Abstract
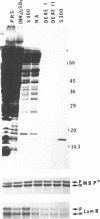
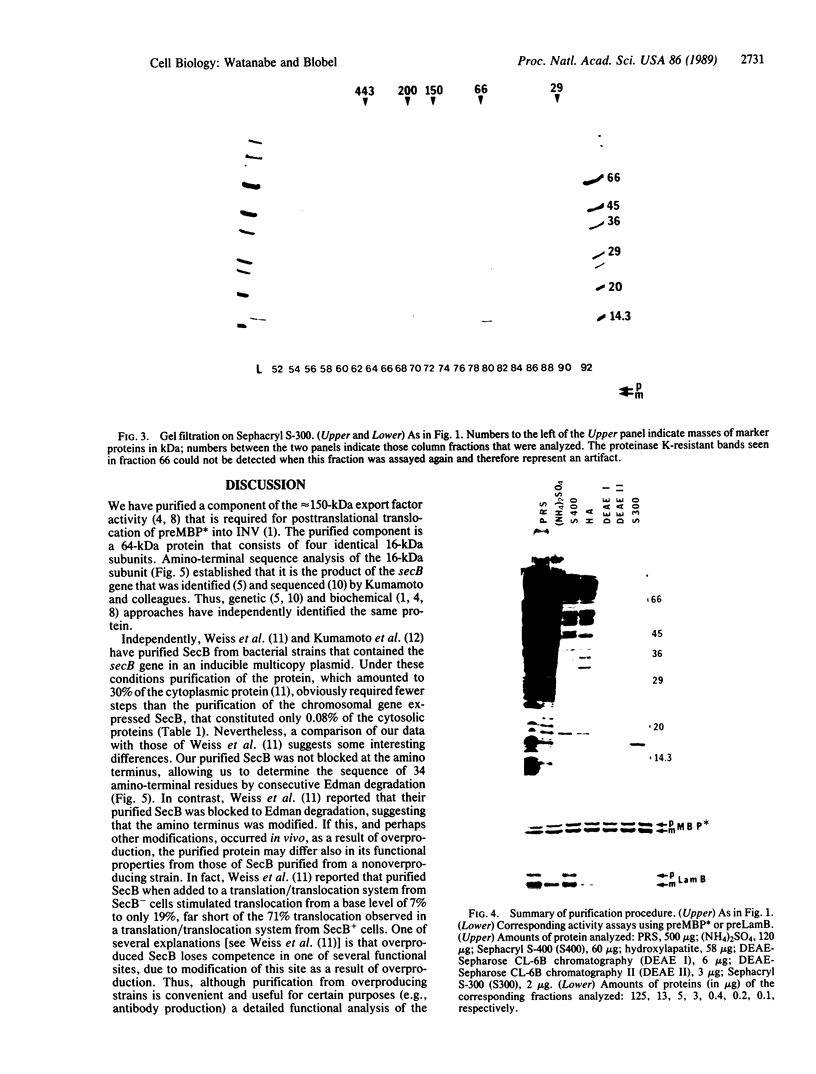
We have purified to homogeneity a cytosolic factor from Escherichia coli that is required for the translocation of a preprotein into inverted vesicles of the E. coli plasma membrane. The preprotein used is a precursor of mutant maltose-binding protein. This mutant contains alterations of the carboxyl terminus. Unlike the precursor for wild-type maltose-binding protein, the mutant precursor does not acquire a protease-resistant conformation after synthesis and retains posttranslational translocation competence. The purified cytosolic factor, added posttranslationally, is necessary and sufficient to yield virtually 100% translocation of the mutant precursor into inverted vesicles. The purified factor amounts to 0.08% of the cytosolic proteins and is a 64-kDa tetramer consisting of four identical 16-kDa subunits. Amino-terminal sequence analysis revealed that it is identical to the secB gene product. The purified SecB homotetramer is part of a larger 150-kDa complex that represents the "export" factor activity. During purification, the export factor activity dissociates into a 64-kDa SecB homotetramer and unidentified component(s). For the posttranslational integration of another preprotein, the precursor for the lamB gene product, into inverted vesicles, the 64-kDa SecB homotetramer is also required but additional factor(s) makes integration more efficient.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collier D. N., Bankaitis V. A., Weiss J. B., Bassford P. J., Jr The antifolding activity of SecB promotes the export of the E. coli maltose-binding protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fecycz I. T., Blobel G. Soluble factors stimulating secretory protein translocation in bacteria and yeast can substitute for each other. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new gene, secB, cause defective protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.253-260.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Chen L., Fandl J., Tai P. C. Purification of the Escherichia coli secB gene product and demonstration of its activity in an in vitro protein translocation system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2242–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Nault A. K. Characterization of the Escherichia coli protein-export gene secB. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90393-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. In vitro translocation of bacterial proteins across the plasma membrane of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7421–7425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Blobel G. Protein export in Escherichia coli requires a soluble activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7737–7741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: a study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Blobel G. Binding of a soluble factor of Escherichia coli to preproteins does not require ATP and appears to be the first step in protein export. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2248–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Hunt J. F., Blobel G. In vitro synthesized bacterial outer membrane protein is integrated into bacterial inner membranes but translocated across microsomal membranes. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):71–73. doi: 10.1038/323071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss J. B., Ray P. H., Bassford P. J., Jr Purified secB protein of Escherichia coli retards folding and promotes membrane translocation of the maltose-binding protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8978–8982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]