Abstract
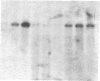
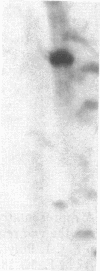
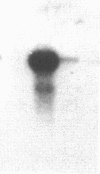
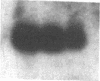
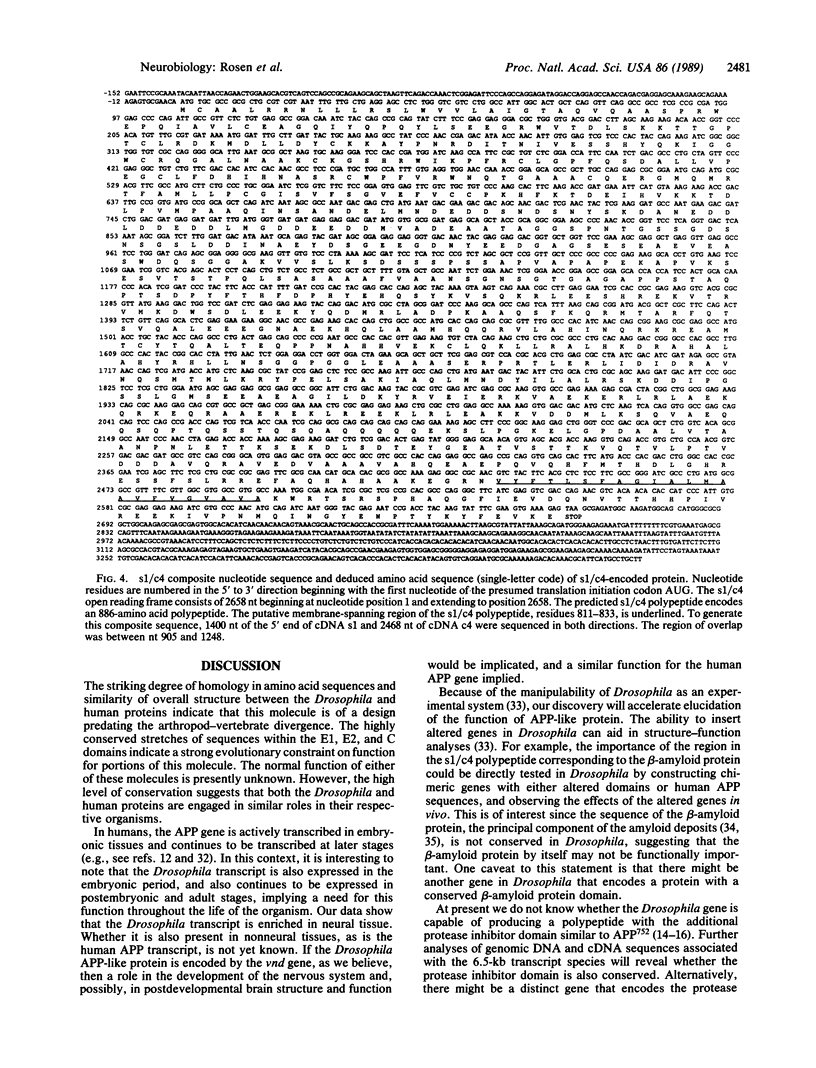
We have isolated genomic and cDNA clones for a Drosophila gene resembling the human beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP). This gene produces a nervous system-enriched 6.5-kilobase transcript. Sequencing of cDNAs derived from the 6.5-kilobase transcript predicts an 886-amino acid polypeptide. This polypeptide contains a putative transmembrane domain and exhibits strong sequence similarity to cytoplasmic and extracellular regions of the human beta-amyloid precursor protein. There is a high probability that this Drosophila gene corresponds to the essential Drosophila locus vnd, a gene required for embryonic nervous system development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Pachl C., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C. The isolation and characterization of Drosophila yolk protein genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. R., Grossman D., White K. Mutant alleles at the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster lead to nervous system defects. A developmental-genetic analysis. J Neurogenet. 1985 Jun;2(3):197–218. doi: 10.3109/01677068509100150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos A. R., Rosen D. R., Robinow S. N., White K. Molecular analysis of the locus elav in Drosophila melanogaster: a gene whose embryonic expression is neural specific. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):425–431. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrks T., Weidemann A., Multhaup G., Salbaum J. M., Lemaire H. G., Kang J., Müller-Hill B., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, transmembrane orientation and biogenesis of the amyloid A4 precursor of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):949–957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Bellido A., Santamaria P. Developmental Analysis of the Achaete-Scute System of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1978 Mar;88(3):469–486. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. A., Ewer J., Reddy P., Hall J. C., Rosbash M. Embryonic expression of the period clock gene in the central nervous system of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2313–2320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04499.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Campos-Ortega J. A. A region of the Drosophila genome necessary for CNS development. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):310–312. doi: 10.1038/282310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Campos-Ortega J. A. Genes in subdivision 1B of the Drosophila melanogaster X-chromosome and their influence on neural development. J Neurogenet. 1987 Jun;4(4):179–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman S. B., Wunsch C. D. A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Hadfield C., Pretorius G. H. Microdissection and cloning of the white locus and the 3B1-3C2 region of the Drosophila X chromosome. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):927–934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Drosophila melanogaster as an experimental organism. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1453–1459. doi: 10.1126/science.3131880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Schroeder R., LaCorbiere M., Saitoh T., Cole G. Amyloid beta protein precursor is possibly a heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2968652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Salbaum M., Beyreuther K., Seeburg P. H. Alzheimer's disease amyloidogenic glycoprotein: expression pattern in rat brain suggests a role in cell contact. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., O'Connell P., Gray M. R., Rosbash M. Drosophila maternal and embryo mRNAs transcribed from a single transcription unit use alternate combinations of exons. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1003–1013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K., DeCelles N. L., Enlow T. C. Genetic and developmental analysis of the locus vnd in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1983 Jul;104(3):433–448. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White K. Defective neural development in Drosophila melanogaster embryos deficient for the tip of the X chromosome. Dev Biol. 1980 Dec;80(2):332–344. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]