Abstract
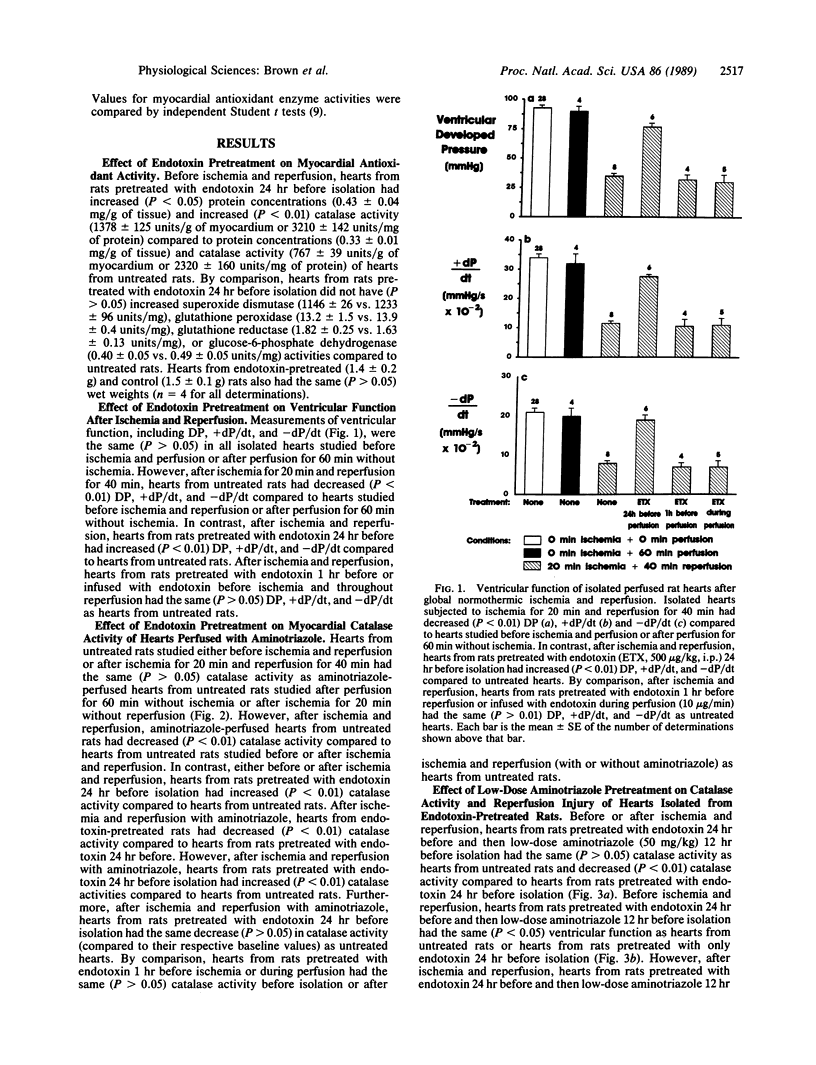
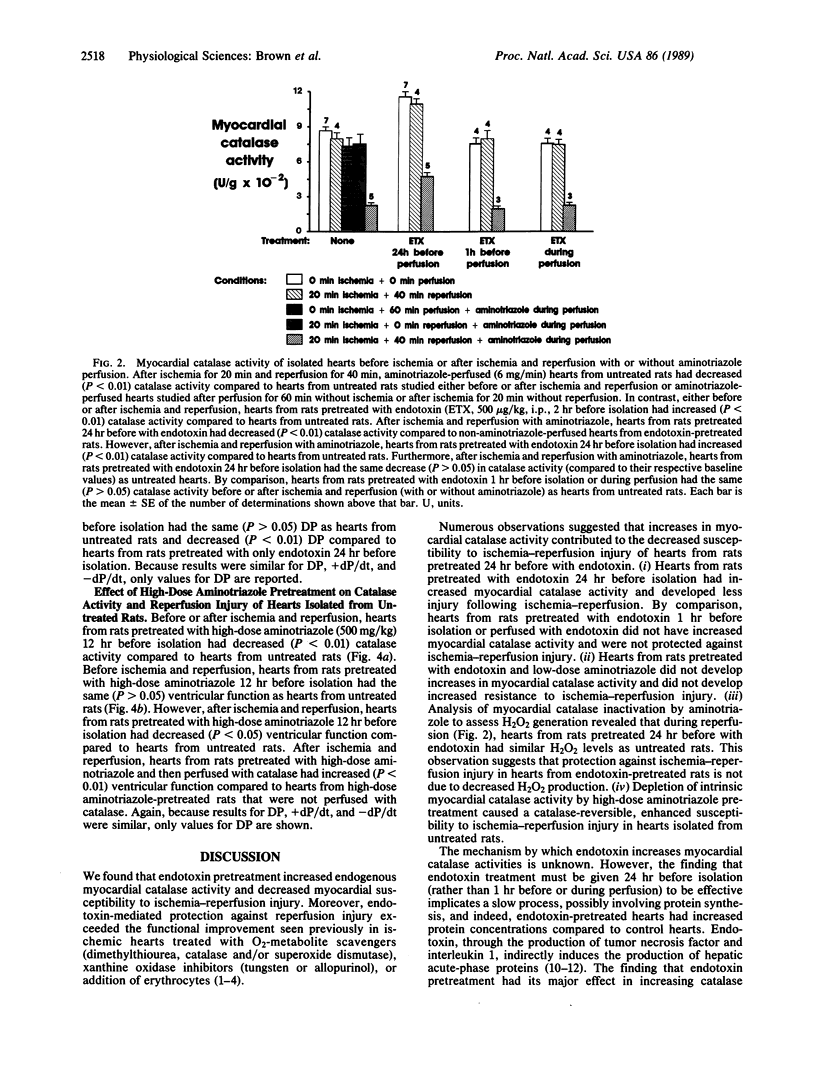
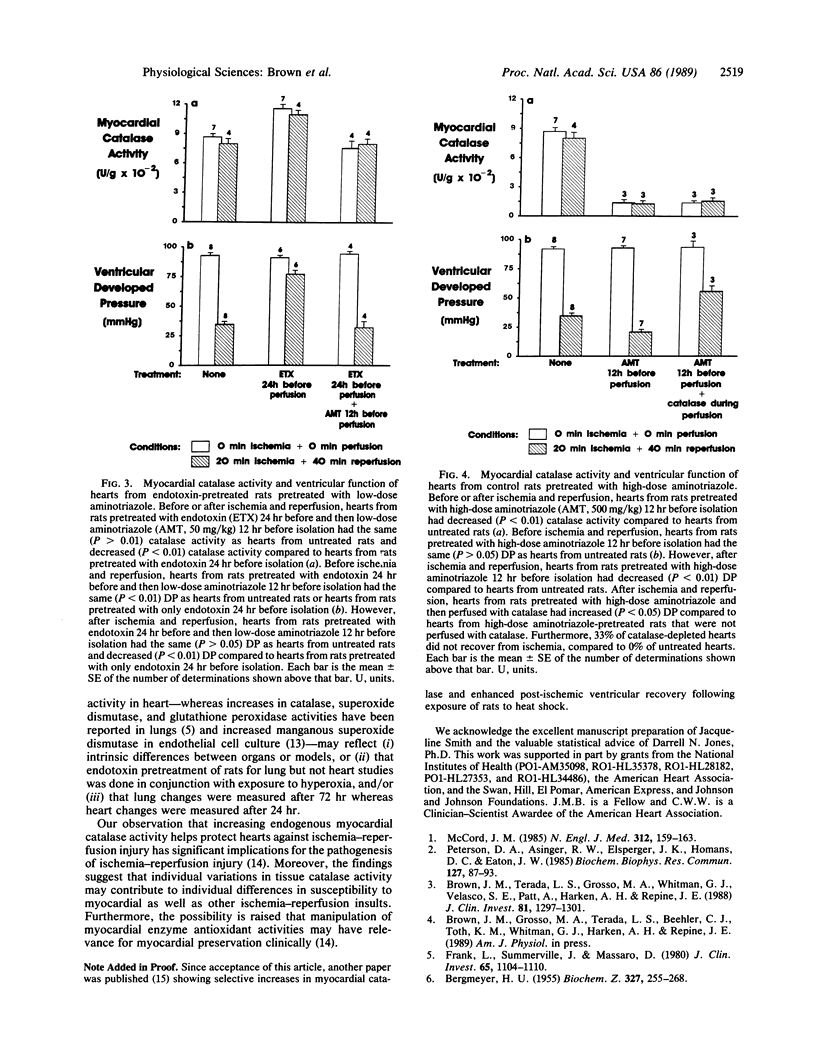
Hearts isolated from rats pretreated 24 hr before with endotoxin had increased myocardial catalase activity, but the same superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activities, as hearts from untreated rats. Hearts isolated from rats pretreated with endotoxin 24 hr before also had increased myocardial function (decreased injury) after ischemia and reperfusion (Langendorff apparatus, 37 degrees C), as assessed by measurement of ventricular developed pressure, contractility (+dP/dt), and relaxation rate (-dP/dt), compared to control hearts. In contrast, hearts isolated from rats pretreated with endotoxin 1 hr before isolation or hearts perfused with endotoxin did not have increased catalase activity or decreased injury following ischemia and reperfusion. Aminotriazole pretreatment prevented increases in myocardial catalase activity and myocardial function after ischemia-reperfusion in hearts from endotoxin-pretreated rats. The results suggest that endotoxin pretreatment decreases cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury and that increases in endogenous myocardial catalase activity contribute to protection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braunwald E., Kloner R. A. Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI112160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Terada L. S., Grosso M. A., Whitmann G. J., Velasco S. E., Patt A., Harken A. H., Repine J. E. Xanthine oxidase produces hydrogen peroxide which contributes to reperfusion injury of ischemic, isolated, perfused rat hearts. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1297–1301. doi: 10.1172/JCI113448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Preparation and assay of superoxide dismutases. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:382–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie R. W., Karmazyn M., Kloc M., Mailer K. Heat-shock response is associated with enhanced postischemic ventricular recovery. Circ Res. 1988 Sep;63(3):543–549. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and the pathogenesis of the acute-phase response. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 29;311(22):1413–1418. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411293112205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Summerville J., Massaro D. Potection from oxygen toxicity with endotoxin. Role of the endogenous antioxidant enzymes of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazuski J. E., Platt J. L., West M. A., Simmons R. L., Towle H. C., Cerra F. B. Direct effects of endotoxin on hepatocytes. Synthesis of a specific secretory protein. Arch Surg. 1988 Mar;123(3):340–344. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400270074011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter D. H., Dinarello C. A., Punsal P. I., Colten H. R. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor regulates hepatic acute-phase gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1172/JCI112721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. A., Asinger R. W., Elsperger K. J., Homans D. C., Eaton J. W. Reactive oxygen species may cause myocardial reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 28;127(1):87–93. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiki Y., Meyrick B. O., Brigham K. L., Burr I. M. Endotoxin increases superoxide dismutase in cultured bovine pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C436–C440. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester J. The statistical method. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 6;274(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601062740106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



