Abstract
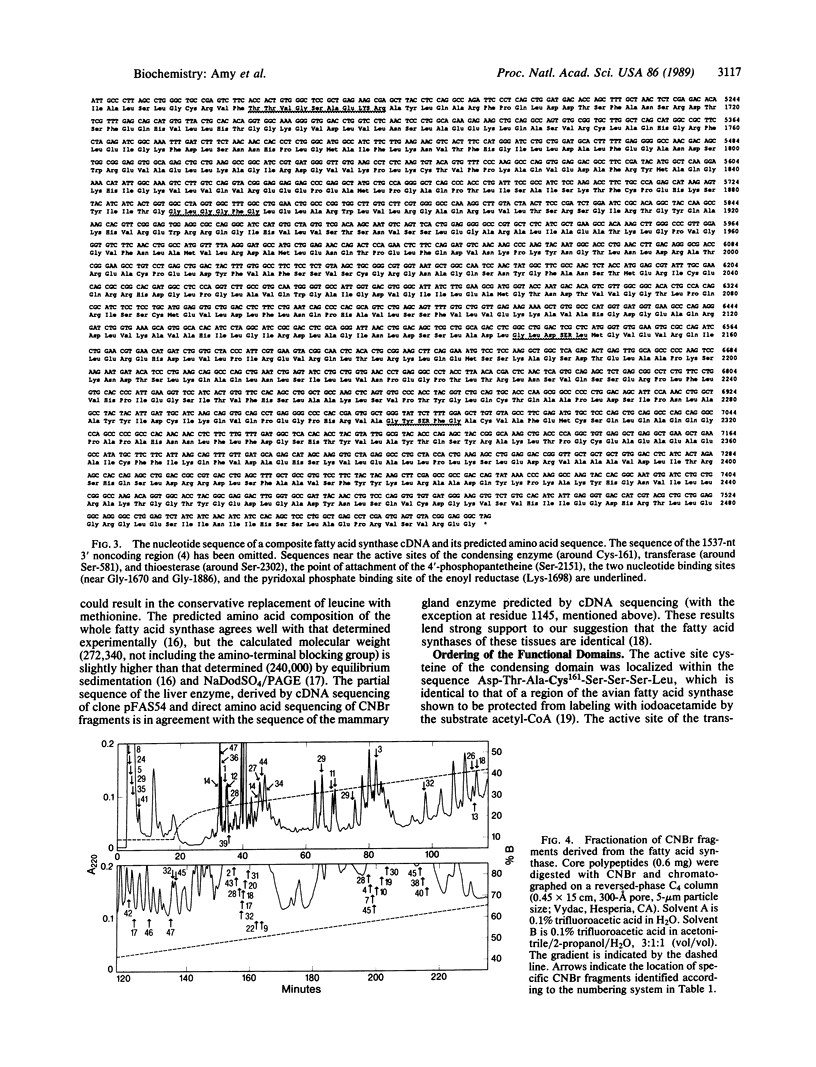
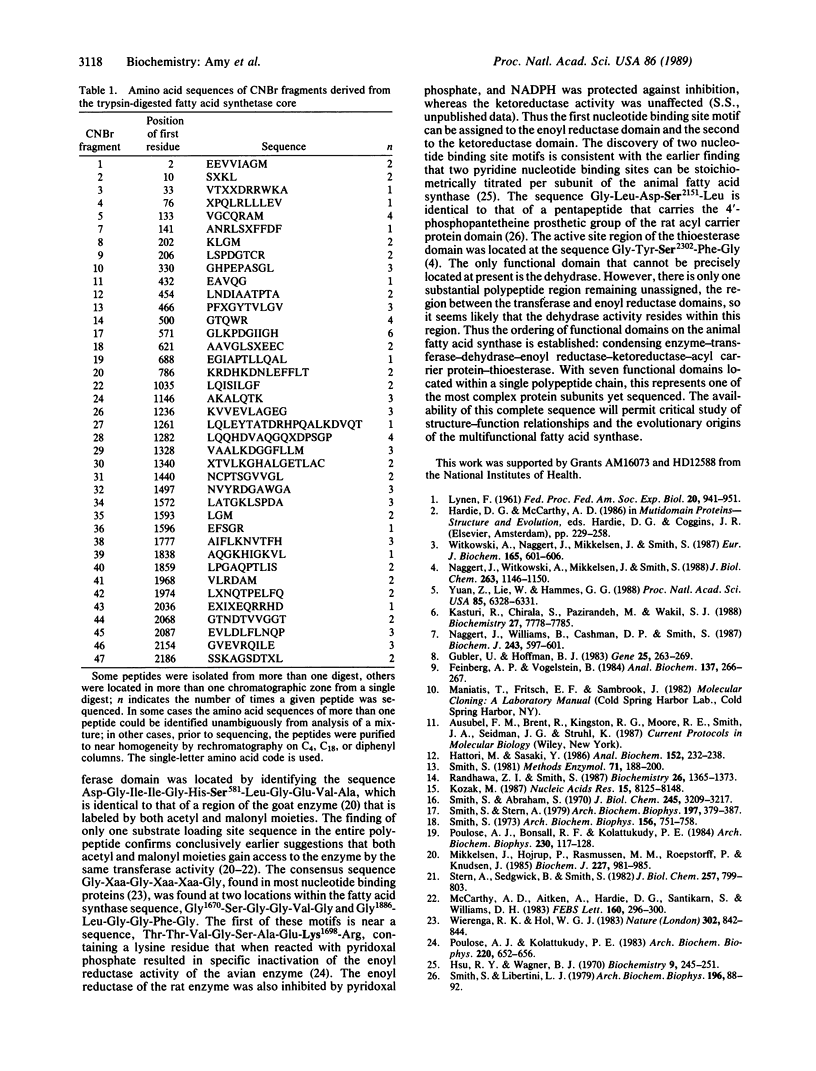
Overlapping cloned cDNAs representing the entire sequence of the rat fatty acid synthase mRNA have been isolated from a cDNA library and sequenced. Authenticity of the cDNA clones was supported by hybridization to fatty acid synthase mRNA and by amino-terminal sequencing of 39 fatty acid synthase CNBr fragments. The full-length fatty acid synthase mRNA is 9156 nucleotides long and includes an 84-nucleotide 5' noncoding region, a 7515-nucleotide coding sequence, and a 1537-nucleotide 3' noncoding region; a second mRNA species containing a shortened 3' noncoding sequence is also transcribed in the rat. The encoded fatty acid synthase subunit contains 2505 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 272,340. Active sites and substrate binding sites were located within the sequence, thus establishing the order of domains on the multifunctional animal fatty acid synthase as condensing enzyme-transferase-dehydrase-enoyl reductase-ketoreductase-acyl carrier protein-thioesterase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu R. Y., Wagner B. J. Reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide binding sites of the fatty acid synthetase of chicken liver. Biochemistry. 1970 Jan 20;9(2):245–251. doi: 10.1021/bi00804a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasturi R., Chirala S., Pazirandeh M., Wakil S. J. Characterization of a genomic and cDNA clone coding for the thioesterase domain and 3' noncoding region of the chicken liver fatty acid synthase gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7778–7785. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYNEN F. Biosynthesis of saturated fatty acids. Fed Proc. 1961 Dec;20:941–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. D., Aitken A., Hardie D. G., Santikarn S., Williams D. H. Amino acid sequence around the active serine in the acyl transferase domain of rabbit mammary fatty acid synthase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 22;160(1-2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80986-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen J., Højrup P., Hansen H. F., Hansen J. K., Knudsen J. Evidence that the medium-chain acyltransferase of lactating-goat mammary-gland fatty acid synthetase is identical with the acetyl/malonyltransferase. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):981–985. doi: 10.1042/bj2270981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naggert J., Williams B., Cashman D. P., Smith S. Cloning and sequencing of the medium-chain S-acyl fatty acid synthetase thioester hydrolase cDNA from rat mammary gland. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):597–601. doi: 10.1042/bj2430597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naggert J., Witkowski A., Mikkelsen J., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the thioesterase domain of the rat fatty acid synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1146–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulose A. J., Bonsall R. F., Kolattukudy P. E. Specific modification of the condensation domain of fatty acid synthase and the determination of the primary structure of the modified active site peptides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Apr;230(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulose A. J., Kolattukudy P. E. Sequence of a tryptic peptide from the NADPH binding site of the enoyl reductase domain of fatty acid synthase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 1;220(2):652–656. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randhawa Z. I., Smith S. Complete amino acid sequence of the medium-chain S-acyl fatty acid synthetase thio ester hydrolase from rat mammary gland. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1365–1373. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Abraham S. Fatty acid synthetase from lactating rat mammary gland. I. Isolation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3209–3217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Libertini L. J. Specificity and site of action of a mammary gland thioesterase which releases acyl moieties from thioester linkage to the fatty acid synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Aug;196(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90554-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. Medium-chain fatty acyl-s-4'-phosphopantetheine-fatty acid synthase thioester hydrolase from lactating mammary gland of rat. Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):188–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71027-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stern A. Subunit structure of the mammalian fatty acid synthetase: further evidence for a homodimer. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 15;197(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. Studies on the immunological cross-reactivity and physical properties of fatty acid synthetases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):751–758. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A., Sedgwick B., Smith S. The free coenzyme A requirement of animal fatty acid synthetase. Participation in the continuous exchange of acetyl and malonyl moieties between coenzyme a thioester and enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):799–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski A., Naggert J., Mikkelsen J., Smith S. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA encoding the acyl carrier protein and its flanking domains in the mammalian fatty acid synthetase. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jun 15;165(3):601–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Z. Y., Liu W., Hammes G. G. Molecular cloning and sequencing of DNA complementary to chicken liver fatty acid synthase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6328–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




