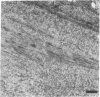
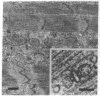
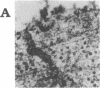
Abstract
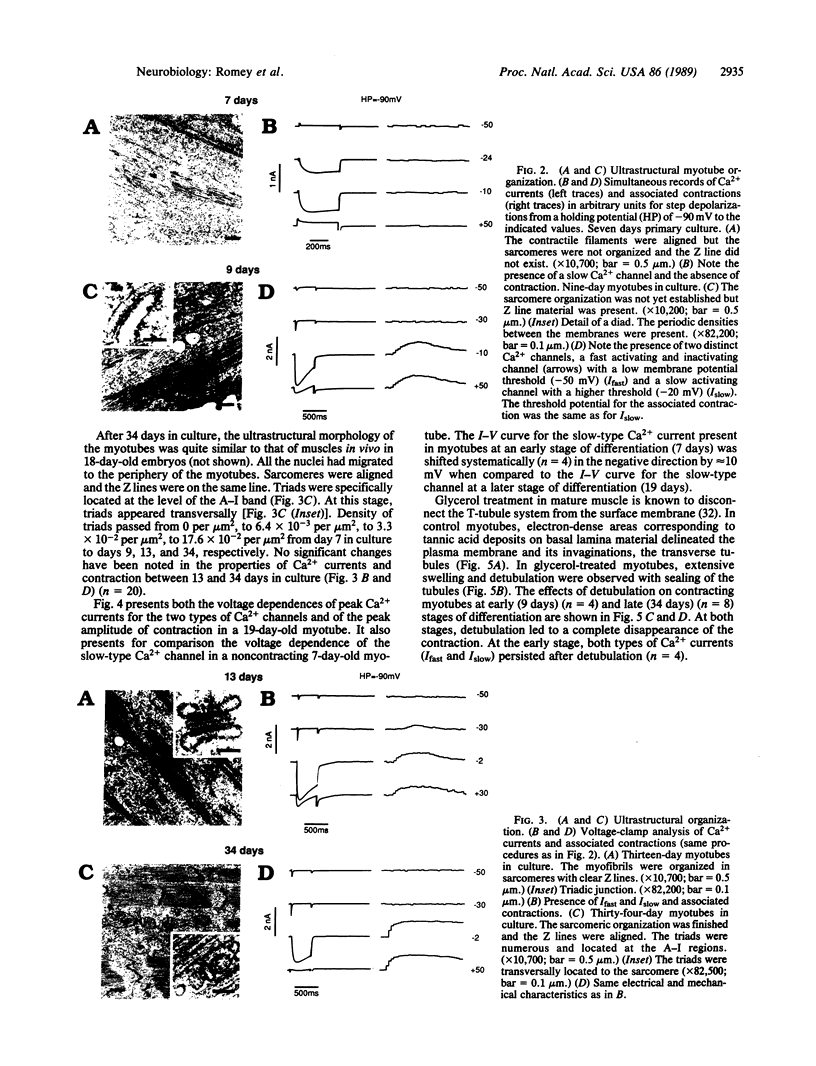
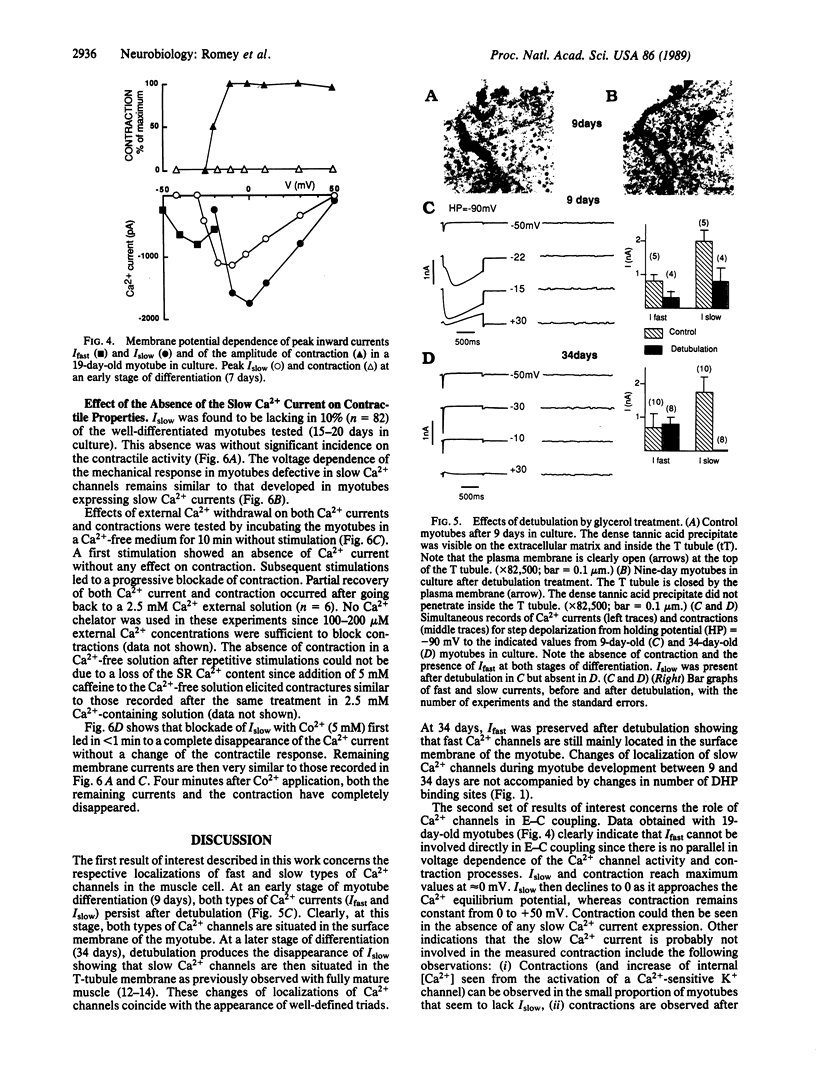
The mechanism of excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling in skeletal muscle is not yet well established. Cultured mouse skeletal muscle cells have been used to study the relationships between triad formation, Ca2+ channel activities, and contractions. The ontogenesis of voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and their localization in relation to the ability of muscle to contract and the ultrastructural organization of sarcomeres and triads have been investigated by using an electrophysiological approach together with an electron microscope study. At an early stage of development, both fast (Ifast) and slow (Islow) types of Ca2+ channels are found at the surface membrane. At later stages of development, fast Ca2+ channels remain at the surface membrane, while slow Ca2+ channels migrate to the transverse-tubule membrane. The voltage dependence of fast Ca2+ channels compared to the voltage dependence of contraction clearly shows that these Ca2+ channels have no direct role in E-C coupling. Detubulation at all stages of development has confirmed that T tubules contain essential elements for E-C coupling. However, this work also shows that Ca2+ flowing through slow Ca2+ channels situated in the T-tubular system is not important for contraction. Myotubes lacking slow Ca2+ channels or having no slow Ca2+ channel transport activity (jumps to high membrane potentials, no external Ca2+, block of Islow by Co2+) still retain contraction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Agonists Bay-K8644 and CGP-28392 open calcium channels reconstituted from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83789-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agnew W. S. Dual roles for DHP receptors in excitation--contraction coupling? Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):297–297. doi: 10.1038/328297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Fink R., Palade P. T. Calcium depletion in frog muscle tubules: the decline of calcium current under maintained depolarization. J Physiol. 1981 Mar;312:177–207. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Knudson C. M. Calcium currents in embryonic and neonatal mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jun;91(6):781–798. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beam K. G., Knudson C. M. Effect of postnatal development on calcium currents and slow charge movement in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jun;91(6):799–815. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.6.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Fitts R., Pizarro G., Ríos E. Voltage sensors of the frog skeletal muscle membrane require calcium to function in excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:475–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brum G., Ríos E., Stéfani E. Effects of extracellular calcium on calcium movements of excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:441–473. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillé J., Ildefonse M., Rougier O. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;46(3):185–239. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognard C., Lazdunski M., Romey G. Different types of Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):517–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognard C., Romey G., Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle cells in culture: electrophysiological properties and interactions with Ca2+ channel activator (Bay K8644) and inhibitor (PN 200-110). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo M., Tanaka M., Ogawa Y. Calcium induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skinned skeletal muscle fibres. Nature. 1970 Oct 3;228(5266):34–36. doi: 10.1038/228034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Calcium-induced release of calcium from the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C1–14. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Jaimovich E., Delpont E., Lazdunski M. [3H]nitrendipine receptors in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6086–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of receptor sites for the Ca2+ channel inhibitors d-cis-diltiazem, (+/-)-bepridil, desmethoxyverapamil, and (+)-PN 200-110 in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. [3H] verapamil binding sites in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Fosset M., Romey G., Laduron P., Lazdunski M. Neuroleptics of the diphenylbutylpiperidine series are potent calcium channel inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7513–7517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goll A., Ferry D. R., Glossmann H. Target size analysis and molecular properties of Ca2+ channels labelled with [3H]verapamil. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):177–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig J., Bournaud R., Powell J. A., Rieger F. Appearance of contractile activity in muscular dysgenesis (mdg/mdg) mouse myotubes during coculture with normal spinal cord cells. Dev Biol. 1982 Jul;92(1):188–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Spiecker W. The effects of calcium deprivation upon mechanical and electrophysiological parameters in skeletal muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:411–429. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potreau D., Raymond G. Calcium-dependent electrical activity and contraction of voltage-clamped frog single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Oct;307:9–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qar J., Barhanin J., Romey G., Henning R., Lerch U., Oekonomopulos R., Urbach H., Lazdunski M. A novel high affinity class of Ca2+ channel blockers. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;33(4):363–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Ion channels in cardiac cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:473–484. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.002353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rios E., Brum G. Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):717–720. doi: 10.1038/325717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Garcia L., Rieger F., Lazdunski M. Targets for calcium channel blockers in mammalian skeletal muscle and their respective functions in excitation-contraction coupling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1324–1332. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80777-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Lazdunski M. The coexistence in rat muscle cells of two distinct classes of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels with different pharmacological properties and different physiological functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 30;118(2):669–674. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Hess P., Reeves J. P., Smilowitz H., Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in planar lipid bilayers: insights into mechanisms of ion permeation and gating. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1564–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2420007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., McCleskey E. W., Almers W. Dihydropyridine receptors in muscle are voltage-dependent but most are not functional calcium channels. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):747–751. doi: 10.1038/314747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siri L. N., Sánchez J. A., Stefani E. Effect of glycerol treatment on the calcium current of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:87–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N. Hormonal and neurotransmitter regulation of Ca++ influx through voltage-dependent slow channels in cardiac muscle membrane. Membr Biochem. 1984;5(2):131–166. doi: 10.3109/09687688409150275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani E., Chiarandini D. J. Ionic channels in skeletal muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:357–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]