Abstract
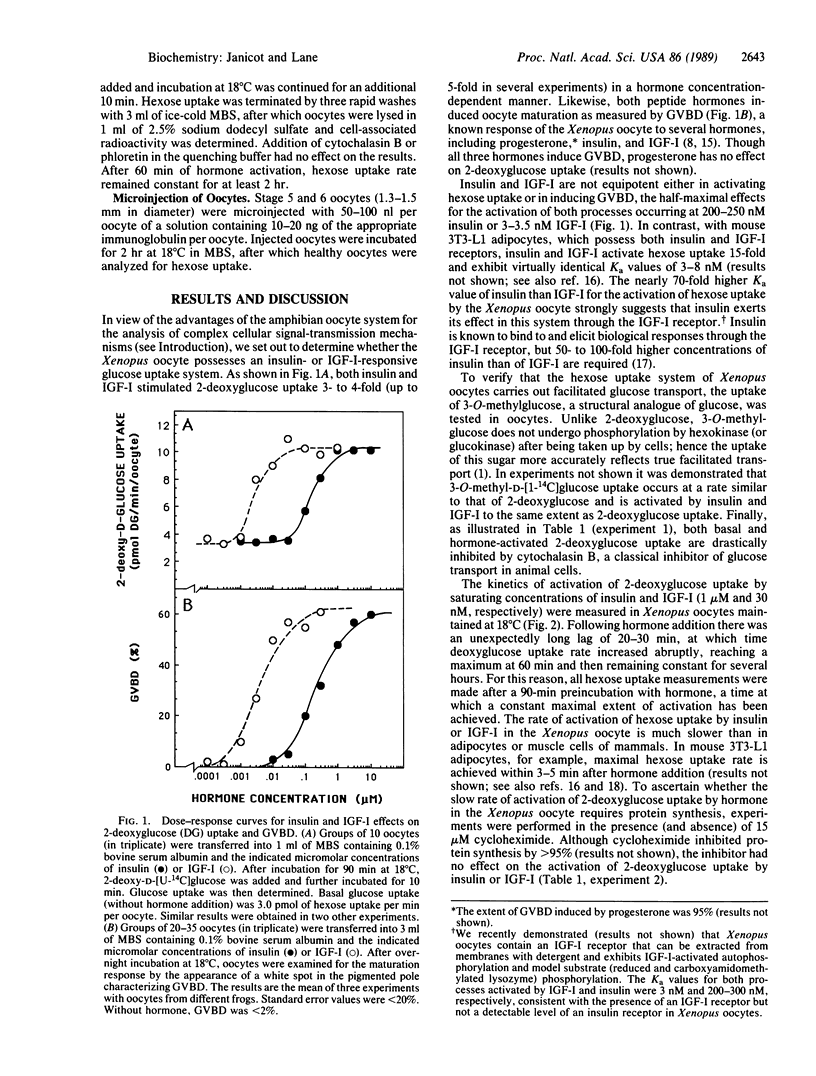
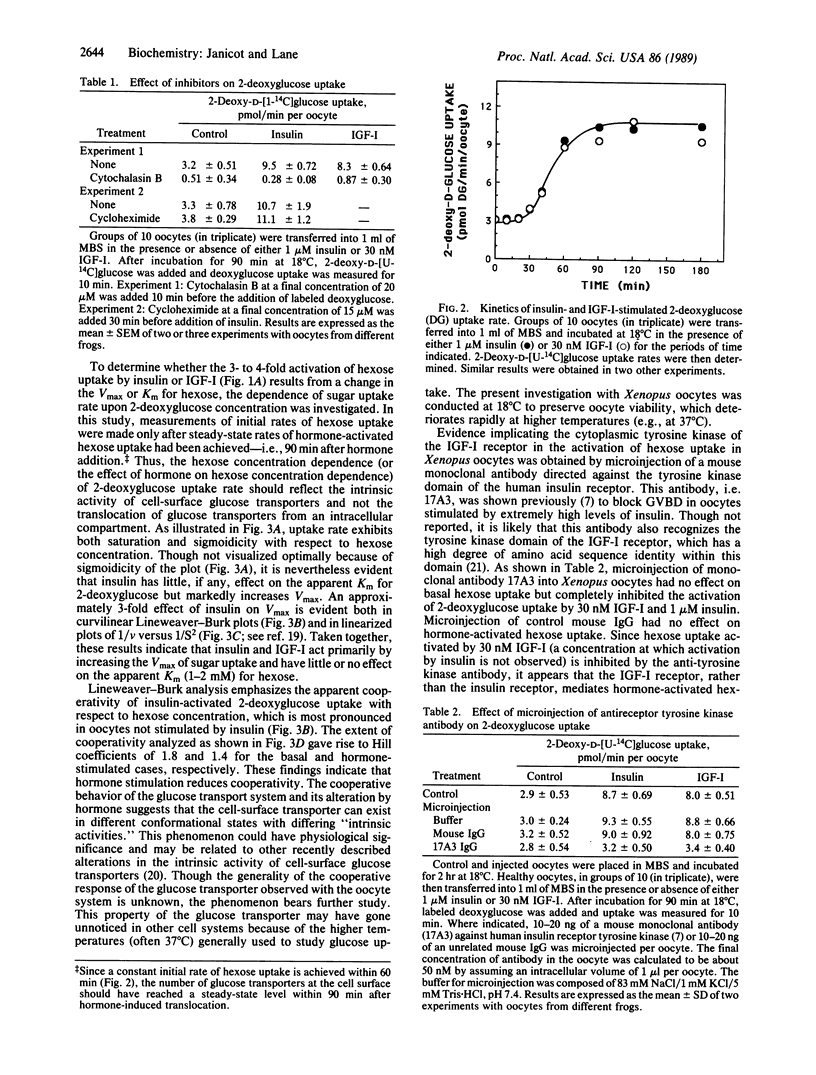
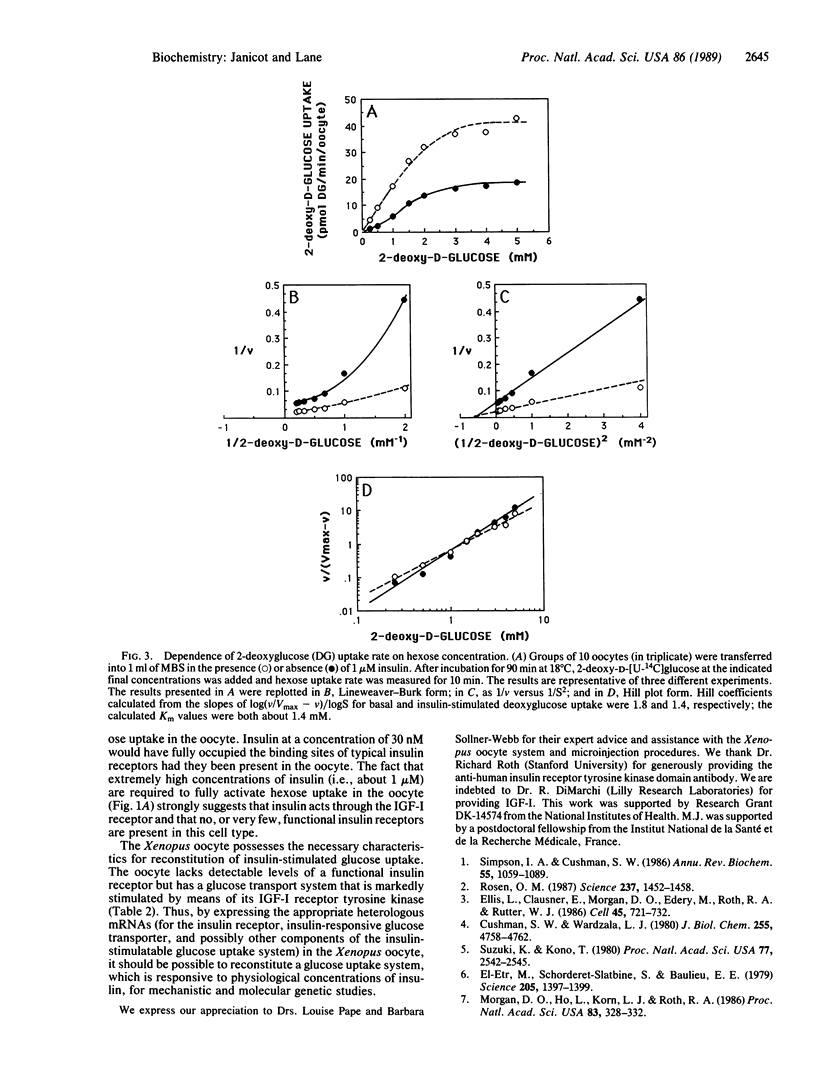
Xenopus laevis oocytes possess a glucose transport system that is activated 3- to 5-fold by insulin-like growth factor I (Ka = 3 nM) and insulin (Ka = 200-250 nM), properties suggesting activation mediated by an insulin-like growth factor I receptor. This activation increases the Vmax of hexose uptake and has little or no effect on the Km for deoxyglucose (Km = 1-2 mM). Activation by hormone requires about 60 min and is inhibited by cytochalasin B but not by cycloheximide. The dependence of hexose uptake rate on hexose concentration exhibits cooperativity with Hill coefficients of 1.8 and 1.4 for the basal and hormone-activated states, respectively. Microinjection of a monoclonal antibody directed against the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor blocks activation of hexose uptake by insulin-like growth factor I and insulin but has no effect on basal uptake. Taken together the results implicate the tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity of a cell-surface insulin-like growth factor I receptor in the activation of glucose transport in the Xenopus oocyte.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Distinct biologically active receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor II in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15892–15898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Etr M., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Baulieu E. E. Meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes initiated by insulin. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1397–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.472755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. C., Lane M. D. Evidence for the involvement of vicinal sulfhydryl groups in insulin-activated hexose transport by 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2646–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Le Goascogne C., Baulieu E. E. Induction of germinal vesicle breakdown in Xenopus laevis oocytes: response of denuded oocytes to progesterone and insulin. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):214–221. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joost H. G., Weber T. M., Cushman S. W., Simpson I. A. Activity and phosphorylation state of glucose transporters in plasma membranes from insulin-, isoproterenol-, and phorbol ester-treated rat adipose cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11261–11267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanski R. A., Frost S. C., Lane M. D. Insulin-dependent phosphorylation of the insulin receptor-protein kinase and activation of glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12272–12281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goascogne C., Sananès N., Gouézou M., Baulieu E. E. Alkaline phosphatase activity in the membrane of Xenopus laevis oocytes: effects of steroids, insulin, and inhibitors during meiosis reinitiation. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Koontz J. W. A study of the induction of cell division in amphibian oocytes by insulin. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 30;85(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. In vivo regulation of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in Xenopus oocytes. Stimulation by insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10644–10650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakanoue Y., Hashimoto E., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Insulin-stimulated serine kinase in Xenopus oocyte plasma membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1176–1184. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90753-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. A., Brooker T., Brooker G. Expression of rat mRNA coding for hormone-stimulated adenylate cyclase in Xenopus oocytes. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):380–387. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2824269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovic D., Erikson E., Pike L. J., Maller J. L. Activation of a ribosomal protein S6 protein kinase in Xenopus oocytes by insulin and insulin-receptor kinase. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):157–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stith B. J., Maller J. L. The effect of insulin on intracellular ph and ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



