Abstract
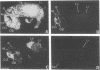
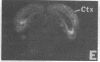
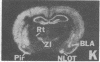
mRNAs for isozymes of phospholipase C (PLC) were localized in rat brain by in situ hybridization with oligonucleotide probes for PLC isozymes I, II, and III of Rhee's group [Suh, P.-G., Ryu, S. H., Moon, K. H., Suh, H. W. & Rhee, S. G. (1988) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5419-5423 and (1988) Cell 54, 161-169], and isozyme I of Bennett and Crooke [Bennett, C. F., Balcarek, J. M., Varrichio, A. & Crooke, S. T. (1988) Nature (London) 334, 268-270], which we designate PLC-A. The isozymes displayed different localizations. PLC-A mRNA was highest in the mitral cell layer of the olfactory bulb, choroid plexus, hippocampus and dentate gyrus, magnocellular hypothalamic nuclei, rostral raphe nuclei, and cerebellar Purkinje cells. PLC-I was highest in the internal granular cell layer of the olfactory bulb, cerebral cortex, caudate, nucleus of the lateral olfactory tract, reticular nucleus of thalamus, hippocampus and dentate gyrus, and granule cell layer of the cerebellum. PLC-II had a more widespread distribution, with relatively high levels in the internal granular layer of the olfactory bulb, hippocampus and dentate gyrus, and cerebellar Purkinje and granule cells. PLC-III label was low throughout the brain. These distributions suggest selective coupling of individual PLC isozymes with particular postsynaptic receptors. PLC-A may be preferentially associated with 5-hydroxytryptamine 1C receptors, vasopressin V1 receptors, and a subtype of glutamate receptors. PLC-I may be linked to muscarinic m1 and m3 receptors as well as other receptors. The distribution of PLC-II mRNA resembles that of src protooncogene, with which it displays sequence homology.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett C. F., Balcarek J. M., Varrichio A., Crooke S. T. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):268–270. doi: 10.1038/334268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Crooke S. T. Purification and characterization of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C from guinea pig uterus. Phosphorylation by protein kinase C in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13789–13797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakely R. D., Coyle J. T. The neurobiology of N-acetylaspartylglutamate. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1988;30:39–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Buckley N. J., Young A. C., Brann M. R. Identification of a family of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):527–532. doi: 10.1126/science.3037705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M., Young W. S., 3rd Distinct patterns of expression of different protein kinase C mRNAs in rat tissues. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley N. J., Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Localization of a family of muscarinic receptor mRNAs in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Dec;8(12):4646–4652. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-12-04646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui T., Lutz R. J., Lowenstein J. M. Purification of a phospholipase C from rat liver cytosol that acts on phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17730–17737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Choi W. C., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Phospholipase C I and II brain isozymes: immunohistochemical localization in neuronal systems in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3208–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Identification and properties of two distinct phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzymes from sheep seminal vesicular glands. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6461–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Imaki J., Nakanishi O., Takenawa T. Isolation and characterization of two different forms of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6592–6598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M. Signal processing in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Physiol Bohemoslov. 1987;36(3):203–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knigge K. M., Piekut D. T., Berlove D. J., Junig J. T., Melrose P. A. Staining of magnocellular neurons of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei with vasopressin anti-idiotype antibody: a potential method for receptor immunocytochemistry. Brain Res. 1987 Apr;388(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Jones D. T., Reed R. R., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. G protein mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Sugimori M. Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:197–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. N., Miller R. J. A glutamate receptor regulates Ca2+ mobilization in hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. M., Greenamyre J. T., Penney J. B., Young A. B. Autoradiographic localization of cerebellar excitatory amino acid binding sites in the mouse. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92969-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):205–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Differential regulation of PI hydrolysis and adenylyl cyclase by muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):434–437. doi: 10.1038/334434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Wright G. E., Resh M. D., Pearson R. C., Snyder S. H. Brain-specific src oncogene mRNA mapped in rat brain by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9831–9835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladeczek F., Pin J. P., Récasens M., Bockaert J., Weiss S. Glutamate stimulates inositol phosphate formation in striatal neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 24;317(6039):717–719. doi: 10.1038/317717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tecott L. H., Barchas J. D., Eberwine J. H. In situ transcription: specific synthesis of complementary DNA in fixed tissue sections. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2454508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiklund L., Toggenburger G., Cuénod M. Aspartate: possible neurotransmitter in cerebellar climbing fibers. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):78–80. doi: 10.1126/science.6121375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Oster-Granite M. L., Herndon R. M., Snyder S. H. Glutamic acid: selective depletion by viral induced granule cell loss in hamster cerebellum. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 14;73(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)91002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry reveals increased levels of corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA after adrenalectomy in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 8;70(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]