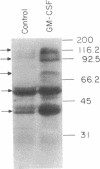
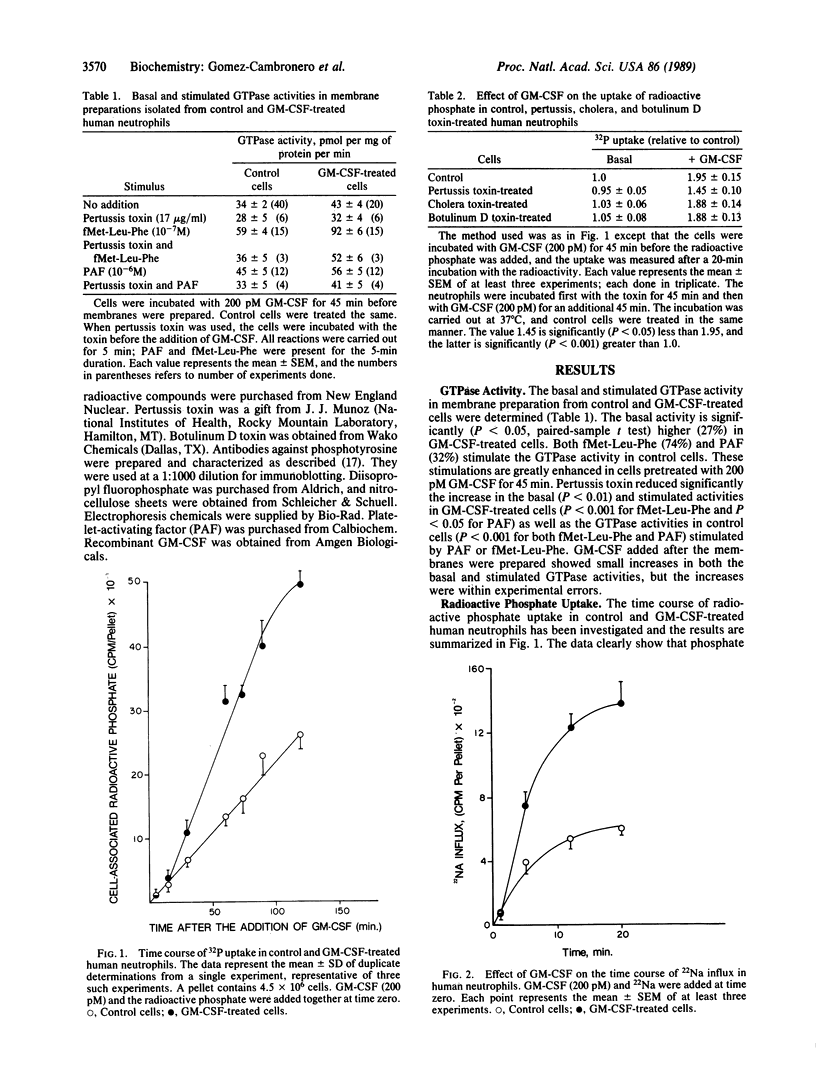
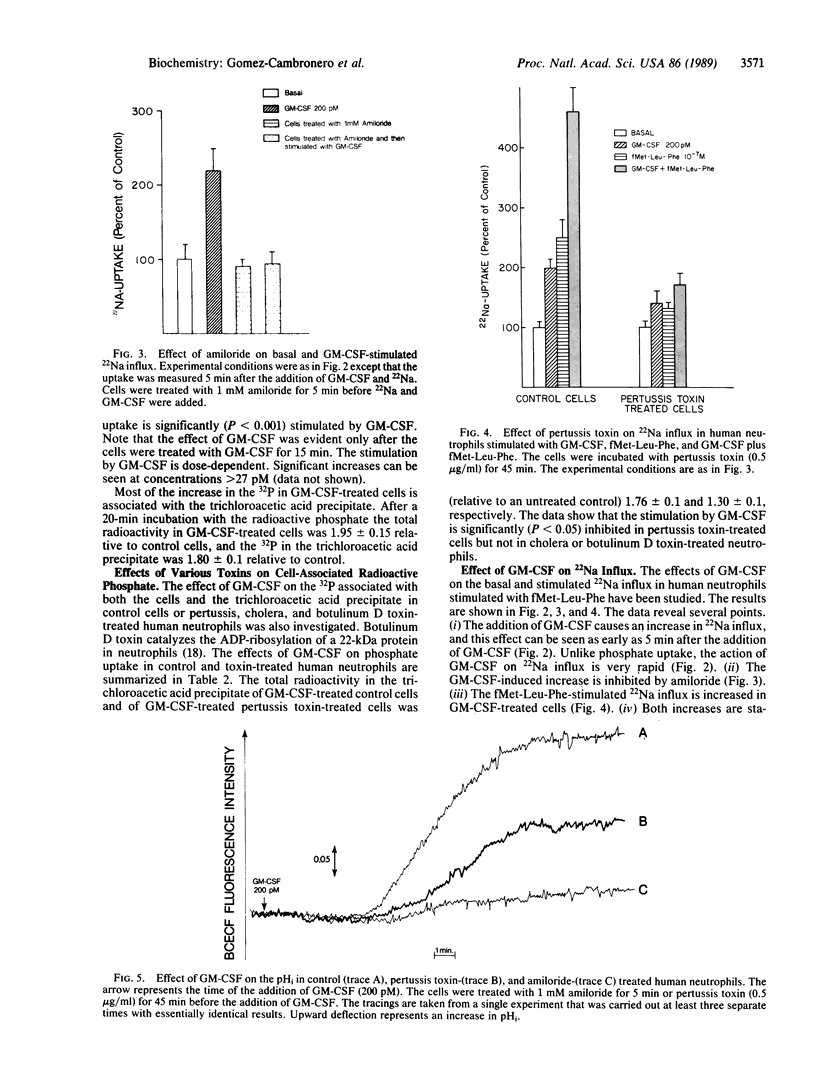
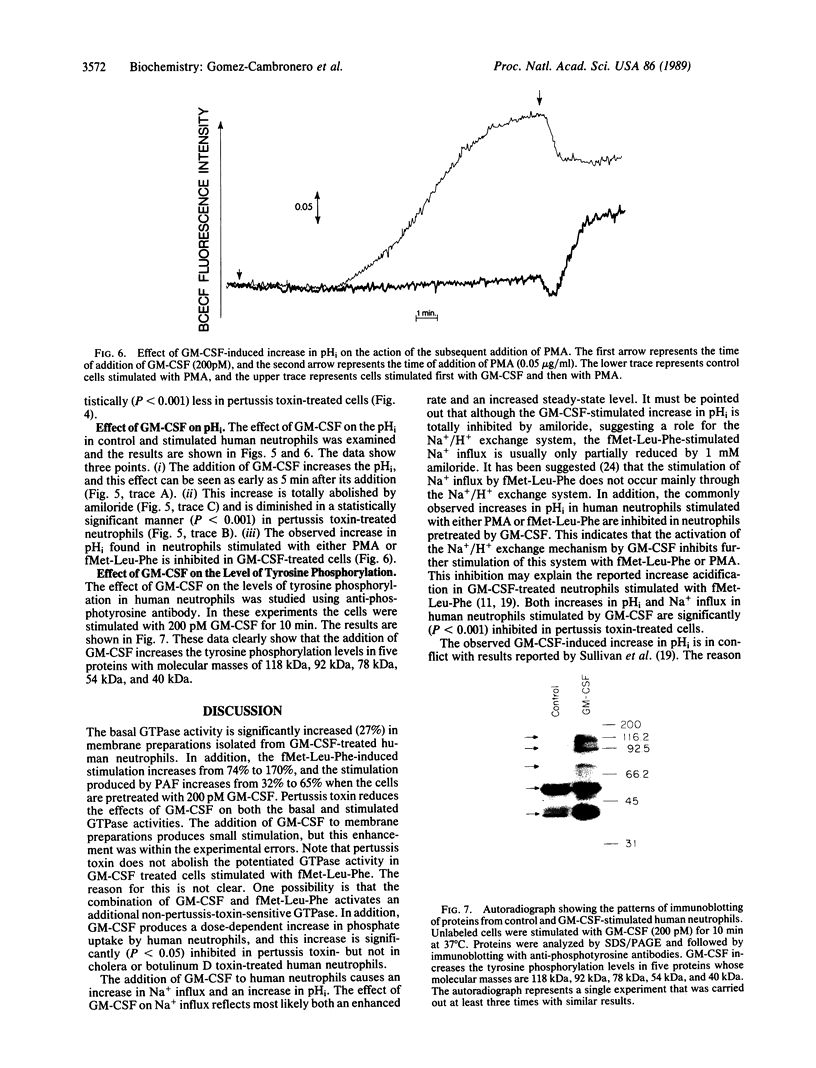
Abstract
The addition of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) to human neutrophils causes a rapid increase in the basal and fMet-Leu-Phe-stimulated Na+ influx and an increase in intracellular pH. The increase can be seen as early as 5 min after the addition of GM-CSF. Changes produced by GM-CSF are totally inhibited by amiloride and are significantly reduced in pertussis toxin-treated cells. The stimulation of the Na+/H+ exchange mechanism by GM-CSF inhibits further stimulation of this system with either fMet-Leu-Phe or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. In addition, membrane preparations isolated from GM-CSF-treated neutrophils have higher basal and stimulated GTPase activities. The basal and the fMet-Leu-Phe- or platelet-activating factor-stimulated GTPase activities are reduced in pertussis toxin-treated cells. Cells pretreated with GM-CSF accumulate more radioactive phosphate than control cells, and this increase is diminished by pertussis toxin treatment. In addition, GM-CSF causes a rapid increase in the tyrosine phosphorylation levels of five proteins with molecular masses of 118 kDa, 92 kDa, 78 kDa, 54 kDa, and 40 kDa. These results clearly show that GM-CSF, on its own, can initiate several changes and that these changes are mediated in part by the pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide regulatory protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chan J. Y., Slamon D. J., Nimer S. D., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Regulation of expression of human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8669–8673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Zingg J., Maly F. E., de Weck A. L. Leukotriene production in human neutrophils primed by recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and stimulated with the complement component C5A and FMLP as second signals. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1281–1295. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPersio J., Billing P., Kaufman S., Eghtesady P., Williams R. E., Gasson J. C. Characterization of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1834–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Kaufman S. E., Weisbart R. H., Tomonaga M., Golde D. W. High-affinity binding of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to normal and leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):669–673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson J. C., Weisbart R. H., Kaufman S. E., Clark S. C., Hewick R. M., Wong G. G., Golde D. W. Purified human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: direct action on neutrophils. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1339–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.6390681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Laramee G. R., Casnellie J. E. Chemotactic factor induced tyrosine phosphorylation of membrane associated proteins in rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):794–801. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80351-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl S. R., Kreis C., DiPersio J. F., Borgeat P., Naccache P. H. Involvement of guanine nucleotide binding proteins in neutrophil activation and priming by GM-CSF. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mege J. L., Volpi M., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Effect of botulinum D toxin on neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Apr 29;152(2):926–932. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tsien R. Y., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Na+/H+ exchange and cytoplasmic pH in the action of growth factors in human fibroblasts. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):645–648. doi: 10.1038/304645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munker R., Gasson J., Ogawa M., Koeffler H. P. Recombinant human TNF induces production of granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):79–82. doi: 10.1038/323079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Faucher N., Borgeat P., Gasson J. C., DiPersio J. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor modulates the excitation-response coupling sequence in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3541–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I. Ionic events relevant to neutrophil activation. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:283–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelz C., Matsumoto T., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Characterization of the membrane-associated GTPase activity: effects of chemotactic factors and toxins. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):197–206. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman E. M., Thom R. R., Casnellie J. E. Activation of a tyrosine protein kinase is an early event in the stimulation of T lymphocytes by interleukin-2. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):6956–6959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha'afi R. I., Molski T. F. Activation of the neutrophil. Prog Allergy. 1988;42:1–64. doi: 10.1159/000318681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraishi T., Domoto T., Imai N., Shimada Y., Watanabe K. Specific inhibitors of tyrosine-specific protein kinase, synthetic 4-hydroxycinnamamide derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 31;147(1):322–328. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Griffin J. D., Simons E. R., Schafer A. I., Meshulam T., Fredette J. P., Maas A. K., Gadenne A. S., Leavitt J. L., Melnick D. A. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte and macrophage colony-stimulating factors on signal transduction pathways in human granulocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3422–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan R., Griffin J. D., Wright J., Melnick D. A., Leavitt J. L., Fredette J. P., Horne J. H., Jr, Lyman C. A., Lazzari K. G., Simons E. R. Effects of recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on intracellular pH in mature granulocytes. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1665–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Mermod J. J., Vassalli P. Phagocytosis and inflammatory stimuli induce GM-CSF mRNA in macrophages through posttranscriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90245-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga M., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Biosynthetic (recombinant) human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: effect on normal bone marrow and leukemia cell lines. Blood. 1986 Jan;67(1):31–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbart R. H., Kwan L., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C. Human GM-CSF primes neutrophils for enhanced oxidative metabolism in response to the major physiological chemoattractants. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):18–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]