Abstract
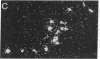
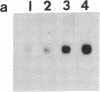
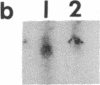
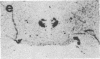
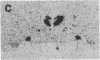
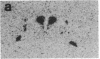
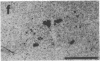
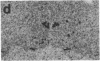
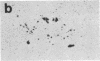
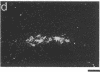
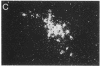
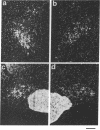
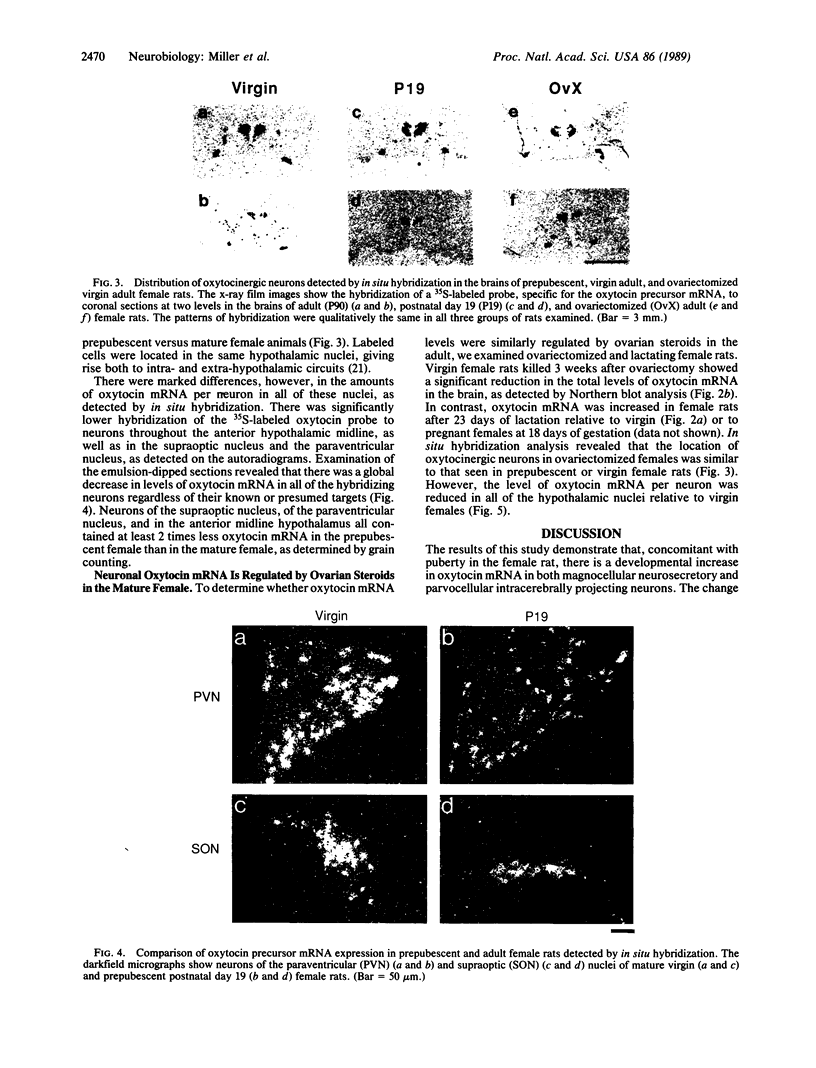
We have examined the changes in neuronal expression of oxytocin mRNA in the perinatal and mature female rat as a function of endogenous gonadal steroids. Northern blot analysis demonstrated a significant developmental increase in the abundance of oxytocin mRNA in the female brain concomitant with puberty. Ovariectomy of adult females decreased total brain oxytocin mRNA to significantly lower levels. In contrast, lactating mothers had increased levels of neuronal oxytocin mRNA. In situ hybridization analysis of neuronal oxytocin mRNA in adolescent, mature virgin, and ovariectomized virgin female brains demonstrated that the location and number of neurons expressing oxytocin mRNA was unchanged and that total brain oxytocin mRNA differences were attributable to amounts expressed per neuron. Differences in mRNA abundance were noted in oxytocin neurons throughout the hypothalamus, including those known to project as magnocellular neurons to the neurohypophysis and those of parvocellular origin thought to make wholly intracerebral connections. This developmental and dynamic regulation of oxytocin mRNA levels during gonadal maturation may coordinate the peripheral and central effects of this peptide on the reproductive biology of the female rat.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arletti R., Bertolini A. Oxytocin stimulates lordosis behavior in female rats. Neuropeptides. 1985 Jun;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbach J. P., Voorhuis T. A., van Tol H. H., Ivell R. In situ hybridization of oxytocin messenger RNA: macroscopic distribution and quantitation in rat hypothalamic cell groups. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. D., Greer E. R., Johnson M. F., Prange A. J., Jr, Pedersen C. A. Oxytocin and vasopressin immunoreactivity in hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic sites in late pregnant and postpartum rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Jun;46(1):39–47. doi: 10.1159/000124794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. D., Jirikowski G. F., Greer E. R., Stumpf W. E., Pedersen C. A. Ovarian steroids and sexual interaction alter oxytocinergic content and distribution in the basal forebrain. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):236–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90882-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kloet E. R., Rotteveel F., Voorhuis T. A., Terlou M. Topography of binding sites for neurohypophyseal hormones in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Mar 26;110(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döcke F., Rohde W., Stahl F., Smollich A., Dörner G. Serum levels of FSH, LH and estradiol-17 beta in female rats around the time of puberty onset. Exp Clin Endocrinol. 1984 Mar;83(1):6–13. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1210306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döhler K. D., Wuttke W. Changes with age in levels of serum gonadotropins, prolactin and gonadal steroids in prepubertal male and female rats. Endocrinology. 1975 Oct;97(4):898–907. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-4-898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivell R., Richter D. Structure and comparison of the oxytocin and vasopressin genes from rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2006–2010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirikowski G. F., Caldwell J. D., Pedersen C. A., Stumpf W. E. Estradiol influences oxytocin-immunoreactive brain systems. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. D., Naus C. C., Durand M., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. Isotypes of alpha-tubulin are differentially regulated during neuronal maturation. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 2):3065–3073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. D., Naus C. C., Higgins G. A., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. Developmentally regulated rat brain mRNAs: molecular and anatomical characterization. J Neurosci. 1987 Aug;7(8):2433–2444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negoro H., Visessuwan S., Holland R. C. Unit activity in the paraventricular nucleus of female rats at different stages of the reproductive cycle and after ovariectomy, with or without oestrogen or progesterone treatment. J Endocrinol. 1973 Dec;59(3):545–558. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0590545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osman P. Preovulatory changes in the ovaries during the first spontaneous pro-oestrus in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1975 Nov;67(2):259–265. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0670259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. R., Jr, Mahesh V. B. Hormonal events surrounding the natural onset of puberty in female rats. Biol Reprod. 1976 Apr;14(3):347–353. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod14.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen C. A., Ascher J. A., Monroe Y. L., Prange A. J., Jr Oxytocin induces maternal behavior in virgin female rats. Science. 1982 May 7;216(4546):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.7071605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMIREZ V. D., SAWYER C. H. ADVANCEMENT OF PUBERTY IN THE FEMALE RAT BY ESTROGEN. Endocrinology. 1965 Jun;76:1158–1168. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-6-1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. H., Morrell J. I., Pfaff D. W. Estrogen-concentrating neurophysin-containing hypothalamic magnocellular neurons in the vasopressin-deficient (Brattleboro) rat: a study combining steroid autoradiography and immunocytochemistry. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1718–1724. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01718.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes C. H., Morrell J. I., Pfaff D. W. Immunohistochemical analysis of magnocellular elements in rat hypothalamus: distribution and numbers of cells containing neurophysin, oxytocin, and vasopressin. J Comp Neurol. 1981 May 1;198(1):45–64. doi: 10.1002/cne.901980106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sar M., Stumpf W. E. Simultaneous localization of [3H]estradiol and neurophysin I or arginine vasopressin in hypothalamic neurons demonstrated by a combined technique of dry-mount autoradiography and immunohistochemistry. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W. Immunohistochemical identification of neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus that project to the medulla or to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Mar 1;205(3):260–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.902050306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman A. J., Zimmerman E. A. Magnocellular neurosecretory system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:357–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Bolwerk E. L., Liu B., Burbach J. P. Oxytocin and vasopressin gene expression in the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal system of the rat during the estrous cycle, pregnancy, and lactation. Endocrinology. 1988 Mar;122(3):945–951. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-3-945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Voorhuis D. T., Burbach J. P. Oxytocin gene expression in discrete hypothalamic magnocellular cell groups is stimulated by prolonged salt loading. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):71–76. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P., Germond J. E., Brown-Luedi M., Givel F., Wahli W. Sequence homologies in the region preceding the transcription initiation site of the liver estrogen-responsive vitellogenin and apo-VLDLII genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8611–8626. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Akaishi T., Negoro H. Effect of estrogen treatment on plasma oxytocin and vasopressin in ovariectomized rats. Endocrinol Jpn. 1979 Apr;26(2):197–205. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.26.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga K., Hawkins R. A., Stocker J. F. Estrogen secretion by the rat ovary in vivo during the estrous cycle and pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1969 Jul;85(1):103–112. doi: 10.1210/endo-85-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leengoed E., Kerker E., Swanson H. H. Inhibition of post-partum maternal behaviour in the rat by injecting an oxytocin antagonist into the cerebral ventricles. J Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;112(2):275–282. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1120275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]