Abstract
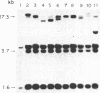
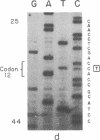
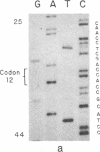
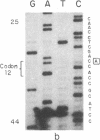
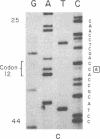
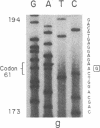
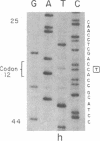
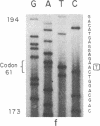
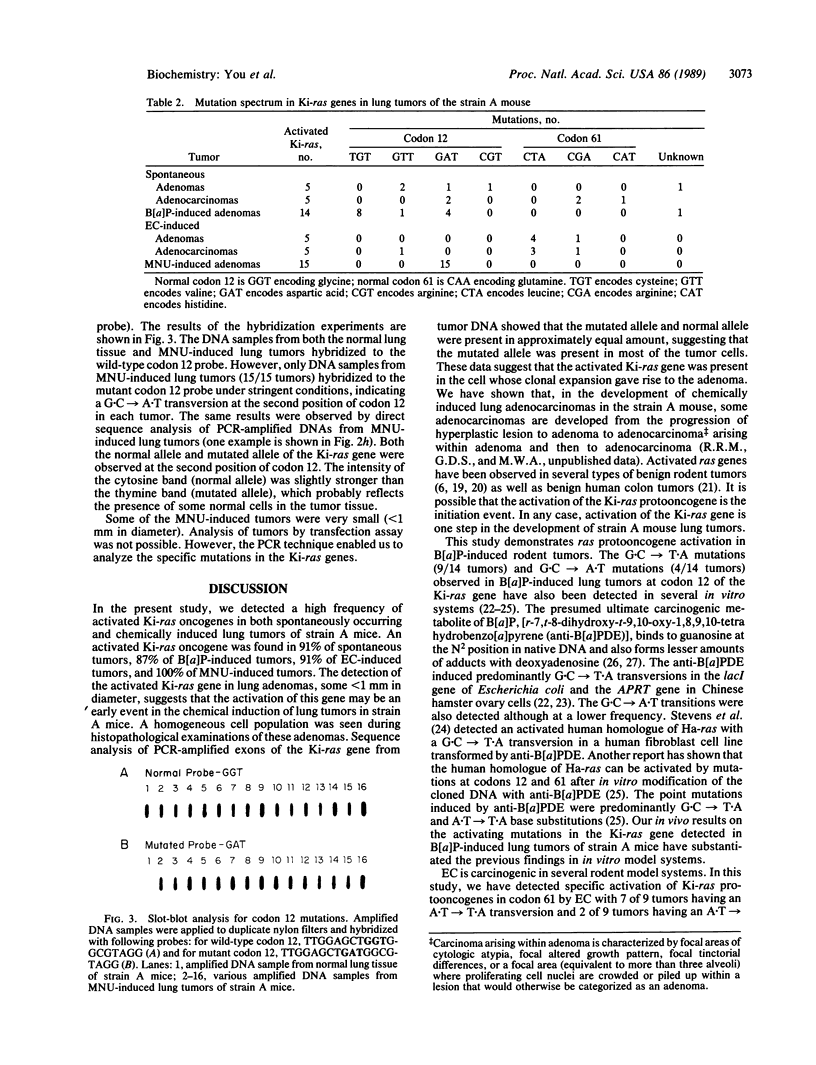
The strain A mouse has a high incidence of spontaneous lung tumors and is susceptible to lung tumor induction by chemical carcinogens. By utilizing transfection assay, Southern blot analysis, and DNA amplification techniques, we have detected an activated Ki-ras gene in the DNAs of both spontaneously occurring and chemically induced lung tumors of strain A mice. The point mutations in the spontaneous lung tumors were in both codon 12 (60%) and codon 61 (30%). In contrast, 100% of the mutations in the Ki-ras gene detected in methylnitrosourea-induced lung tumors and 93% of the mutations in the Ki-ras genes detected in benzo[a]pyrene-induced lung tumors were in codon 12, whereas 90% of the mutations in the Ki-ras genes detected in ethyl carbamate-induced lung tumors were in codon 61. The selectivity of mutations in the Ki-ras oncogene observed in chemically induced tumors, as compared to spontaneous tumors, suggests that these chemicals directly induce point mutations in the Ki-ras protooncogene. These data indicate that the strain A mouse lung tumor model is a very sensitive system to detect the ability of chemicals to activate the Ki-ras protooncogene in lung tissue.
Full text
PDF

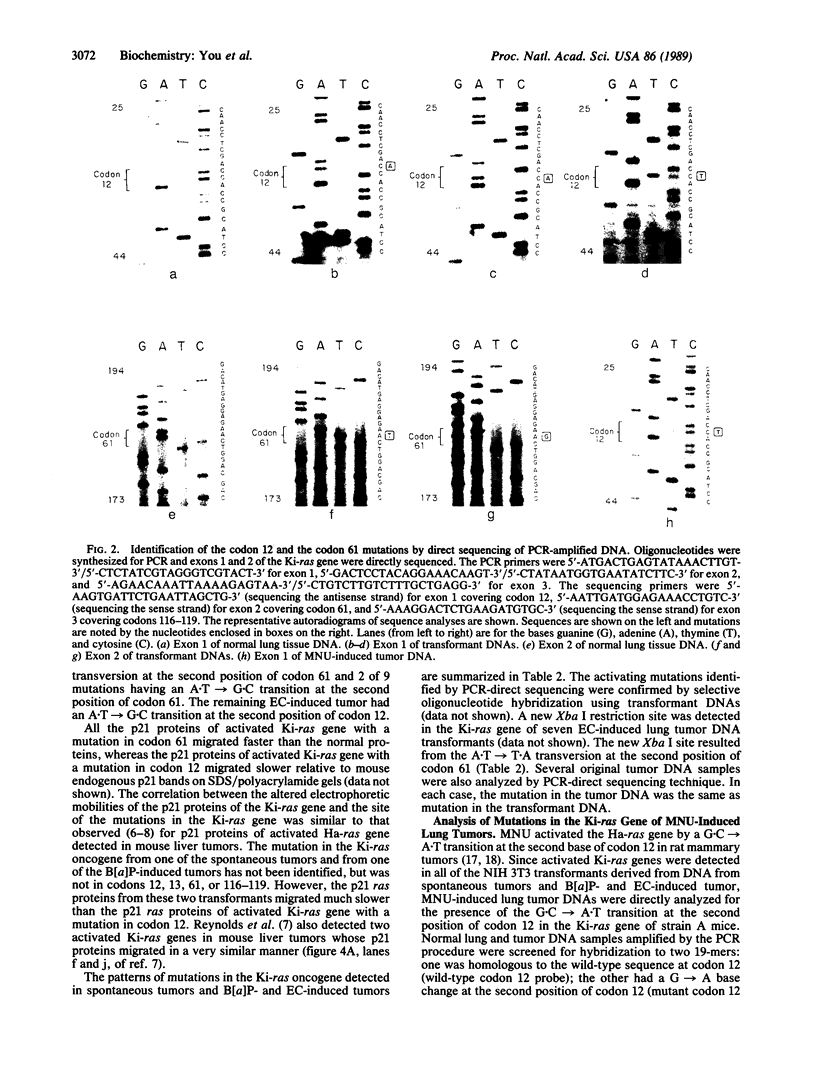

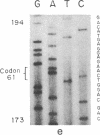
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balmain A., Ramsden M., Bowden G. T., Smith J. Activation of the mouse cellular Harvey-ras gene in chemically induced benign skin papillomas. Nature. 1984 Feb 16;307(5952):658–660. doi: 10.1038/307658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbin A., Besson F., Perrard M. H., Béréziat J. C., Kaldor J., Michel G., Bartsch H. Induction of specific base-pair substitutions in E. coli trpA mutants by chloroethylene oxide, a carcinogenic vinyl chloride metabolite. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov-Dec;152(2-3):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns P. A., Gordon A. J., Glickman B. W. Mutational specificity of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Sep;9(9):1607–1610. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.9.1607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Warren A. J., Porter J., Atkins D., Miller J. H. Carcinogenic epoxides of benzo[a]pyrene and cyclopenta[cd]pyrene induce base substitutions via specific transversions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. R., Watanabe P. G. Detection of a cellular oncogene in spontaneous liver tumors of B6C3F1 mice. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):596–597. doi: 10.1126/science.3983645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Scott A. F., Trusko S., Glick B., Ford E., Dorney D. J. Structure and expression of amplified cKi-ras gene sequences in Y1 mouse adrenal tumor cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1199–1203. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Chang R. L., Wood A. W., Newmark H. L., Sayer J. M., Yagi H., Jerina D. M., Conney A. H. Inhibition of the mutagenicity of bay-region diol-epoxides of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by tannic acid, hydroxylated anthraquinones and hydroxylated cinnamic acid derivatives. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Feb;6(2):237–242. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K. Progression of pulmonary tumor in mice. 1. Histological studies of primary and transplanted pulmonary tumors. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1971 Feb;21(1):13–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1971.tb00108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur M., Glickman B. W. Sequence specificity of mutations induced by benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide at endogenous aprt gene in CHO cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jul;14(4):393–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01534647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Miller E. C. The metabolic activation and nucleic acid adducts of naturally-occurring carcinogens: recent results with ethyl carbamate and the spice flavors safrole and estragole. Br J Cancer. 1983 Jul;48(1):1–15. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1983.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. H., Stowers S. J., Maronpot R. R., Anderson M. W., Aaronson S. A. Detection and identification of activated oncogenes in spontaneously occurring benign and malignant hepatocellular tumors of the B6C3F1 mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):33–37. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds S. H., Stowers S. J., Patterson R. M., Maronpot R. R., Aaronson S. A., Anderson M. W. Activated oncogenes in B6C3F1 mouse liver tumors: implications for risk assessment. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1309–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.3629242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. K., Richardson F. C., Crosby R. M., Swenberg J. A., Skopek T. R. DNA base changes and alkylation following in vivo exposure of Escherichia coli to N-methyl-N-nitrosourea or N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):344–348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenhuis S., van de Wetering M. L., Mooi W. J., Evers S. G., van Zandwijk N., Bos J. L. Mutational activation of the K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 8;317(15):929–935. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710083171504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkin M. B., Stoner G. D. Lung tumors in mice: application to carcinogenesis bioassay. Adv Cancer Res. 1975;21:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60970-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Abbott L. G., Spengler S. J. Assessment of mutagenic efficiency of two carcinogen-modified nucleosides, 1,N6-ethenodeoxyadenosine and O4-methyldeoxythymidine, using polymerases of varying fidelity. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Sep;5(9):1165–1171. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.9.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. W., Manoharan T. H., Fahl W. E. Characterization of mutagen-activated cellular oncogenes that confer anchorage independence to human fibroblasts and tumorigenicity to NIH 3T3 cells: sequence analysis of an enzymatically amplified mutant HRAS allele. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3875–3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. D., Greisiger E. A., Schut H. A., Pereira M. A., Loeb T. R., Klaunig J. E., Branstetter D. G. A comparison of the lung adenoma response in strain A/J mice after intraperitoneal and oral administration of carcinogens. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1984 Feb;72(2):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(84)90316-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowers S. J., Glover P. L., Reynolds S. H., Boone L. R., Maronpot R. R., Anderson M. W. Activation of the K-ras protooncogene in lung tumors from rats and mice chronically exposed to tetranitromethane. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3212–3219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukumar S., Notario V., Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M. Induction of mammary carcinomas in rats by nitroso-methylurea involves malignant activation of H-ras-1 locus by single point mutations. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):658–661. doi: 10.1038/306658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verlaan-de Vries M., Bogaard M. E., van den Elst H., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Bos J. L. A dot-blot screening procedure for mutated ras oncogenes using synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Bos J. L., Marshall C. J., Phillips D. H. Mutations activating human c-Ha-ras1 protooncogene (HRAS1) induced by chemical carcinogens and depurination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1222–1226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg L. W. Inhibitors of chemical carcinogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;26:197–226. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]