Abstract
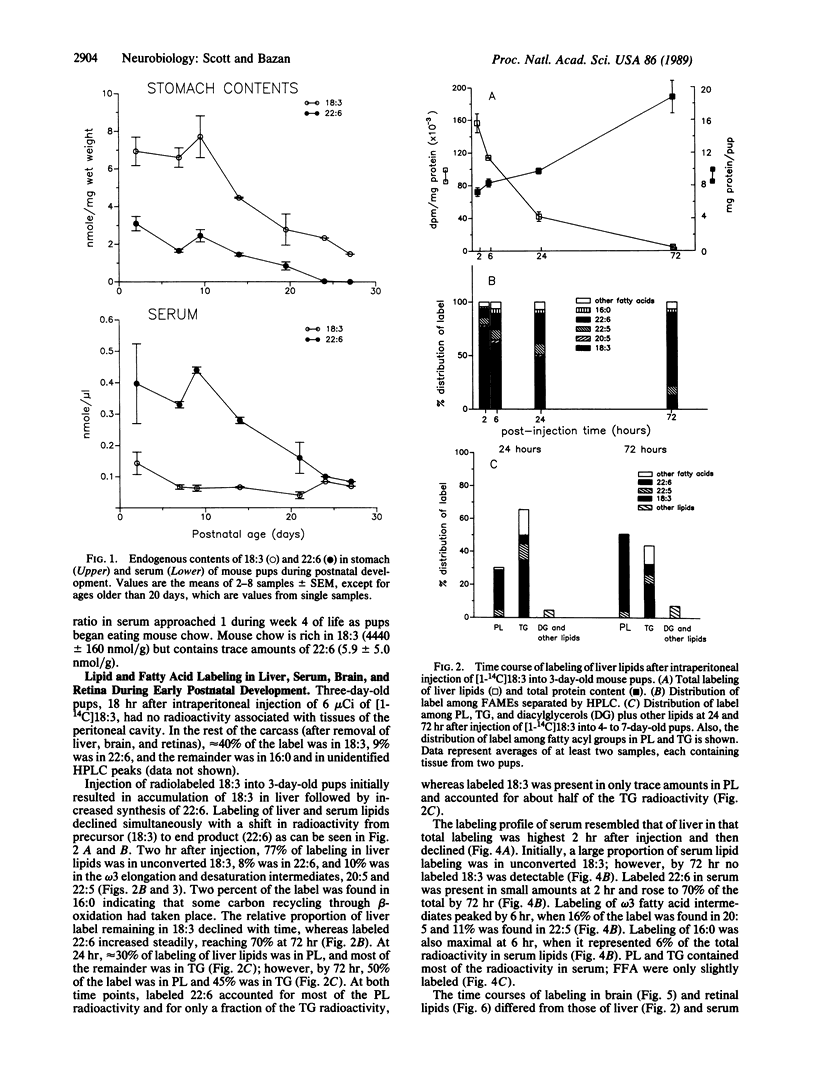
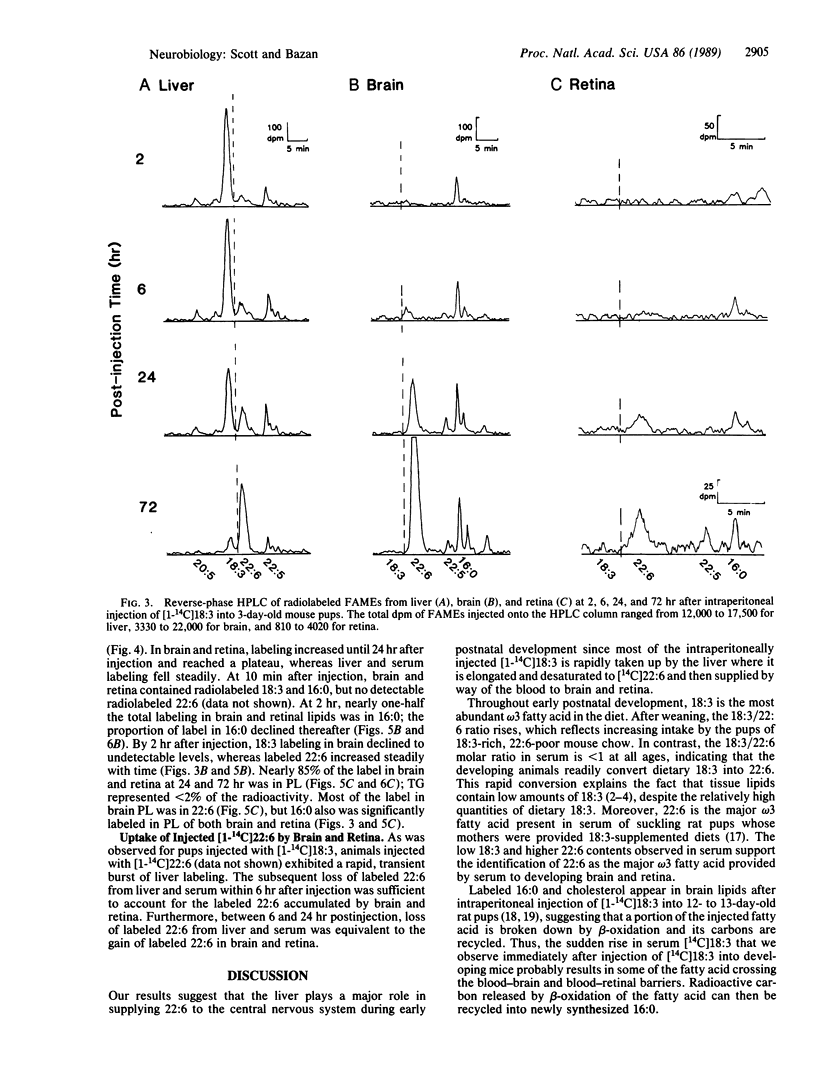
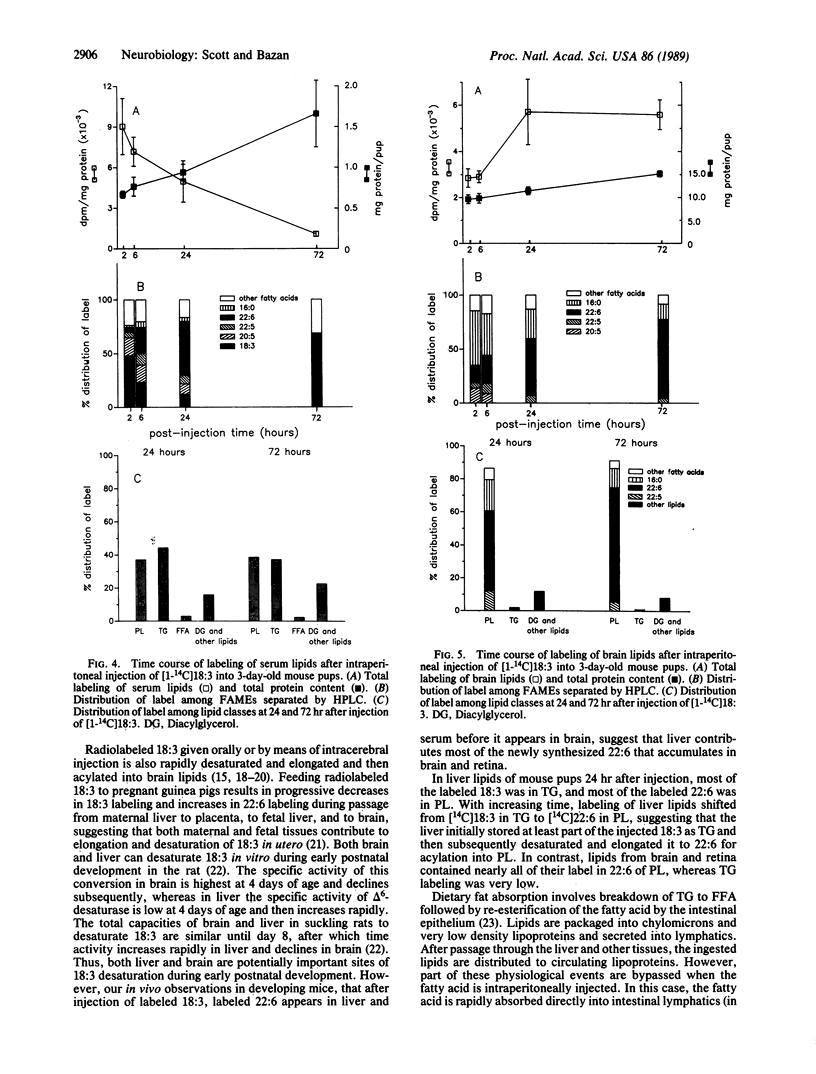
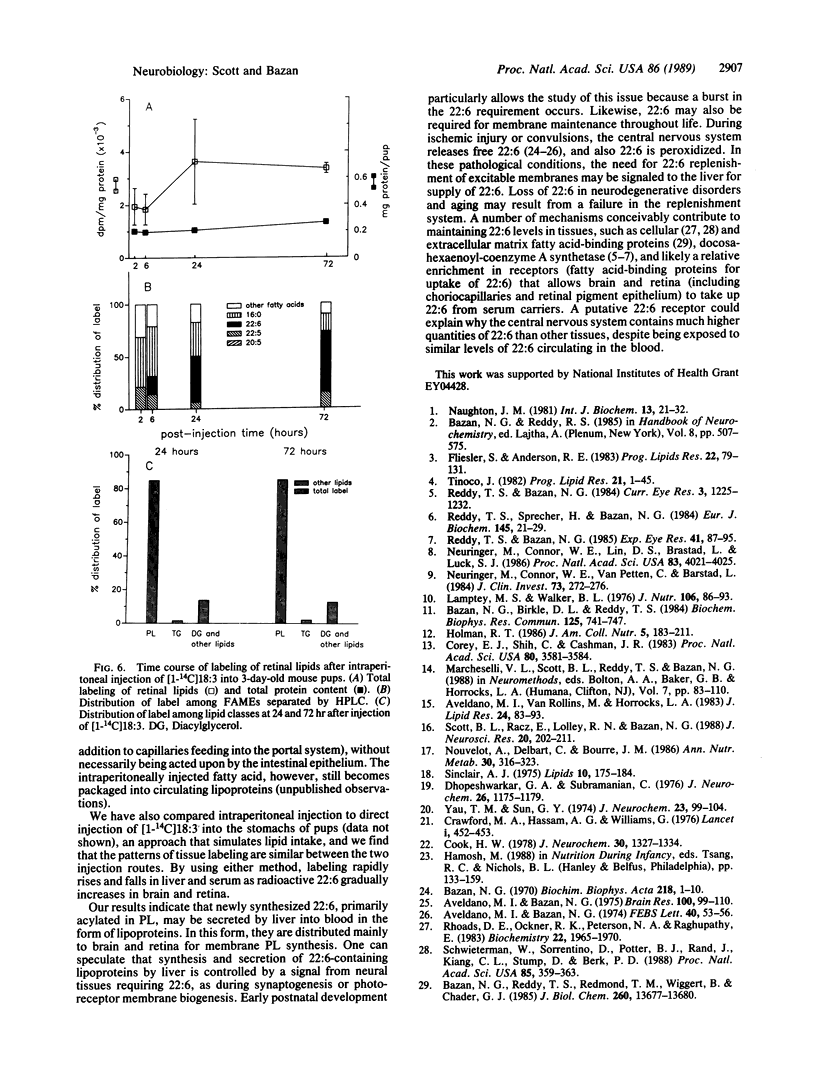
Docosahexaenoic acid [22:6 omega 3; 22:6(4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19)] is concentrated in phospholipids of cellular membranes from brain and retina. Although linolenic acid [18:3 omega 3; 18:3(9, 12, 15)] is the major omega 3 fatty acid of mouse dams' milk, 22:6 is the prevalent omega 3 fatty acid in serum and tissues. Intraperitoneal injection of [1-14C]18:3 into 3-day-old mouse pups resulted in liver and serum lipid labeling that was initially high, followed by a rapid decline. In contrast, labeling of brain and retinal lipids were initially low and increased with time. Labeled 22:6 first appeared in liver 2 hr after injection and later in brain and retina. We suggest that 22:6 synthesized from 18:3 by the liver is secreted into the bloodstream in lipoproteins, taken up by brain and retina, and incorporated into cell membranes. We hypothesize that the 22:6 requirements of membranes (e.g., during synaptogenesis, photoreceptor membrane biogenesis, or repair after ischemic injury or neurodegenerative disorders) are met by a signal that is sent by the appropriate tissues to the liver to evoke the secretion of 22:6-containing lipoproteins.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aveldano M. I., VanRollins M., Horrocks L. A. Separation and quantitation of free fatty acids and fatty acid methyl esters by reverse phase high pressure liquid chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jan;24(1):83–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveldaño M. I., Bazán N. G. Differential lipid deacylation during brain ischemia in a homeotherm and a poikilotherm. Content and composition of free fatty acids and triacylglycerols. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aveldaño M. I., Bazán N. G. Displacement into incubation medium by albumin of highly unsaturated retina free fatty acids arising from membrane lipids. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80892-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan N. G., Birkle D. L., Reddy T. S. Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6, n-3) is metabolized to lipoxygenase reaction products in the retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90601-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan N. G., Reddy T. S., Redmond T. M., Wiggert B., Chader G. J. Endogenous fatty acids are covalently and noncovalently bound to interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein in the monkey retina. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13677–13680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazán N. G., Jr Effects of ischemia and electroconvulsive shock on free fatty acid pool in the brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 6;218(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook H. W. In vitro formation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by desaturation in rat brain: some properties of the enzymes in developing brain and comparisons with liver. J Neurochem. 1978 Jun;30(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb10463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey E. J., Shih C., Cashman J. R. Docosahexaenoic acid is a strong inhibitor of prostaglandin but not leukotriene biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford M. A., Hassam A. G., Williams G. Essential fatty acids and fetal brain growth. Lancet. 1976 Feb 28;1(7957):452–453. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhopeshwarkar G. A., Subramanian C. Intracranial conversion of linoleic acid to arachidonic acid: evidence for lack of delta8 desaturase in the brain. J Neurochem. 1976 Jun;26(6):1175–1179. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb07003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliesler S. J., Anderson R. E. Chemistry and metabolism of lipids in the vertebrate retina. Prog Lipid Res. 1983;22(2):79–131. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(83)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman R. T. Control of polyunsaturated acids in tissue lipids. J Am Coll Nutr. 1986;5(2):183–211. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1986.10720125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamptey M. S., Walker B. L. A possible essential role for dietary linolenic acid in the development of the young rat. J Nutr. 1976 Jan;106(1):86–93. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naughton J. M. Supply of polyenoic fatty acids to the mammalian brain: the ease of conversion of the short-chain essential fatty acids to their longer chain polyunsaturated metabolites in liver, brain, placenta and blood. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90132-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer M., Connor W. E., Lin D. S., Barstad L., Luck S. Biochemical and functional effects of prenatal and postnatal omega 3 fatty acid deficiency on retina and brain in rhesus monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4021–4025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer M., Connor W. E., Van Petten C., Barstad L. Dietary omega-3 fatty acid deficiency and visual loss in infant rhesus monkeys. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):272–276. doi: 10.1172/JCI111202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouvelot A., Delbart C., Bourre J. M. Hepatic metabolism of dietary alpha-linolenic acid in suckling rats, and its possible importance in polyunsaturated fatty acid uptake by the brain. Ann Nutr Metab. 1986;30(5):316–323. doi: 10.1159/000177209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy T. S., Bazan N. G. Synthesis of arachidonoyl coenzyme A and docosahexaenoyl coenzyme A in retina. Curr Eye Res. 1984 Oct;3(10):1225–1232. doi: 10.3109/02713688409000826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy T. S., Bazan N. G. Synthesis of docosahexaenoyl-, arachidonoyl- and palmitoyl-coenzyme A in ocular tissues. Exp Eye Res. 1985 Jul;41(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(85)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy T. S., Sprecher H., Bazan N. G. Long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase from rat brain microsomes. Kinetic studies using [1-14C]docosahexaenoic acid substrate. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 15;145(1):21–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. E., Ockner R. K., Peterson N. A., Raghupathy E. Modulation of membrane transport by free fatty acids: inhibition of synaptosomal sodium-dependent amino acid uptake. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1965–1970. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwieterman W., Sorrentino D., Potter B. J., Rand J., Kiang C. L., Stump D., Berk P. D. Uptake of oleate by isolated rat adipocytes is mediated by a 40-kDa plasma membrane fatty acid binding protein closely related to that in liver and gut. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):359–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. L., Racz E., Lolley R. N., Bazan N. G. Developing rod photoreceptors from normal and mutant Rd mouse retinas: altered fatty acid composition early in development of the mutant. J Neurosci Res. 1988;20(2):202–211. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490200209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. J. Incorporation of radioactive polyunsaturated fatty acids into liver and brain of developing rat. Lipids. 1975 Mar;10(3):175–184. doi: 10.1007/BF02534156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco J. Dietary requirements and functions of alpha-linolenic acid in animals. Prog Lipid Res. 1982;21(1):1–45. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(82)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau T. M., Sun G. Y. The metabolism of (1-14C)arachidonic acid in the neutral glycerides and phosphoglycerides of mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1974 Jul;23(1):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



