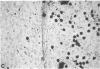
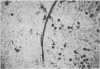
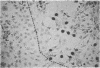
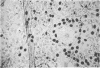
Abstract
Two inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C (PLC) isozymes (PLC-I and -II) have been purified from bovine brain. When PLC-I or PLC-II was microinjected (100-700 micrograms/ml) into quiescent NIH 3T3 cells, a time- and dose-dependent induction of DNA synthesis occurred, as demonstrated by [3H]thymidine incorporation into nuclear DNA. In addition, approximately to 8 hr after PLC injection, NIH 3T3 fibroblasts appeared spindle-shaped, refractile, and highly vacuolated, displaying a morphology similar to transformed cells. The morphologic transformation was apparent for 26-30 hr after which the injected cells reverted back to a normal phenotype. Microinjected PLC at a high concentration (1 mg/ml) was cytotoxic, dissolving the cytoplasmic membrane and leaving behind cellular ghosts. PLC is a key regulatory enzyme involved in cellular membrane signal transduction. Introduction of exogenous PLC into NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection induced a growth and oncogenic potential, as demonstrated by the ability of microinjected PLC (approximately 10,000 molecules per cell) to override the cellular G0 block, inducing DNA synthesis and morphologic transformation of growth-arrested fibroblast cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Balcarek J. M., Varrichio A., Crooke S. T. Molecular cloning and complete amino-acid sequence of form-I phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):268–270. doi: 10.1038/334268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Wallace M. A., Wojcikiewicz R. J. Evidence for involvement of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins in the activation of phospholipases by hormones. FASEB J. 1988 Jul;2(10):2569–2574. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.10.2838362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Hyland J. K., Watt R., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Microinjected c-myc as a competence factor. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1313–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.4001943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Kung H. F. Effects of ras-encoded proteins and platelet-derived growth factor on inositol phospholipid turnover in NRK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5799–5803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide breakdown by guanine nucleotides. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 21;39(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuoka K., Fukami K., Nakanishi O., Kawai S., Takenawa T. Mitogenesis in response to PDGF and bombesin abolished by microinjection of antibody to PIP2. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):640–643. doi: 10.1126/science.2829356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B. J., Hamaguchi M., Hanafusa H. A novel viral oncogene with structural similarity to phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):272–275. doi: 10.1038/332272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Fink J. S., Gilman M. Z., Walsh D. A., Goodman R. H., Feramisco J. R. The catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces expression of genes containing cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):83–86. doi: 10.1038/336083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Two forms of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Suh P. G., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Bovine brain cytosol contains three immunologically distinct forms of inositolphospholipid-specific phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6649–6653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl M. L., Ferenz C. R., Kelleher K. L., Kriz R. W., Knopf J. L. Sequence similarity of phospholipase C with the non-catalytic region of src. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):269–272. doi: 10.1038/332269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]