Abstract
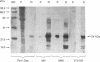
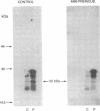
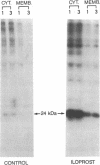
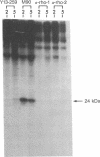
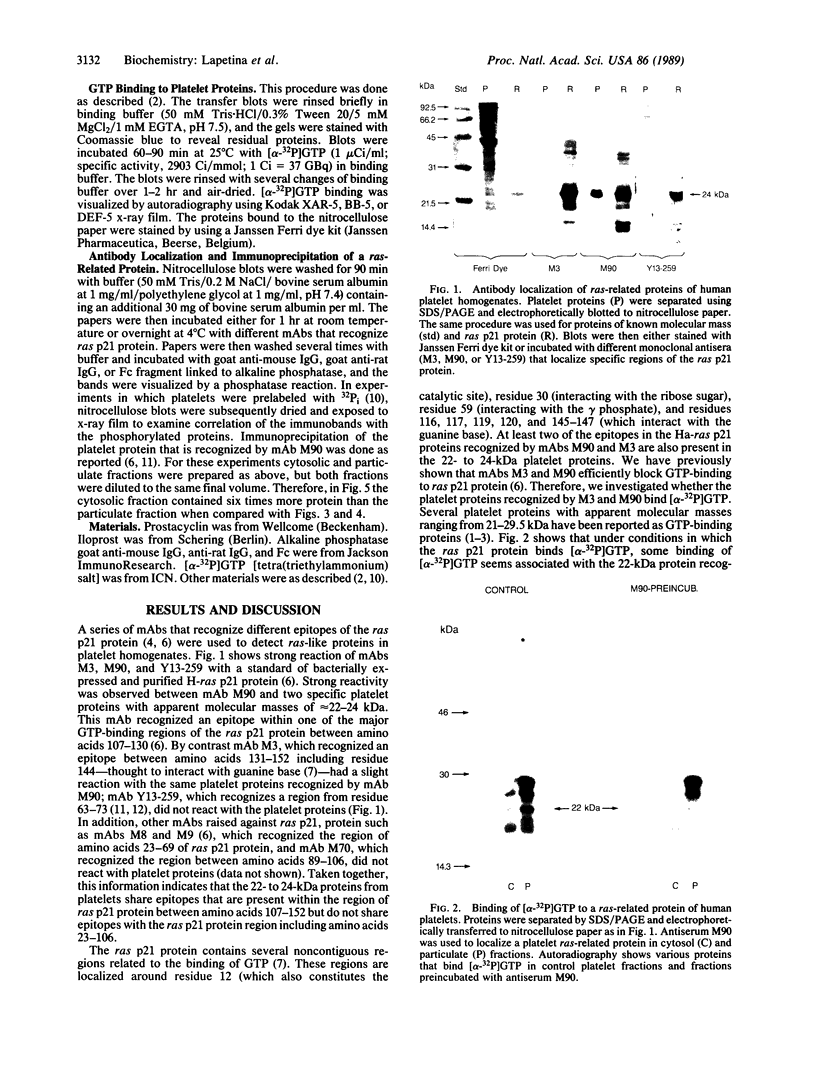
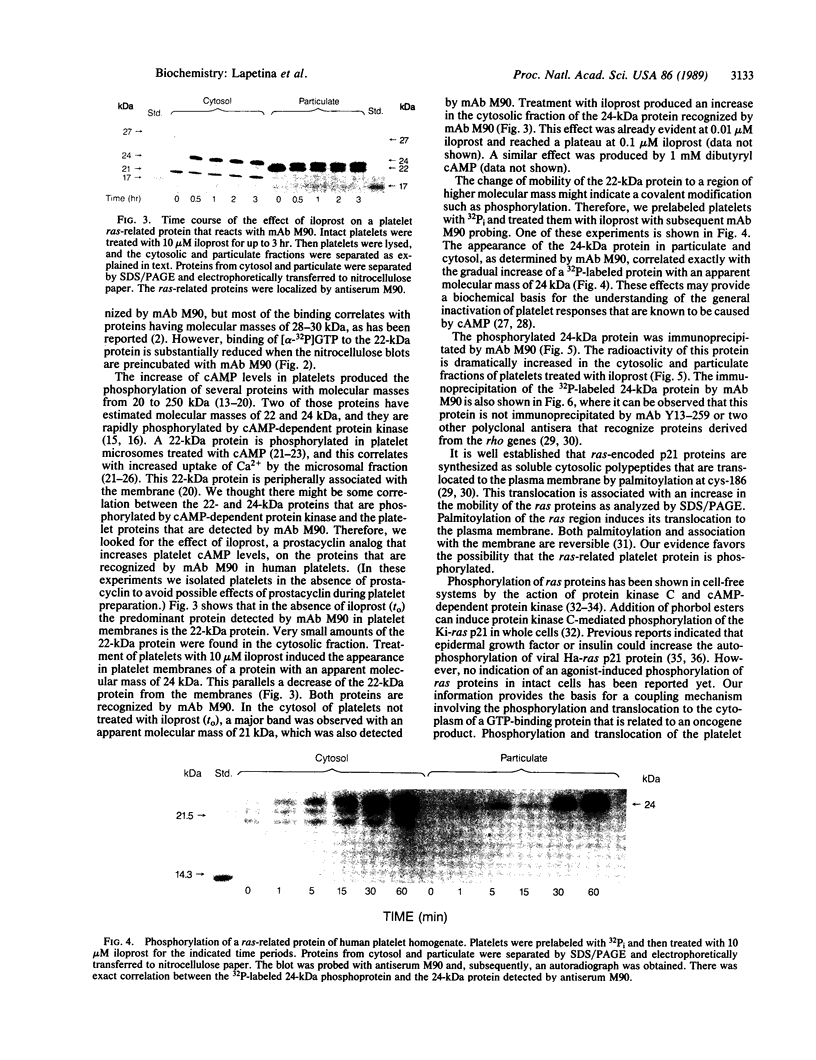
The antigenicity of platelet proteins was assayed against various monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that recognize specific epitopes of the ras-encoded p21 protein. mAb M90, which detects the region of p21 protein within amino acids 107-130 and inhibits its GTP-binding activity, strongly reacted with a 22-kDa protein present in the particulate fraction of human platelets. Other mAbs against ras-encoded proteins, including Y13-259, which efficiently detects ras proteins from a variety of organisms, did not recognize the platelet 22-kDa protein. Transfer of the platelet 22-kDa protein to nitrocellulose paper showed that the protein binds [alpha-32P]GTP. Moreover, preincubation of the transferred protein with mAb M90 drastically reduced its GTP-binding activity. Treatment of platelets with iloprost, a prostacyclin analog, caused (i) a time-dependent increase of a 24-kDa protein that is recognized by mAb M90 in particulate and cytosolic fractions and (ii) the gradual decrease of the 22-kDa protein from the particulate fraction. When platelets were labeled with 32P and then treated with iloprost, the 24-kDa protein was found to be phosphorylated. The 32P-labeled 24-kDa protein was specifically immunoprecipitated by mAb M90. These results suggest that appearance of the 24-kDa protein results from phosphorylation of the 22-kDa protein, which shifts its mobility to a higher molecular mass area.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apitz-Castro R., Fonseca G., Michelena V., Cruz M. R. Inhibition of the platelet reaction by a high molecular weight phosphoglycoprotein isolated from human platelet plasma membranes. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Apr 30;45(2):130–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apitz-Castro R., Ramírez E., Maingon R., de Murciano A., Ribbi A. Plasma membrane phosphorylation by endogenous phosphate donors in human blood platelets. Selectivity of the action of dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 2;455(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90312-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Majerus P. W. Isolation of human platelets and platelet surface membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:149–155. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballester R., Furth M. E., Rosen O. M. Phorbol ester- and protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of the cellular Kirsten ras gene product. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2688–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhullar R. P., Haslam R. J. Detection of 23-27 kDa GTP-binding proteins in platelets and other cells. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 15;245(2):617–620. doi: 10.1042/bj2450617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch M. F., Lapetina E. G. A role for Gi in control of thrombin receptor-phospholipase C coupling in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3363–3371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enouf J., Bredoux R., Boucheix C., Mirshahi M., Soria C., Levy-Toledano S. Possible involvement of two proteins (phosphoprotein and CD9 (p24)) in regulation of platelet calcium fluxes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):398–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80819-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enouf J., Giraud F., Bredoux R., Bourdeau N., Levy-Toledano S. Possible role of a cAMP-dependent phosphorylation in the calcium release mediated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in human platelet membrane vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 2;928(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein M. B., Fraser C. Human platelet secretion and aggregation induced by calcium ionophores. Inhibition by PGE1 and dibutyryl cyclic AMP. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Nov;66(5):561–581. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.5.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T. H., White G. C., 2nd Partial purification and characterization of thrombolamban, a 22,000 dalton cAMP-dependent protein kinase substrate in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):700–706. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90424-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Say A. K., Haslam R. J. Subcellular distribution of the different platelet proteins phosphorylated on exposure of intact platelets to ionophore A23187 or to prostaglandin E1. Possible role of a membrane phosphopolypeptide in the regulation of calcium-ion transport. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 15;184(3):651–661. doi: 10.1042/bj1840651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., Lynham J. A., Fox J. E. Effects of collagen, ionophore A23187 and prostaglandin E1 on the phosphorylation of specific proteins in blood platelets. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):397–406. doi: 10.1042/bj1780397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng A. Y., Srivastava S. K., Lacal J. C., Blumberg P. M. Phosphorylation of ras oncogene product by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jun 15;145(2):782–788. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Feramisco J. R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates guanine nucleotide binding activity and phosphorylation of ras oncogene proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):147–150. doi: 10.1038/310147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Kathuria S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation level of v-Ha-ras protein in membrane fraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya T., Kume S., Tanabe A., Kaneko T., Yamanaka M., Oda T. Effects of prostaglandin E1 on protein kinase activity and endogenous phosphorylation of intact human platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Sep 15;28(18):2747–2751. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90558-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchberger M. A., Tada M., Katz A. M. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase-catalyzed phosphorylation reaction and its relationship to calcium transport in cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6166–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käser-Glanzmann R., Gerber E., Lüscher E. F. Regulation of the intracellular calcium level in human blood platelets: cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate dependent phosphorylation of a 22,000 dalton component in isolated Ca2+-accumulating vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 12;558(3):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Aaronson S. A. Monoclonal antibody Y13-259 recognizes an epitope of the p21 ras molecule not directly involved in the GTP-binding activity of the protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1002–1009. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Aaronson S. A. ras p21 deletion mutants and monoclonal antibodies as tools for localization of regions relevant to p21 function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5400–5404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B. R. Specific binding of [alpha-32P]GTP to cytosolic and membrane-bound proteins of human platelets correlates with the activation of phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2261–2265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Le Peuch D. A., Katz S., Demaille J. G., Hincke M. T., Bredoux R., Enouf J., Levy-Toledano S., Caen J. Regulation of calcium accumulation and efflux from platelet vesicles. Possible role for cyclic-AMP-dependent phosphorylation and calmodulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 23;731(3):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Thrombin-induced protein phosphorylation in human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):924–936. doi: 10.1172/JCI108172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Gutierrez L., McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Dynamic fatty acylation of p21N-ras. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3353–3357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick R. J., Racker E. Phosphorylation of the RAS2 gene product by protein kinase A inhibits the activation of yeast adenylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2474–2478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Lui P., Wang J. H. The use of monoclonal antibodies for the species and tissues distribution of phospholamban. Cell Calcium. 1986 Feb;7(1):41–47. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(86)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace W. C., Bensusan H. B. The effects of platelet secretion inhibitors on protein phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 11;721(2):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Tong L., Milburn M. V., Matias P. M., Jancarik J., Noguchi S., Nishimura S., Miura K., Ohtsuka E., Kim S. H. Three-dimensional structure of an oncogene protein: catalytic domain of human c-H-ras p21. Science. 1988 Feb 19;239(4842):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2448879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]