Abstract
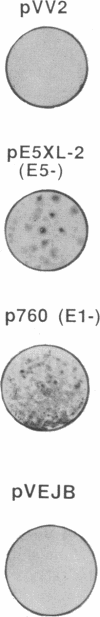
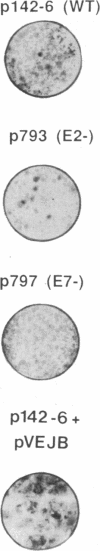
Transfer of neor and bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV1) DNA into rat embryo fibroblasts led to colony formation in G418-containing medium, with no detectable background in controls with neor DNA alone. More than 50% of the drug-resistant clones could be further propagated in culture. The genetic functions of BPV1 involved in colony formation and in long-term immortalization were investigated by both translation termination mutations in the full-length genome, which inactivate individual open reading frames, and constructs in which these open reading frames were separately expressed under control of long terminal repeat promoter enhancers. Expression of either open reading frame E2 or E5 was sufficient for formation of a drug-resistant colony, but long-term growth in culture required that of E6. No significant cooperative effect was observed upon cotransfection of BPV1 and ras oncogene DNAs. Expression of the early region of the human papillomavirus type 16 also led to immortalization of rat embryo fibroblast cells in the same assay, and, unlike what was previously reported in baby rat kidney cells, it required neither activation by a heterologous promoter, nor a cooperating ras oncogene.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahola H., Stenlund A., Moreno-López J., Pettersson U. Promoters and processing sites within the transforming region of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2240–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2240-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2996134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuzin F. The polyoma virus oncogenes. Coordinated functions of three distinct proteins in the transformation of rodent cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 5;781(3):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Guralski D., Schiller J. T. Translation of open reading frame E5 of bovine papillomavirus is required for its transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D. Nonsense mutation in open reading frame E2 of bovine papillomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):475–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.475-480.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Loewenstein P. M. Demonstration that a chemically synthesized BPV1 oncoprotein and its C-terminal domain function to induce cellular DNA synthesis. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):795–802. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Androphy E. J. Bovine papilloma virus-transformed cells contain multiple E2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5864–5868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Kaczmarek L., DiMaio D. Stimulation of cellular DNA synthesis by wild type and mutant bovine papillomavirus DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Baker C. C., Howley P. M. The genetics of bovine papillomavirus type 1. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:235–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallon R. G., Wojciechowicz D., Defendi V. DNA-binding activity of papillomavirus proteins. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1655–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1655-1660.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneguzzi G., Binétruy B., Grisoni M., Cuzin F. Plasmidial maintenance in rodent fibroblasts of a BPV1-pBR322 shuttle vector without immediately apparent oncogenic transformation of the recipient cells. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):365–371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougneau E., Cerni C., Tillier F., Cuzin F. Tumorigenic transformation of rat FR3T3 fibroblasts carrying an activated myc oncogene requires subsequent mutational events. Oncogene Res. 1988;2(2):177–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M. S., Yee C., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 3' early region transformation and plasmid maintenance functions. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Gaudray P., Canning M., Trejo-Avila L., Cuzin F. Two polyoma virus gene functions involved in the expression of the transformed phenotype in FR 3T3 rat cells. I. Localization of a transformation maintenance function in the proximal half of the large T coding region. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Vousden K. H., Lowy D. R. E5 open reading frame of bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes a transforming gene. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.1-6.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade-Glass M., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small, hydrophobic polypeptide. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.3014660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Krämmer G., Dürst M., Suhai S., Röwekamp W. G. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA sequence. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Malignant transformation of early passage rodent cells by a single mutated human oncogene. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):469–475. doi: 10.1038/310469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Zabielski J., Ahola H., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the transforming region of bovine papilloma virus type I. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):541–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Oncogenes and the molecular basis of cancer. Harvey Lect. 1984 1985;80:129–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerlin M., Julius M. A., Cerni C., Marcu K. B. Elevated expression of an exogenous c-myc gene is insufficient for transformation and tumorigenic conversion of established fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1987 Mar;1(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zouzias D., Jha K. K., Mulder C., Basilico C., Ozer H. L. Human fibroblasts transformed by the early region of SV40 DNA: analysis of "free" viral DNA sequences. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90346-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]