Abstract
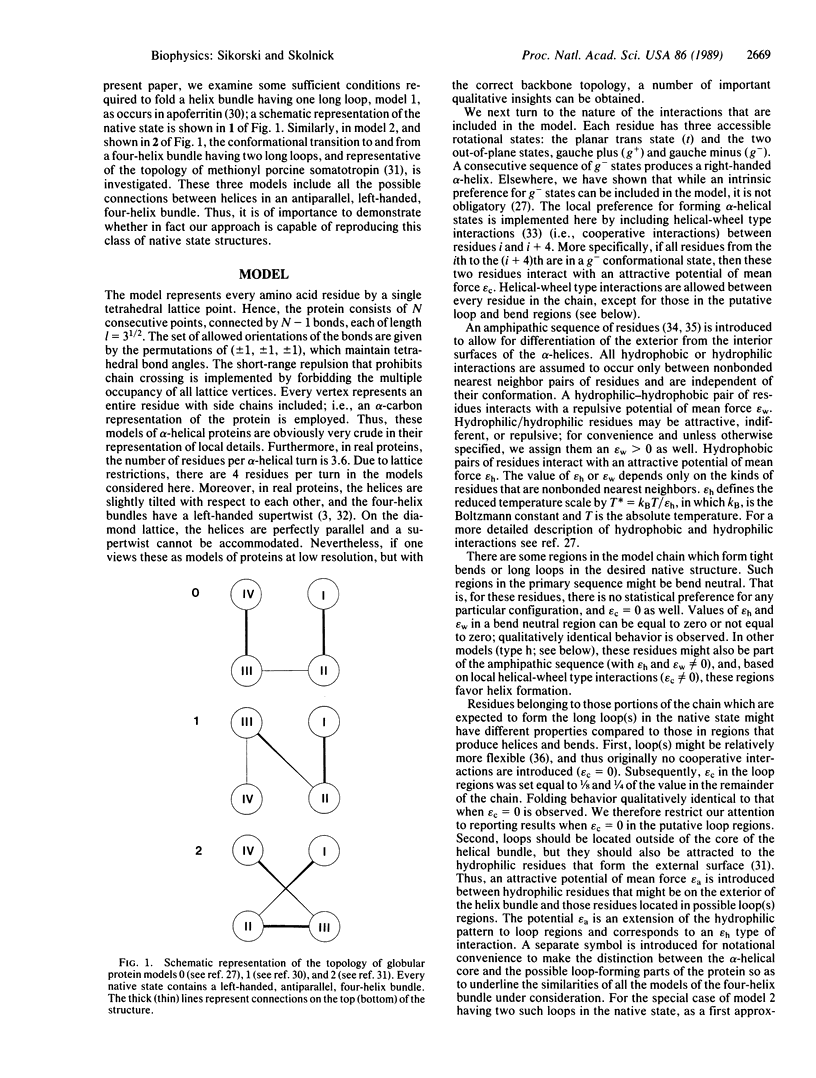
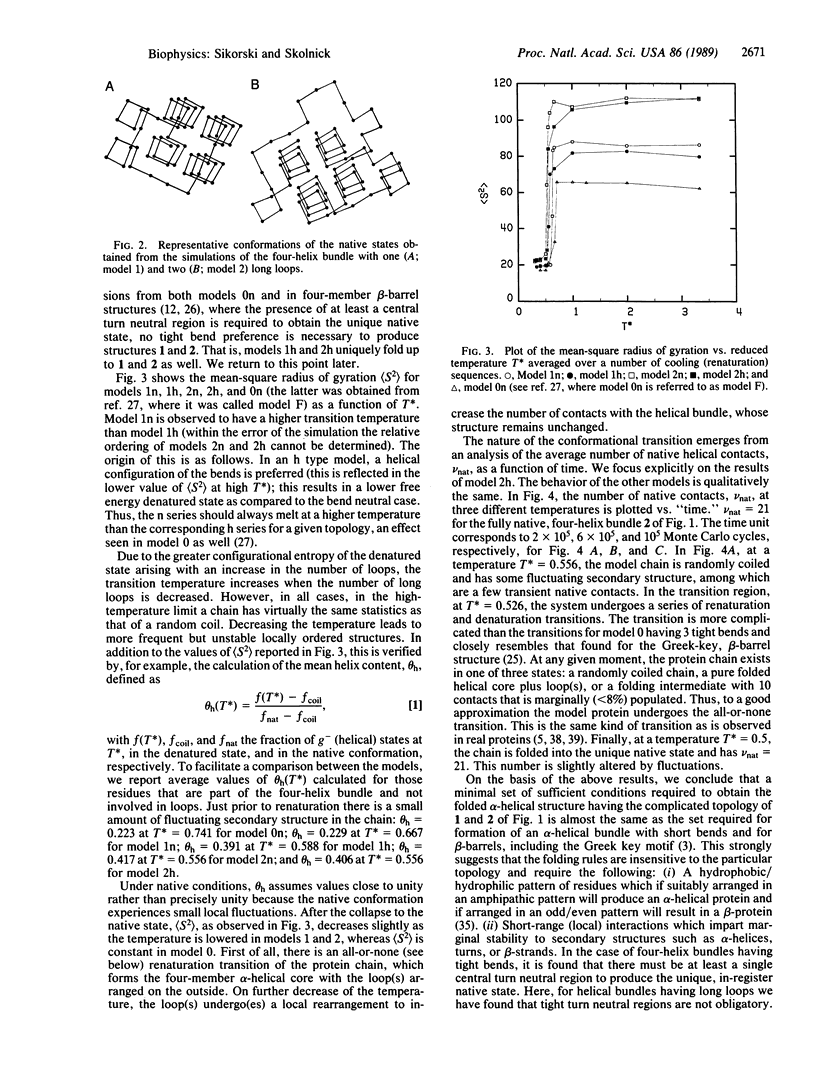
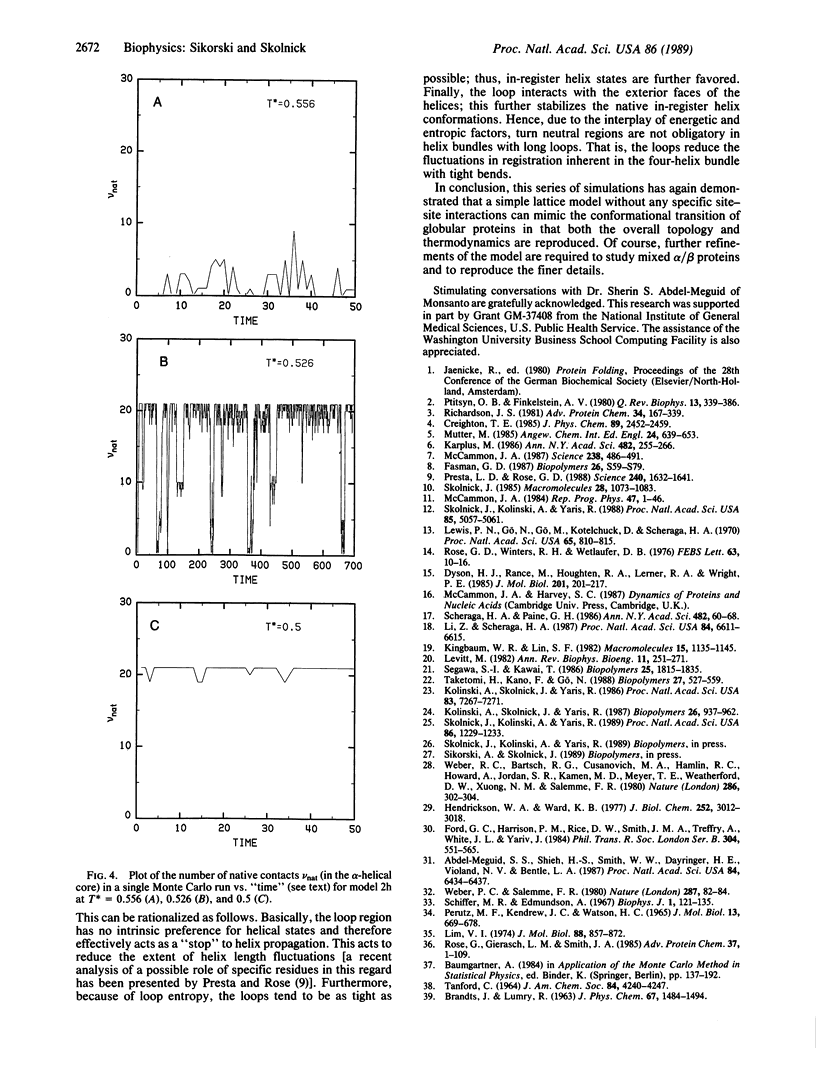
To help elucidate the general rules of globular protein folding, computer simulations of the conformational transition in model proteins having the left-handed, four-helix bundle motif in which the helices are joined by one or two long loops, as in apoferritin and somatotropin, respectively, have been undertaken. In the context of simple tetrahedral lattice protein models, these unique native helix bundle motifs can be obtained by a set of interactions similar to those found in previous simulations of the folding of four-member alpha-helical bundles with tight bends and beta-barrel proteins including the Greek key motif. The essential features sufficient to produce the four-helix bundle motif with long loops are as follows: (i) a general pattern of hydrophobic and hydrophilic type residues which differentiate the interior from the exterior of the molecule; (ii) the existence of hydrophilic regions in the amino acid sequence that, on the basis of short-range interactions, are indifferent to loop formation but that interact favorably with all the exterior residues of the helix bundle. Thus, these simulations indicate that, to reproduce all varieties of the left-handed four-helix bundle motif, site-specific interactions are not required.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Shieh H. S., Smith W. W., Dayringer H. E., Violand B. N., Bentle L. A. Three-dimensional structure of a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6434–6437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson H. J., Rance M., Houghten R. A., Wright P. E., Lerner R. A. Folding of immunogenic peptide fragments of proteins in water solution. II. The nascent helix. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):201–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D. The road from poly(alpha-amino acids) to the prediction of protein conformation. Biopolymers. 1987;26 (Suppl):S59–S79. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford G. C., Harrison P. M., Rice D. W., Smith J. M., Treffry A., White J. L., Yariv J. Ferritin: design and formation of an iron-storage molecule. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 13;304(1121):551–565. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A., Ward K. B. Pseudosymmetry in the structure of myohemerythrin. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3012–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus M. Molecular dynamics: applications to proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;482:255–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolinski A., Skolnick J., Yaris R. Monte Carlo simulations on an equilibrium globular protein folding model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7267–7271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolinski A., Skolnick J., Yaris R. Monte Carlo studies on equilibrium globular protein folding. I. Homopolymeric lattice models of beta-barrel proteins. Biopolymers. 1987 Jun;26(6):937–962. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. Protein conformation, dynamics, and folding by computer simulation. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:251–271. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. N., Go N., Go M., Kotelchuck D., Scheraga H. A. Helix probability profiles of denatured proteins and their correlation with native structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):810–815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Scheraga H. A. Monte Carlo-minimization approach to the multiple-minima problem in protein folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6611–6615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim V. I. Structural principles of the globular organization of protein chains. A stereochemical theory of globular protein secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):857–872. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCammon J. A. Computer-aided molecular design. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):486–491. doi: 10.1126/science.3310236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta L. G., Rose G. D. Helix signals in proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1632–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.2837824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptitsyn O. B., Finkelstein A. V. Similarities of protein topologies: evolutionary divergence, functional convergence or principles of folding? Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Aug;13(3):339–386. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D., Gierasch L. M., Smith J. A. Turns in peptides and proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:1–109. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D., Winters R. H., Wetlaufer D. B. A testable model for protein folding. FEBS Lett. 1976 Mar 15;63(1):10–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheraga H. A., Paine G. H. Conformational energy calculations on polypeptides and proteins: use of a statistical mechanical procedure for evaluating structure and properties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;482:60–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa S., Kawai T. Computer simulation of the folding-unfolding transition of island-model proteins--folding pathway, transition process, and fluctuations. Biopolymers. 1986 Oct;25(10):1815–1835. doi: 10.1002/bip.360251002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick J., Kolinski A., Yaris R. Dynamic Monte Carlo study of the folding of a six-stranded Greek key globular protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1229–1233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnick J., Kolinski A., Yaris R. Monte Carlo simulations of the folding of beta-barrel globular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5057–5061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketomi H., Kanô F., Go N. The effect of amino acid substitution on protein-folding and -unfolding transition studied by computer simulation. Biopolymers. 1988 Apr;27(4):527–559. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Bartsch R. G., Cusanovich M. A., Hamlin R. C., Howard A., Jordan S. R., Kamen M. D., Meyer T. E., Weatherford D. W., Nguyen huu Xuong Structure of cytochrome c': a dimeric, high-spin haem protein. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):302–304. doi: 10.1038/286302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Salemme F. R. Structural and functional diversity in 4-alpha-helical proteins. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):82–84. doi: 10.1038/287082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



