Abstract
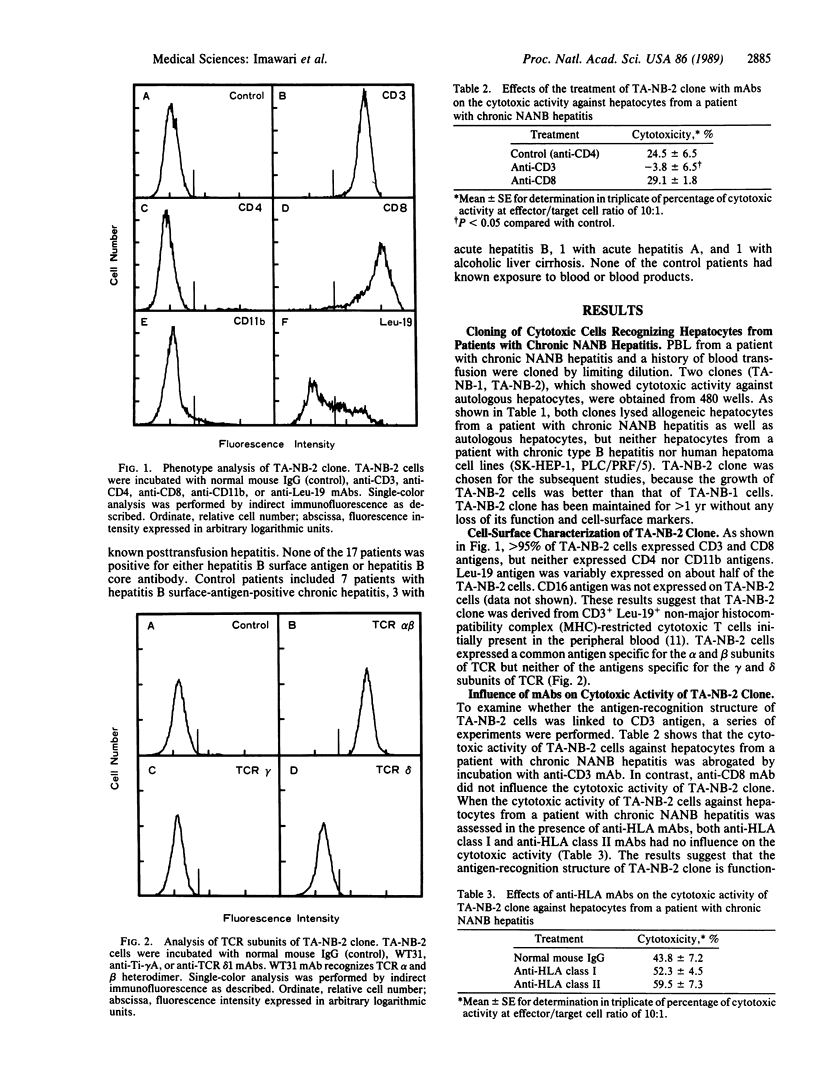
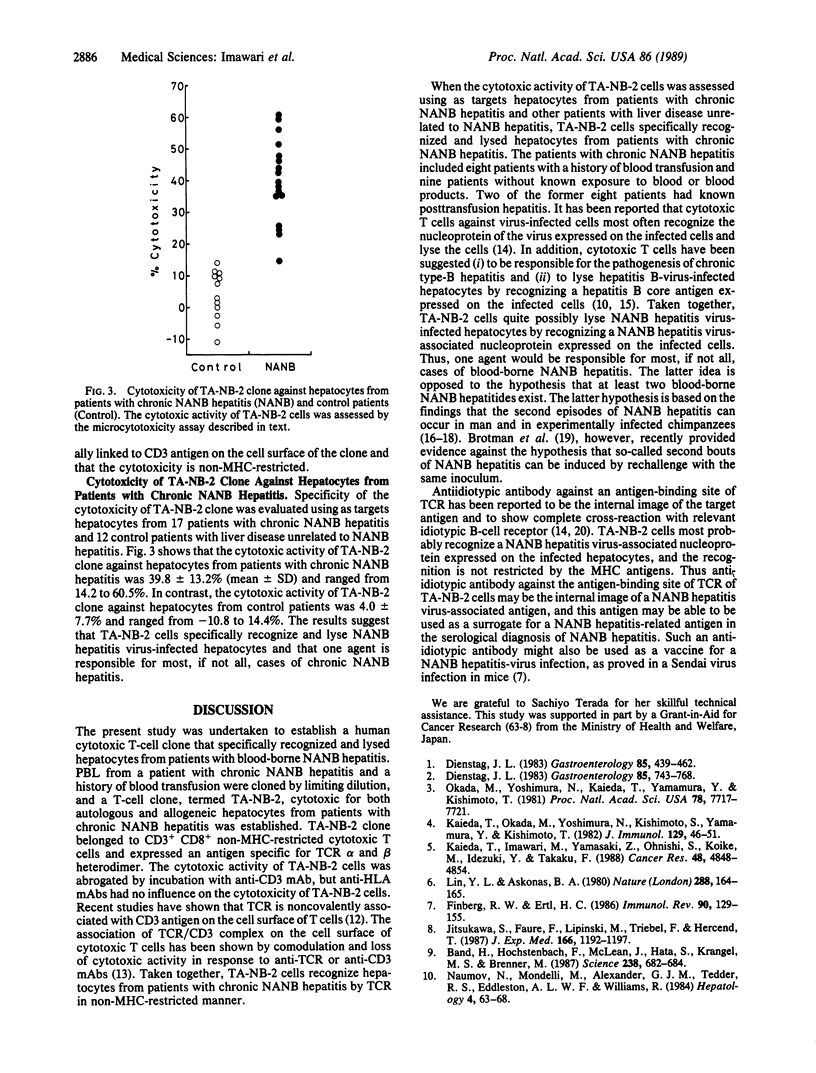
A human T-cell clone (TA-NB-2) that could lyse both autologous and allogeneic hepatocytes from chronic hepatitis patients with type non-A, non-B virus (NANB) was established. This clone produced CD3+ CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes and expressed an antigen specific for alpha and beta subunits of T-cell receptor. The cytotoxic activity of the clone was abrogated by incubation with anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody. Anti-HLA monoclonal antibodies did not block the lysis of the target hepatocytes by TA-NB-2 cells. The cytotoxicity of TA-NB-2 clone against hepatocytes from patients with chronic NANB hepatitis was 39.8 +/- 13.2% (mean +/- SD; n = 17) (range, 14.2-60.5%), whereas that against hepatocytes from control patients with chronic type-B hepatitis, acute hepatitis B, acute hepatitis A, or alcoholic liver cirrhosis was 4.0 +/- 7.7% (n = 12) (range, -10.8 to 14.0%). The results suggest that TA-NB-2 cells specifically recognize a hepatitis NANB-related antigen expressed on hepatitis NANB-infected hepatocytes by T-cell receptor and that the recognition is not restricted by the major histocompatibility complex antigens. The results also suggest that most, if not all, cases of chronic hepatitis due to NANB are caused by one agent; TA-NB-2 clone may be useful as a tool to identify this particular hepatitis-related antigen.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band H., Hochstenbach F., McLean J., Hata S., Krangel M. S., Brenner M. B. Immunochemical proof that a novel rearranging gene encodes the T cell receptor delta subunit. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.3672118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H. Shared idiotypic determinants on B and T lymphocytes reactive against the same antigenic determinants. I. Demonstration of similar or identical idiotypes on IgG molecules and T-cell receptors with specificity for the same alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):197–211. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotman B., Prince A. M., Huima T. Non-A, non-B hepatitis: is there more than a single blood-borne strain? J Infect Dis. 1985 Apr;151(4):618–625. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.4.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L. Non-A, non-B hepatitis. I. Recognition, epidemiology, and clinical features. Gastroenterology. 1983 Aug;85(2):439–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L. non-A, Non-B hepatitis. II. Experimental transmission, putative virus agents and markers, and prevention. Gastroenterology. 1983 Sep;85(3):743–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finberg R. W., Ertl H. C. Use of T cell-specific anti-idiotypes to immunize against viral infections. Immunol Rev. 1986 Apr;90:129–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1986.tb01481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jitsukawa S., Faure F., Lipinski M., Triebel F., Hercend T. A novel subset of human lymphocytes with a T cell receptor-gamma complex. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1192–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaieda T., Imawari M., Yamasaki Z., Ohnishi S., Koike M., Idezuki Y., Takaku F. Identification of a tumor-associated target antigen, ATM-1, for a human T-cell clone with activated killer activity and its existence in sera of cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 1;48(17):4848–4854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaieda T., Okada M., Yoshimura N., Kishimoto S., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. A human helper T cell clone secreting both killer helper factor(s) and T cell-replacing factor(s). J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L. Y., Askonas B. A. Cross-reactivity for different type A influenza viruses of a cloned T-killer cell line. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):164–165. doi: 10.1038/288164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Acuto O., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Evidence for the T3-associated 90K heterodimer as the T-cell antigen receptor. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):808–810. doi: 10.1038/303808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Hussey R. E., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Clonotypic structures involved in antigen-specific human T cell function. Relationship to the T3 molecular complex. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley J. W., Redeker A. G., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H. Mutliple hepatitis viruses in multiple attacks of acute viral hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 13;296(2):75–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701132960204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov N. V., Mondelli M., Alexander G. J., Tedder R. S., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Relationship between expression of hepatitis B virus antigens in isolated hepatocytes and autologous lymphocyte cytotoxicity in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkrans G., Frösner G., Hermodsson S., Iwarson S. Multiple hepatitis attacks in drug addicts. JAMA. 1980 Mar 14;243(10):1056–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada M., Yoshimura N., Kaieda T., Yamamura Y., Kishimoto T. Establishment and characterization of human T hybrid cells secreting immunoregulatory molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7717–7721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Norley S., Martin S. Antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction and vaccination. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):16–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor E., Snoy P., Jackson D. R., Schaff Z., Blatt P. M., Gerety R. J. Additional evidence for more than one agent of human non-A, non-B hepatitis. Transmission and passage studies in chimpanzees. Transfusion. 1984 May-Jun;24(3):224–230. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24384225027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



