Abstract
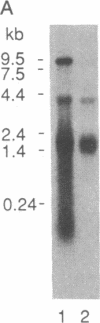
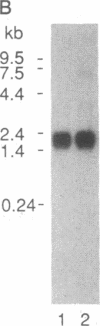
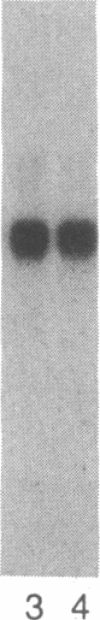
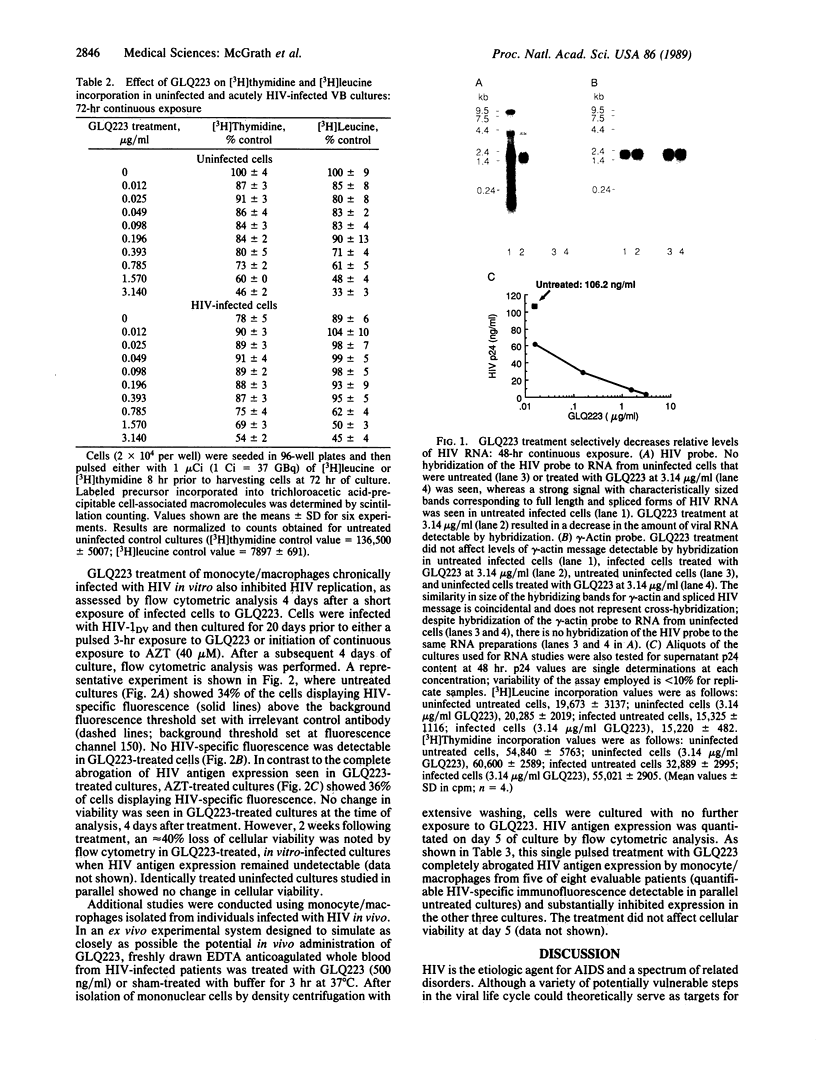
GLQ223 is a highly purified, formulated preparation of trichosanthin, a 26-kDa plant-derived ribosome-inactivating protein with potent inhibitory activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vitro. The compound produced concentration-dependent inhibition of HIV replication in acutely infected cultures of T-lymphoblastoid cells (VB cell line). Treatment with GLQ223 selectively reduced levels of detectable viral proteins compared to total cellular protein synthesis and produced a selective decrease in levels of viral RNA relative to total cellular RNA in acutely infected cells. Substantial inhibition of viral replication was observed at concentrations of GLQ223 that showed little inhibition of parallel uninfected cultures. Selective anti-HIV activity was also observed in cultures of primary monocyte/macrophages chronically infected with HIV in vitro. When freshly drawn blood samples from HIV-infected patients were treated with a single 3-hr exposure to GLQ223. HIV replication was blocked for at least 5 days in subsequently cultured monocyte/macrophages, without further treatment. The anti-HIV activity of GLQ223 in both acutely and chronically infected cells and its activity in cells of both lymphoid and mononuclear phagocytic lineage make it an interesting candidate as a potential therapeutic agent in HIV infection and AIDS.
Full text
PDF

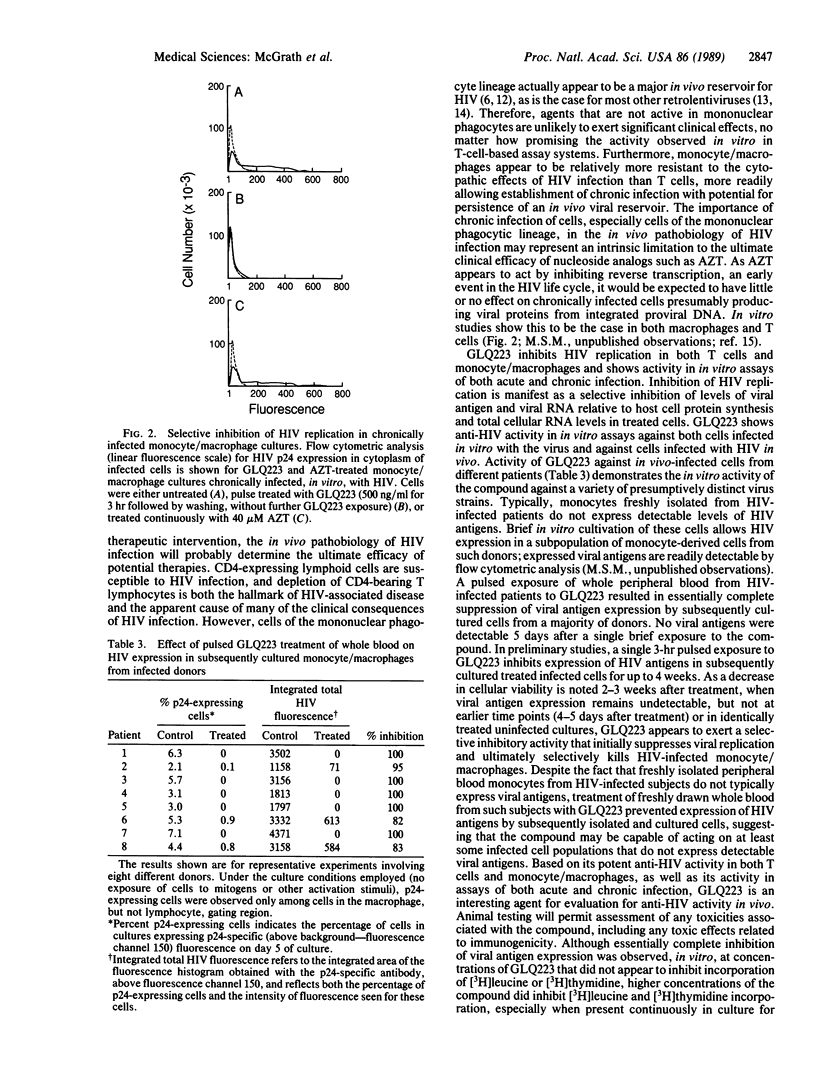

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe S., Mills J., McGrath M. S. Quantitative immunocytofluorographic analysis of CD4 surface antigen expression and HIV infection of human peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Summer;3(2):135–145. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Puentes C., Carrasco L. Viral infection permeabilizes mammalian cells to protein toxins. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):769–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Collalti E., Ratner L., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. A molecular clone of HTLV-III with biological activity. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):262–265. doi: 10.1038/316262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foà-Tomasi L., Campadelli-Fiume G., Barbieri L., Stirpe F. Effect of ribosome-inactivating proteins on virus-infected cells. Inhibition of virus multiplication and of protein synthesis. Arch Virol. 1982;71(4):323–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01315062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T. Pathogenesis of lentivirus infections. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):130–136. doi: 10.1038/322130a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo-Fen C. Midtrimester abortion induced by Radix trichosanthis: morphologic observations in placenta and fetus. Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Apr;59(4):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Reyes G. R., McGrath M. S., Stein B. S., Engleman E. G. AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3010463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Cabradilla C. D., Benton C. V., Lasky L. A., Capon D. J. Nucleic acid structure and expression of the human AIDS/lymphadenopathy retrovirus. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):450–458. doi: 10.1038/313450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Zink M. C. Lentivirus-host interactions: lessons from visna and caprine arthritis-encephalitis viruses. Ann Neurol. 1988;23 (Suppl):S95–100. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perno C. F., Yarchoan R., Cooney D. A., Hartman N. R., Gartner S., Popovic M., Hao Z., Gerrard T. L., Wilson Y. A., Johns D. G. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1/HTLV-IIIBa-L) replication in fresh and cultured human peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages by azidothymidine and related 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):1111–1125. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Bailey S., Miller S. P., Bodley J. W. Modification of ribosomal RNA by ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1349–1357. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. J., Wang J. H. Homology of trichosanthin and ricin A chain. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):477–478. doi: 10.1038/321477b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]