Abstract
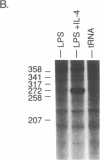
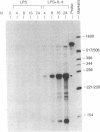
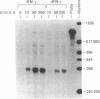
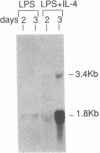
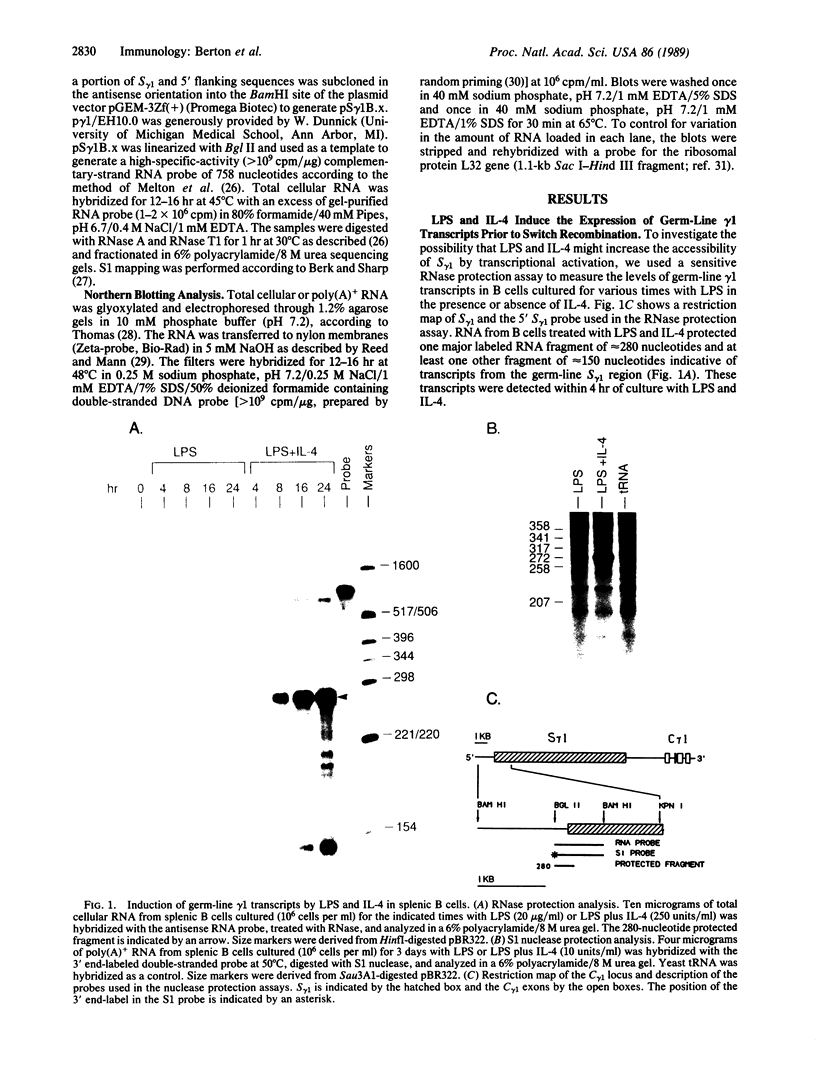
Interleukin 4 (IL-4) induces the expression of IgG1 and IgE in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated B cells. Previous studies have suggested that heavy-chain class switching may be regulated by increasing the accessibility of specific switch regions to switch recombinases. In this study, we have used an RNase protection assay to demonstrate that IL-4 induces expression of germ-line gamma 1 transcripts in B cells within 4 hr of culture; induction is dose-dependent and is inhibited by interferon gamma. IL-4 alone is capable of inducing the expression of germ-line gamma 1 transcripts in small, resting B cells, but lipopolysaccharide enhances expression. The germ-line transcripts are the same size (1.8 and 3.4 kilobases) as the secreted and membrane forms of the functional gamma 1 mRNAs and presumably result from the splicing of an upstream switch-region exon(s) to the gamma 1 constant-region exon(s). These data strongly support the "accessibility" model for the regulation of isotype switching and suggest that lymphokines such as IL-4 may direct specific switch events by transcriptional activation of the corresponding switch regions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., DePinho R. A., Reth M. G., Yancopoulos G. D. Regulation of genome rearrangement events during lymphocyte differentiation. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:5–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstedt-Lindqvist S., Moon H. B., Persson U., Möller G., Heusser C., Severinson E. Interleukin 4 instructs uncommitted B lymphocytes to switch to IgG1 and IgE. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1073–1077. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Spliced early mRNAs of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1274–1278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Carty J. A T cell activity that enhances polyclonal IgE production and its inhibition by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Ohara J., Bond M. W., Carty J., Zlotnik A., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1 enhances the IgE response of lipopolysaccharide-activated B cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4538–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. Properties of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8545–8549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Berry J. K., Dunnick W. Switch region content of hybridomas: the two spleen cell Igh loci tend to rearrange to the same isotype. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3539–3548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Chen Y. W., Isakson P., Layton J., Pure E., Word C., Krammer P. H., Tucker P., Vitetta E. S. Effect of T cell-derived lymphokines containing B cell differentiation factor(s) for IgG (BCDF gamma) on gamma-specific mRNA in murine B cells. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3049–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton J. E., Krammer P. H., Hamaoka T., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Small and large B cells respond differently to T cell-derived B cell growth and differentiation factors. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1985;2(3):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layton J. E., Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W., Krammer P. H. Clonal analysis of B cells induced to secrete IgG by T cell-derived lymphokine(s). J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1850–1863. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of germ line immunoglobulin gamma 2b transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1849–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Rothman P., Pollock R., Coffman R., Alt F. W. Mitogen- and IL-4-regulated expression of germ-line Ig gamma 2b transcripts: evidence for directed heavy chain class switching. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowatt M. R., Dunnick W. A. DNA sequence of the murine gamma 1 switch segment reveals novel structural elements. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2674–2683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noelle R., Krammer P. H., Ohara J., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. Increased expression of Ia antigens on resting B cells: an additional role for B-cell growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6149–6153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J., Paul W. E. Production of a monoclonal antibody to and molecular characterization of B-cell stimulatory factor-1. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):333–336. doi: 10.1038/315333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver K., Noelle R. J., Uhr J. W., Krammer P. H., Vitetta E. S. B-cell growth factor (B-cell growth factor I or B-cell-stimulating factor, provisional 1) is a differentiation factor for resting B cells and may not induce cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2465–2467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puré E., Vitetta E. S. The murine B cell response to TNP-polyacrylamide beads: the relationship between the epitope density of the antigen and the requirements for T cell help and surface IgD. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):420–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Burger C., Klein S., Müller W. Control of immunoglobulin class switch recombination. Immunol Rev. 1986 Feb;89:69–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Müller W., Rajewsky K. Class switch recombination is IgG1 specific on active and inactive IgH loci of IgG1-secreting B-cell blasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3954–3957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Clarke P., Salser W. Sequence analysis of cloned cDNA encoding part of an immunoglobulin heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3305–3321. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman P., Lutzker S., Cook W., Coffman R., Alt F. W. Mitogen plus interleukin 4 induction of C epsilon transcripts in B lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2385–2389. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):801–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Finkelman F. D., Paul W. E. Differential regulation of IgG1 and IgE synthesis by interleukin 4. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):183–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Finkelman F. D., Stefany D., Conrad D. H., Paul W. E. IL-4 induces co-expression of intrinsic membrane IgG1 and IgE by murine B cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. B cell stimulatory factor-1 (interleukin 4) prepares resting murine B cells to secrete IgG1 upon subsequent stimulation with bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):10–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer-Nordgren J., Sirlin S. Specificity of immunoglobulin heavy chain switch correlates with activity of germline heavy chain genes prior to switching. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):95–102. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavnezer J., Radcliffe G., Lin Y. C., Nietupski J., Berggren L., Sitia R., Severinson E. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain switching may be directed by prior induction of transcripts from constant-region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7704–7708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Ohara J., Myers C. D., Layton J. E., Krammer P. H., Paul W. E. Serological, biochemical, and functional identity of B cell-stimulatory factor 1 and B cell differentiation factor for IgG1. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1726–1731. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Krawinkel U., Radbruch A. Directed Ig class switch recombination in activated murine B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1663–1671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Alt F. W. Developmentally controlled and tissue-specific expression of unrearranged VH gene segments. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D., Weiss E. A., Layton J. E., Krammer P. H., Vitetta E. S. Activation of the gamma 1 gene by lipopolysaccharide and T cell-derived lymphokines containing a B cell differentiation factor for IgG1 (BCDF gamma). J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1465–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]