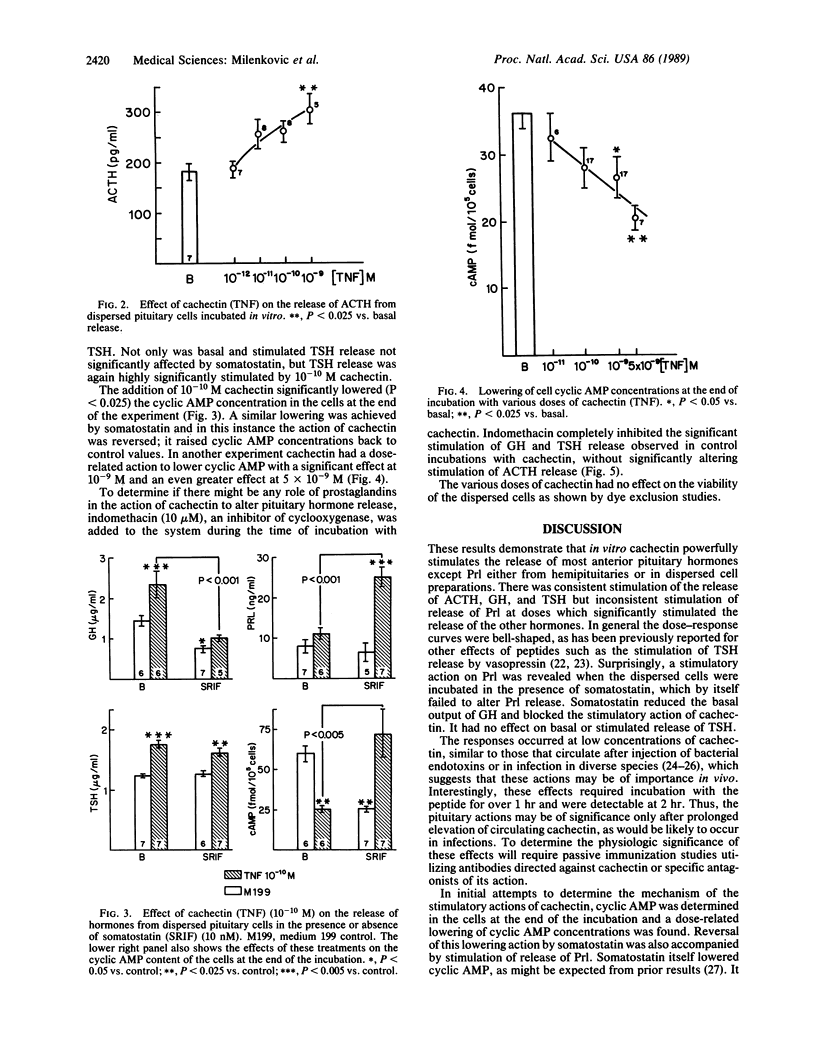
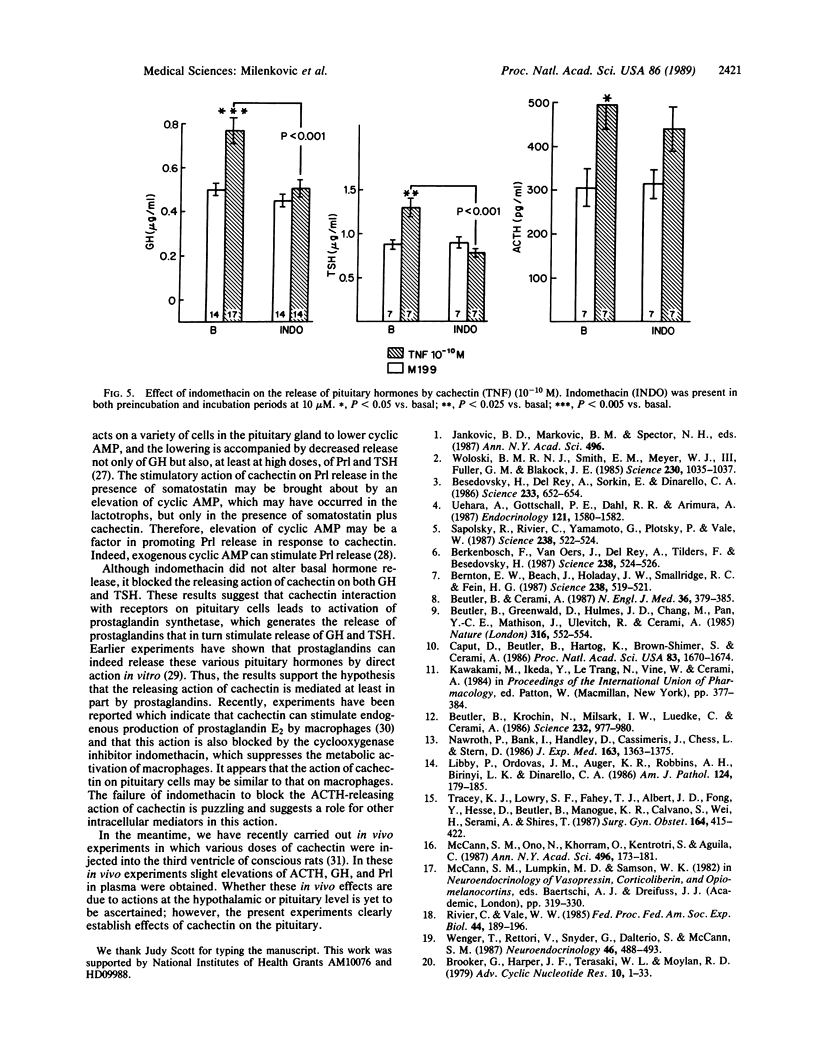
Cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) is a powerful macrophage hormone released during infection, which circulates in blood to produce diverse effects in the organism. We examined the effect of cachectin on release of anterior pituitary hormones from either hemipituitaries or dispersed pituitary cells incubated in vitro. The action of cachectin on dispersed cells was demonstrable only after 2 hr of incubation. With this incubation time, the protein produced a dose-related stimulation of release of adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), growth hormone (GH), and thyrotropin (TSH), but not of prolactin (Prl), from both hemipituitaries and dispersed cells. The doses required for stimulation were low in the case of hemipituitaries, usually of the order of 10(-12) M, whereas they were higher by one or two orders of magnitude with the dispersed pituitary cells. This may be related either to loss of receptors for the protein during the dispersion procedure or to the fact that in the hemipituitary system cell interactions are facilitated because the cells are close to each other. In the dispersed cell system cachectin evoked a dose-related decrease in cyclic AMP content. Incubation with somatostatin lowered the cyclic AMP content of the cells and depressed GH output without altering output of TSH or Prl. When somatostatin and cachectin were incubated together with the cells, the suppression of cyclic AMP production was abolished; TSH and Prl release were stimulated, but the action of cachectin to stimulate GH release was blocked. The stimulation of Prl release by cachectin in the presence of somatostatin may be related to the elevation of cyclic AMP, a known stimulator of Prl release. The cyclooxygenase inhibitor indomethacin nearly completely blocked the stimulatory effect of cachectin on release of GH and TSH from dispersed pituitary cells but had only a slight and nonsignificant attenuating effect on its ACTH-releasing action. These results suggest that at least part of the stimulatory action of the peptide on pituitary hormone release is brought about by prostaglandins. The failure of indomethacin to block the release of ACTH induced by cachectin suggests that other mechanisms may be involved in the release of ACTH induced by this peptide. Since the concentrations of cachectin required to stimulate pituitary hormone release are similar to those that are encountered in plasma during infection, it is likely that this direct pituitary action has pathophysiological significance.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Gatanaga T., Yamazaki M., Soma G., Mizuno D. Purification of rabbit tumor necrosis factor. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 28;180(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenbosch F., van Oers J., del Rey A., Tilders F., Besedovsky H. Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2443979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Beach J. E., Holaday J. W., Smallridge R. C., Fein H. G. Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2821620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. A., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor: production, distribution, and metabolic fate in vivo. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3972–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khorram O., McCann S. M. On the presence of a nondopaminergic, peptidergic prolactin release-inhibiting factor in hypothalamic extracts of infantile rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;44(1):65–69. doi: 10.1159/000124623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABELLA F. S. RELEASE OF THYROTROPHIN IN VIVO AND IN VITRO BY SYNTHETIC NEUROHYPOPHYSIAL HORMONES. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1964 Jan;42:75–83. doi: 10.1139/y64-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmmann V., Benninghoff B., Dröge W. Tumor necrosis factor-induced activation of peritoneal macrophages is regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cAMP. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):587–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Ordovas J. M., Auger K. R., Robbins A. H., Birinyi L. K., Dinarello C. A. Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor induce interleukin-1 gene expression in adult human vascular endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):179–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin M. D., Samson W. K., McCann S. M. Arginine vasopressin as a thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1070–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2881350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M., Ono N., Khorram O., Kentroti S., Aguila C. The role of brain peptides in neuroimmunomodulation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;496:173–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb35763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann S. M. Physiology and pharmacology of LHRH and somatostatin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1982;22:491–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.22.040182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda S. R., Capdevila J., Snyder G., McCann S. M., Negro-Vilar A., Falck J. R. Involvement of arachidonic acid metabolites in the control of hypothalamic-pituitary function. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1985;15:559–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Vale W. Effects of corticotropin-releasing factor, neurohypophyseal peptides, and catecholamines on pituitary function. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 2):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Albert J. D., Fong Y., Hesse D., Beutler B., Manogue K. R., Calvano S., Wei H. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces lethal shock and stress hormone responses in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987 May;164(5):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara A., Gottschall P. E., Dahl R. R., Arimura A. Interleukin-1 stimulates ACTH release by an indirect action which requires endogenous corticotropin releasing factor. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1580–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger T., Rettori V., Snyder G. D., Dalterio S., McCann S. M. Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on the hypothalamic-pituitary control of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in adult male rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Dec;46(6):488–493. doi: 10.1159/000124870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Smith E. M., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Fuller G. M., Blalock J. E. Corticotropin-releasing activity of monokines. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1035–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2997929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



