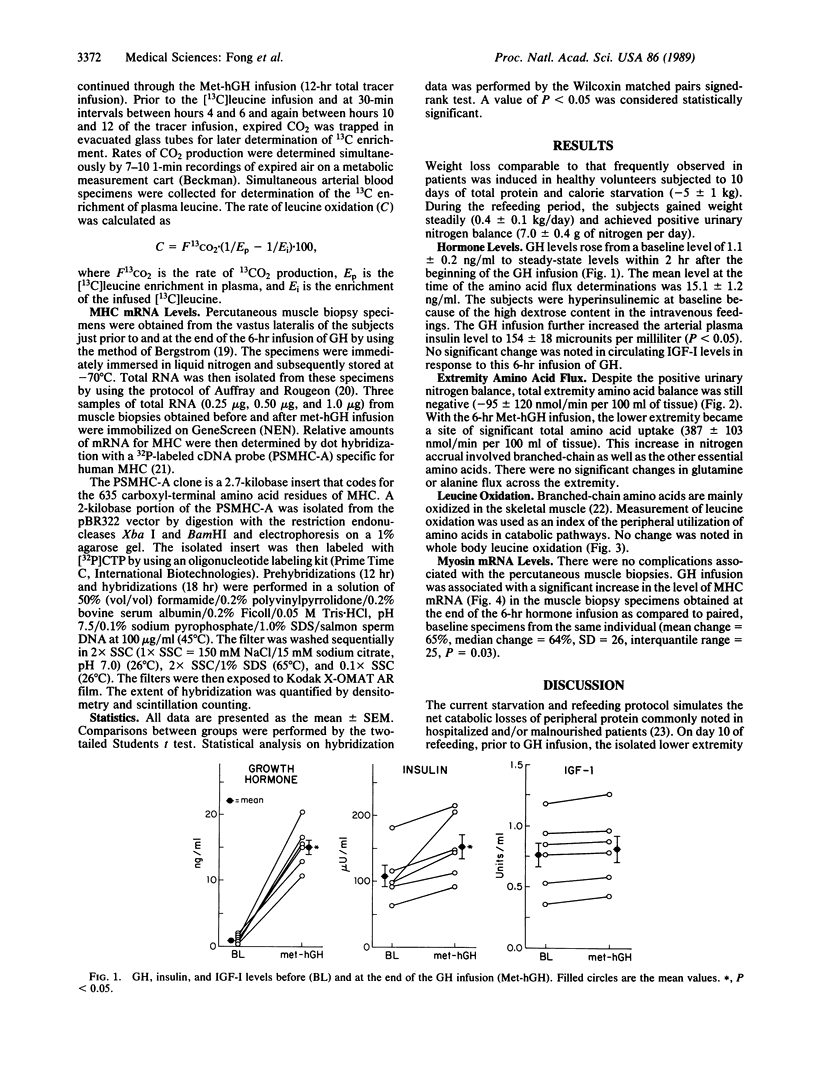
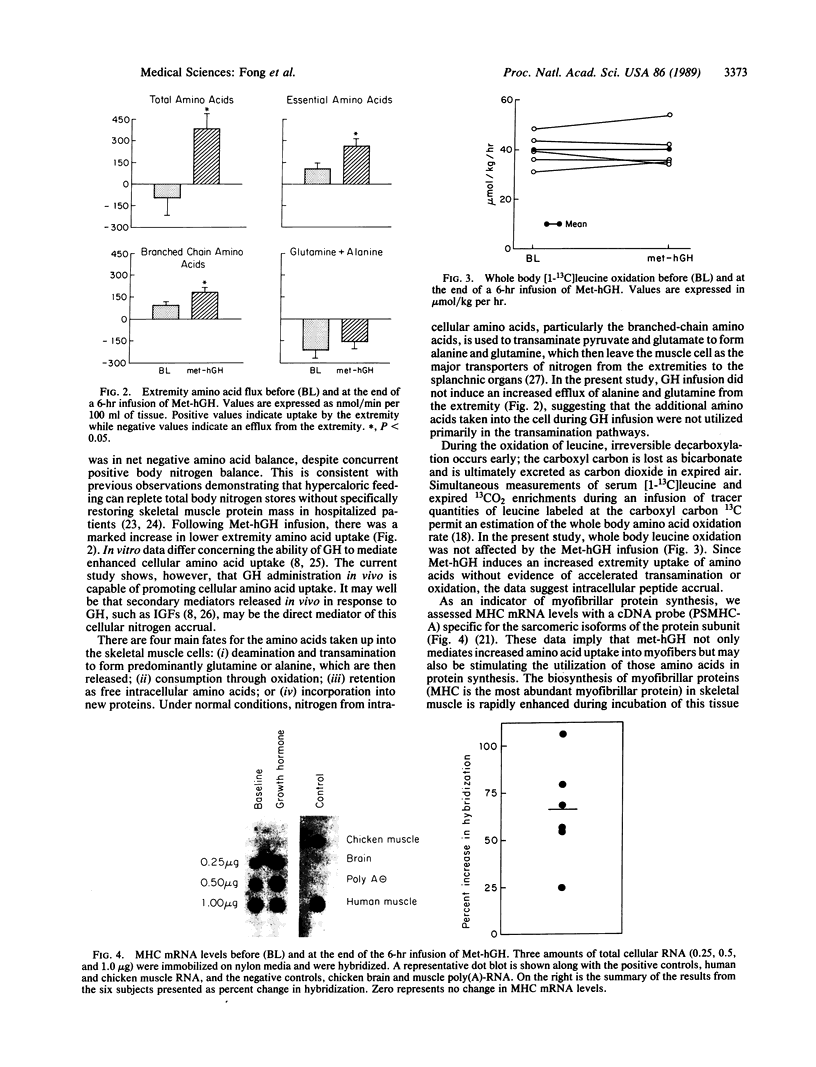
Abstract
A potentially lethal complication of trauma, malignancy, and infection is a progressive erosion of muscle protein mass that is not readily reversed by nutritional support. Growth hormone is capable of improving total body nitrogen balance, but its role in myofibrillar protein synthesis in humans is unknown. The acute, in situ muscle protein response to an infusion of methionyl human growth hormone was investigated in the limbs of nutritionally depleted subjects during a period of intravenous refeeding. A 6-hr methionyl growth hormone infusion achieved steady-state serum levels comparable to normal physiologic peaks and was associated with a significant increase in limb amino acid uptake, without a change in body amino acid oxidation. Myosin heavy-chain mRNA levels, measured by quantitative dot blot hybridization, were also significantly elevated after growth hormone administration. The data indicate that methionyl growth hormone can induce intracellular amino acid accrual and increased levels of myofibrillar protein mRNA during hospitalized nutritional support and suggest growth hormone to be a potential therapy of lean body wasting.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J. D., Legaspi A., Horowitz G. D., Tracey K. J., Brennan M. F., Lowry S. F. Extremity amino acid metabolism during starvation and intravenous refeeding in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):E604–E610. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.5.E604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom J. Percutaneous needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in physiological and clinical research. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1975 Nov;35(7):609–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland K. C., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Induction of immunoreactive somatomedin C human serum by growth hormone: dose-response relationships and effect on chromatographic profiles. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Apr;50(4):690–697. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-4-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P. Amino acid metabolism in man. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:933–955. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R. Hormonal control of muscle growth. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Sep;10(7):577–598. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Nicholson M. L., Dulak N. C. Effects of peptide anabolic hormones on growth of myoblasts in culture. Endocrinology. 1977 Jul;101(1):32–41. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Albert J. D., Legaspi A., Brennan M. F., Lowry S. F. Submaximal exercise during intravenous hyperalimentation of depleted subjects. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):297–304. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198803000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUMP F. E., SCHWARTZ M. S., PRUDDEN J. F. Studies on growth hormone. VI. Dependence of anabolism on the level of intake. Am J Med Sci. 1960 Jan;239:27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand R. A., Barrett E. J. Effect of physiologic hyperinsulinemia on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI113033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill G. L., King R. F., Smith R. C., Smith A. H., Oxby C. B., Sharafi A., Burkinshaw L. Multi-element analysis of the living body by neutron activation analysis-application to critically ill patients receiving intravenous nutrition. Br J Surg. 1979 Dec;66(12):868–872. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800661210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton P., Allison S. P., Littlejohn S., Lloyd J. Insulin and glucose to reduce catabolic response to injury in burned patients. Lancet. 1971 Apr 17;1(7703):767–769. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91213-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Baker J. P., Wolman S. L., Wesson D. E., Langer B., Harrison J. E., McNeill K. G. Critical evaluation of the role of clinical assessment and body composition studies in patients with malnutrition and after total parenteral nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 May;35(5 Suppl):1117–1127. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/35.5.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan S. L., Underwood L. E., August G. P., Bell J. J., Blethen S. L., Blizzard R. M., Brown D. R., Foley T. P., Hintz R. L., Hopwood N. J. Clinical studies with recombinant-DNA-derived methionyl human growth hormone in growth hormone deficient children. Lancet. 1986 Mar 29;1(8483):697–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyo J. L., Reagan C. R. The biology of growth hormone. Pharmacol Ther B. 1976;2(3):591–604. doi: 10.1016/0306-039x(76)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L. Single-column system for accelerated amino acid analysis of physiological fluids using five lithium buffers. Biochem Med. 1974 Jun;10(2):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(74)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manson J. M., Wilmore D. W. Positive nitrogen balance with human growth hormone and hypocaloric intravenous feeding. Surgery. 1986 Aug;100(2):188–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Motil K. J., Rohrbaugh D. K., Burke J. F., Young V. R., Bier D. M. Measurement of leucine metabolism in man from a primed, continuous infusion of L-[1-3C]leucine. Am J Physiol. 1980 May;238(5):E473–E479. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.5.E473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Florini J. R., Dulak N. C. Effects of multiplication stimulating activity (MSA) on AIB transport into myoblast and myotube cultures. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Nov;93(2):173–182. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy L. J., Bell G. I., Duckworth M. L., Friesen H. G. Identification, characterization, and regulation of a rat complementary deoxyribonucleic acid which encodes insulin-like growth factor-I. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):684–691. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski C. C., Chernausek S. D. Discordance of serum and tissue somatomedin levels in growth hormone-stimulated growth in the rat. Endocrinology. 1988 Jul;123(1):44–49. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-1-44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M., Tamborlane W. V., Sherwin R. S. Importance of raised growth hormone levels in mediating the metabolic derangements of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 29;310(13):810–815. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403293101302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rillema J. A., Kostyo J. L. Studies on the delayed action of growth hormone on the metabolism of the rat diaphragm. Endocrinology. 1971 Jan;88(1):240–248. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-1-240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALCH D. S., PARKER M. L. A SENSITIVE DOUBLE ANTIBODY IMMUNOASSAY FOR HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE IN PLASMA. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1141–1142. doi: 10.1038/2031141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saez L., Leinwand L. A. Characterization of diverse forms of myosin heavy chain expressed in adult human skeletal muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2951–2969. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigdell J. E. Venous occlusion plethysmography. Part 1: basic principles and applications. Biomed Eng. 1975 Aug;10(8):300–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Slone D. Critical variables in the radioimmunoassay of serum insulin using the double antibody technic. Diabetes. 1965 Dec;14(12):771–779. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.12.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Legaspi A., Albert J. D., Jeevanandam M., Matthews D. E., Brennan M. F., Lowry S. F. Protein and substrate metabolism during starvation and parenteral refeeding. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Feb;74(2):123–132. doi: 10.1042/cs0740123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweedle D., Walton C., Johnston I. D. The effect of an anabolic steroid on postoperative nitrogen balance. Br J Clin Pract. 1973 Apr;27(4):130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Czech M. P. The type I insulin-like growth factor receptor mediates the rapid effects of multiplication-stimulating activity on membrane transport systems in rat soleus muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3090–3095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


